Supercritical carbon dioxide method for extraction separation of magnetosomes from magnetotactic bacteria
A technology of carbon dioxide and magnetotactic bacteria, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as poor stability, poor monodispersity, and low yield, and achieve the effect of overcoming long extraction cycle, good monodispersity, and large particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) Organic solvent pretreatment: The magnetotactic bacteria culture medium cultured to the stable phase was separated in a centrifuge (4000 rmp, 20 min), the supernatant was discarded, the bacteria were collected, and the bacteria cells were transferred to 50 mL In the beaker, dissolve the bacterial cells with 0.3 ml of a mixed solvent of chloroform and methanol with a volume ratio of 2:1, shake for 5 min, and the color of the sample changes from pale yellow to milky white.
[0027] (2) Supercritical CO 2 Extraction and removal of organic solvent: add 5mL of redistilled water in the above-mentioned beaker, magnetically stir it to form a suspension, add the above-mentioned suspension to the supercritical carbon dioxide reactor, and put the reactor into a constant temperature of a certain temperature. Stable for a while in a water bath. Pour carbon dioxide gas into the reaction kettle, stir and extract for one hour at a temperature of 35 °C and a pressure of 10 Mpa in a...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Organic solvent pretreatment: The magnetotactic bacteria culture medium cultured to the stable phase was separated in a centrifuge (4000 rmp, 20 min), the supernatant was discarded, the bacteria were collected, and the bacteria cells were transferred to 50 mL In the beaker, dissolve the bacterial cells with 0.3 ml of a mixed solvent of chloroform and methanol with a volume ratio of 2:1, shake for 5 min, and the color of the sample changes from pale yellow to milky white.
[0031] (2) Supercritical CO 2 Extraction and removal of organic solvent: add 5mL of redistilled water in the above-mentioned beaker, magnetically stir it to form a suspension, add the above-mentioned suspension to the supercritical carbon dioxide reactor, and put the reactor into a constant temperature of a certain temperature. Stable for a while in a water bath. Pour carbon dioxide gas into the reaction kettle, stir and extract for one hour at a temperature of 40 °C and a pressure of 25 Mpa in a...
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Organic solvent pretreatment: separate the magnetotactic bacteria culture solution cultivated to the stationary phase in a centrifuge (4000 rpm, 20 min), discard the supernatant, collect the bacteria, and transfer the bacteria cells to 50 mL In a beaker, dissolve the bacterial cells with 0.3ml of a mixed solvent of chloroform and methanol with a volume ratio of 2:1, shake well for 5 minutes, and the color of the sample changes from light yellow to milky white.
[0035] (2) Supercritical CO 2 Extraction and removal of organic solvents: add 5mL double-distilled water to the above beaker, stir magnetically to form a suspension, add the above suspension to a supercritical carbon dioxide reactor, and put the reactor into a constant temperature constant temperature Stabilize in a water bath for a period of time. Introduce carbon dioxide gas into the reaction kettle, under the conditions of a certain temperature of the reaction kettle of 60°C and a pressure of 20Mpa, stir...
PUM
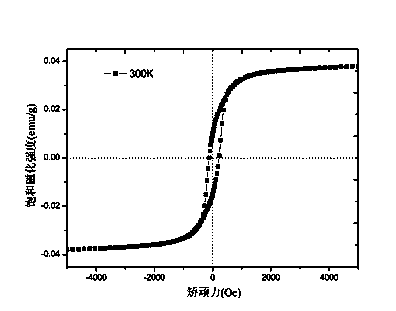
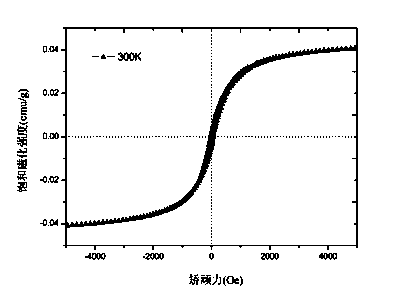
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Coercivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com