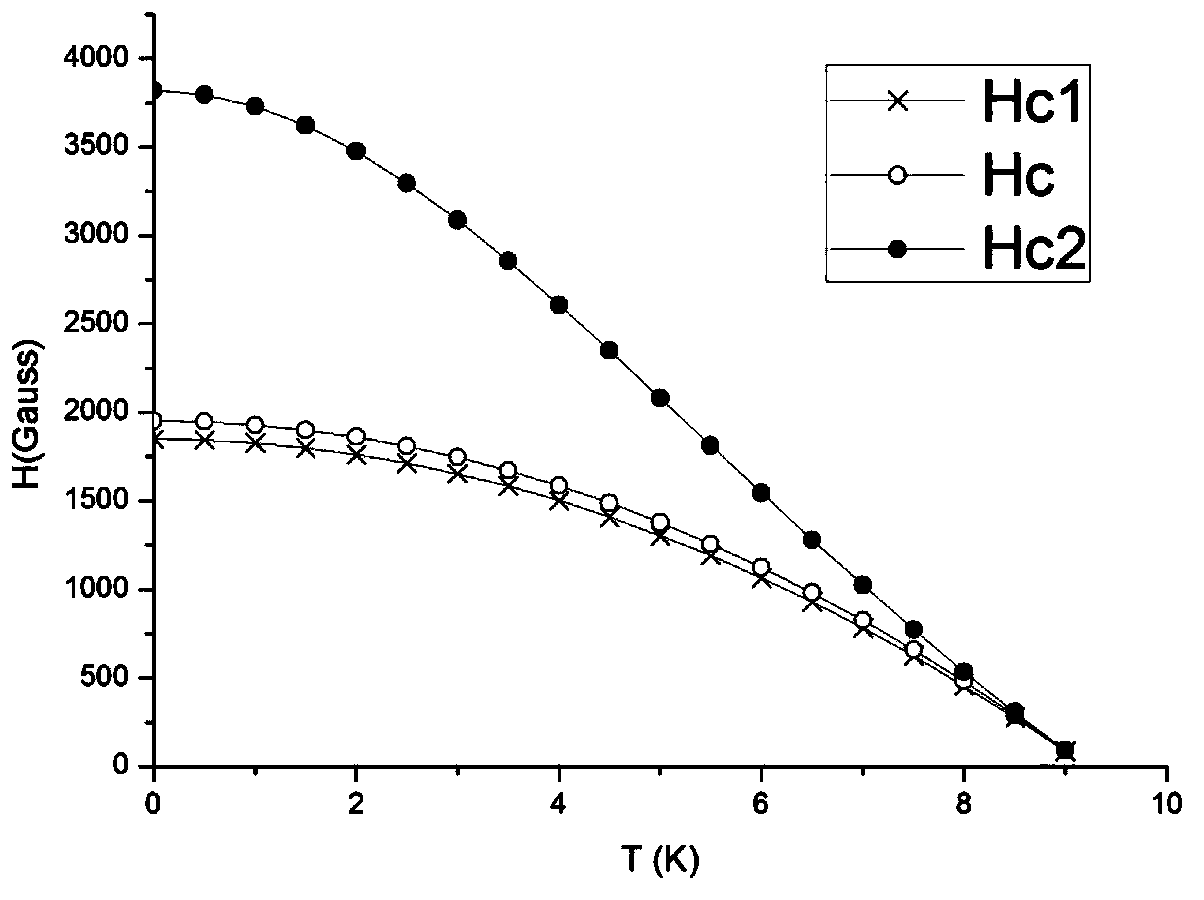
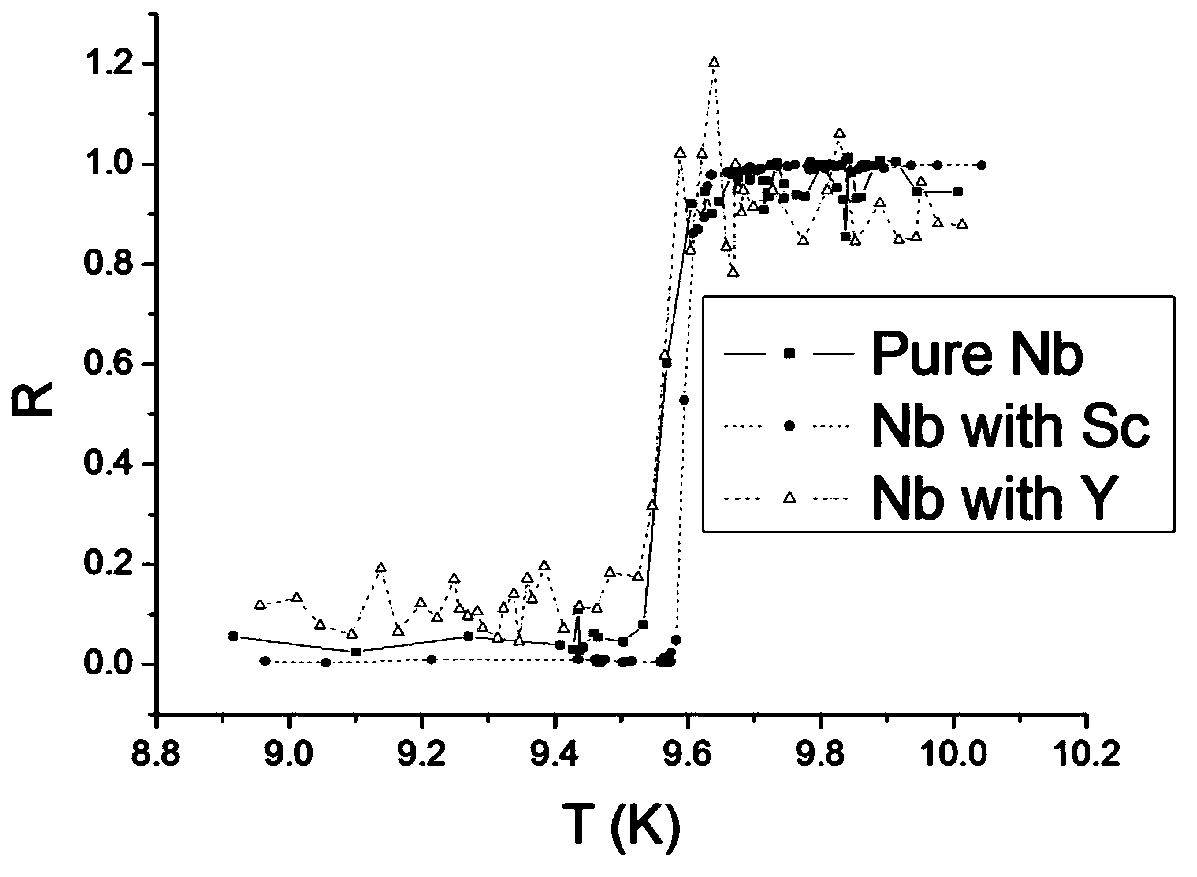
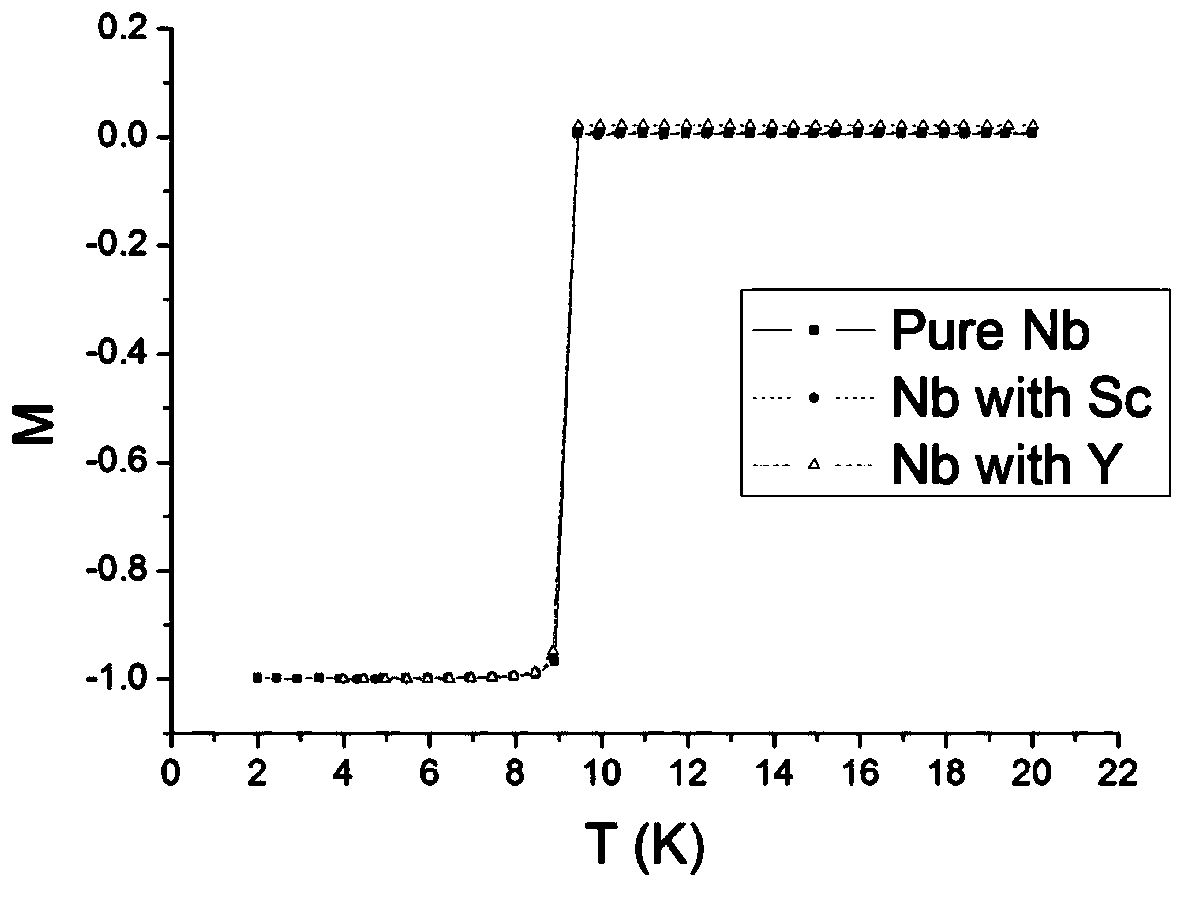
Rare earth doped niobium material for radio frequency superconducting cavity and preparation method thereof
A radio-frequency superconducting cavity and rare earth doping technology, which is applied in the coating process of metal materials, heating by discharge, coating, etc., can solve problems such as long time, difficult process technology, and not knowing whether there is a problem with the texture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1) Select high-purity niobium sheets of different widths so that they are stacked together with a gap in them to form a semi-cylindrical body, with a diameter of 115mm, a length of 240mm, and a mass of 10.8kg;
[0040] 2) Evenly add 26g of pure scandium into the gap between the niobium sheets, and make a semi-cylindrical consumable electrode by electron beam welding;
[0041] 3) Place the consumable electrode in a vacuum electric arc furnace and melt it under the protection of argon to obtain a niobium ingot doped with scandium;
[0042] 4) Machining to remove defects of poor crystallization on the surface, and forging into slabs;
[0043] 5) Anneal the slab at 800°C for 2 hours in an annealing furnace;
[0044] 6) Rolling and slicing the slab to obtain niobium-doped slabs;
[0045] 7) Use an annealing furnace to anneal the niobium-doped plate at 800°C for half an hour to obtain a niobium material containing 0.5% scandium.
Embodiment 2
[0047] 1) Select high-purity niobium sheets of different widths so that they are stacked together with a gap in them to form a semi-cylindrical body, with a diameter of 115mm, a length of 240mm, and a mass of 10.8kg;
[0048] 2) Evenly add 1.5g of pure yttrium into the gap between the niobium sheets, and make a semi-cylindrical consumable electrode by electron beam welding;
[0049] 3) Place the consumable electrode in a vacuum electric arc furnace and melt it under the protection of argon to obtain a niobium ingot doped with yttrium;
[0050] 4) Machining to remove defects of poor crystallization on the surface, and forging into slabs;
[0051] 5) Anneal the slab at 700°C for 5 hours in an annealing furnace;
[0052] 6) Rolling and slicing the slab to obtain niobium-doped slabs;
[0053] 7) Use an annealing furnace to anneal the niobium-doped plate at 1200°C for 5 hours to obtain a niobium material containing 0.01% yttrium.
Embodiment 3
[0055] 1) Perform buffer chemical polishing on the 2.8mm thick high-purity niobium plate;
[0056] 2) Use SRIM software to calculate the energy and dose of incident scandium ions, and determine that the dose of 100keV energy is 6.0×10 14 / cm -2 , the dose of 300keV energy is 1.1×10 14 / cm -2 , the dose of 500keV energy is 1.4×10 14 / cm -2 , so that the content of scandium atoms in the surface layer of the niobium plate is 0.5%;
[0057] 3) According to the above calculation results, use an ion accelerator or an ion implanter to implant scandium ions with corresponding energy and dose into the niobium plate;
[0058] 4) Anneal the implanted niobium plate at 1200°C for half an hour in an annealing furnace;
[0059] 5) Measure the depth distribution of scandium ions in niobium materials by RBS method;
[0060] 6) Use buffer chemical polishing to remove a 50nm thin layer on the surface of the niobium material to obtain a niobium material containing 0.5% scandium.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Long trail | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Short diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Opening diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com