Method for producing cationic surface sizing agent, and sizing agent obtained by method
A surface sizing agent, cationic technology, applied in the field of paper and cardboard, can solve the problem of poor sizing effect, and achieve the effect of excellent sizing and excellent dispersion stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
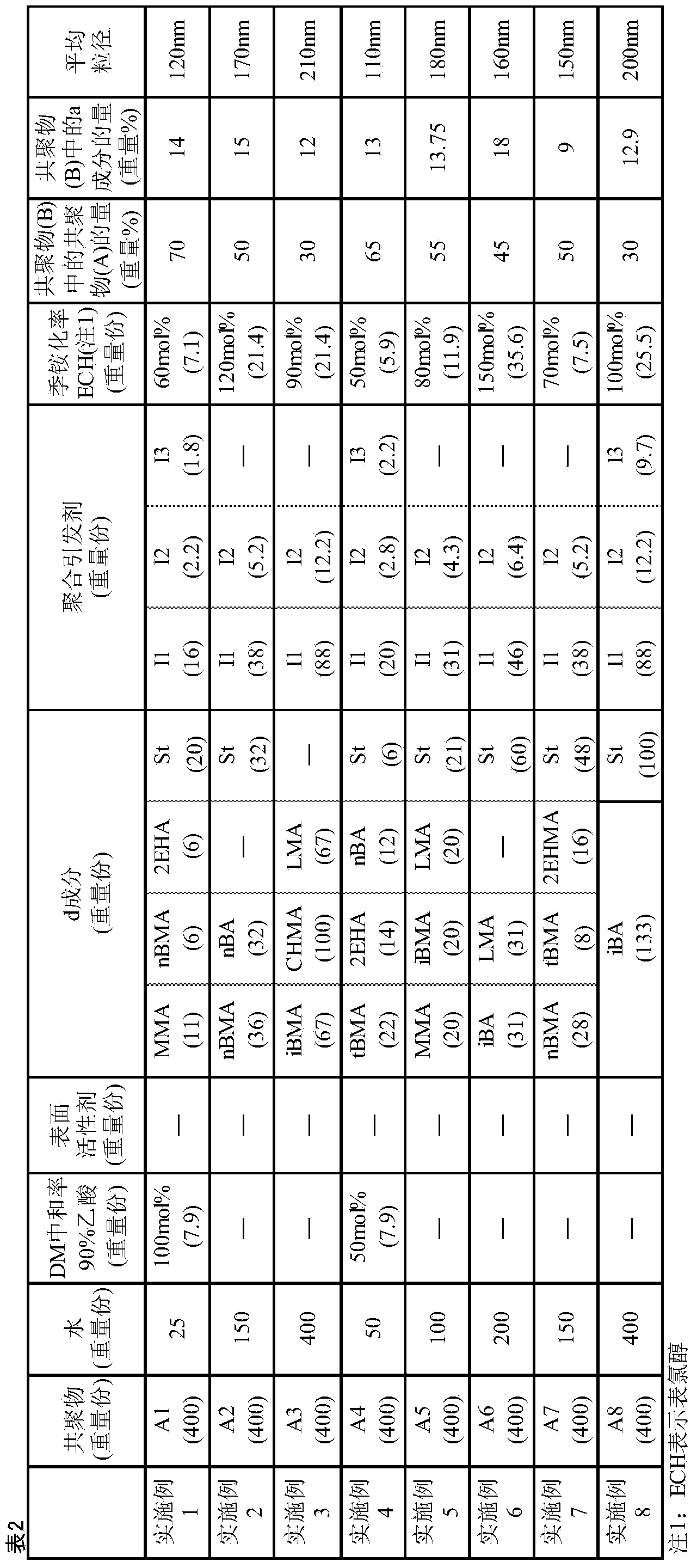
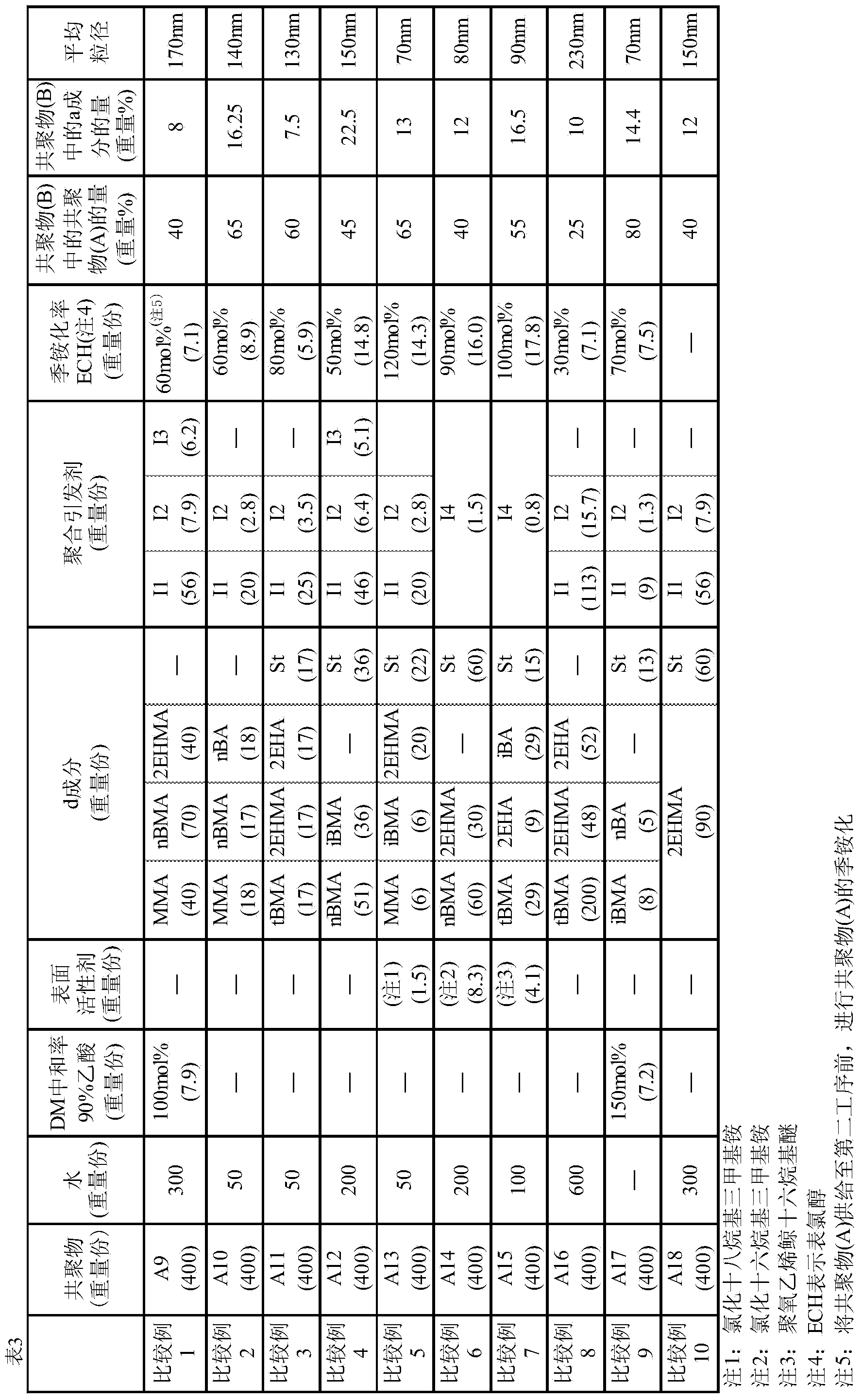
[0086] Hereinafter, although an Example and a comparative example are given and this invention is concretely demonstrated, this invention is not limited to these Examples.
[0087] The abbreviations described in Examples, Comparative Examples and Tables represent the following compounds.
[0088] DM: Dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate
[0089] DMAPAA: Dimethylaminopropylacrylamide
[0090] St: Styrene
[0091] 2EHA: 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate
[0092] 2EHMA: 2-ethylhexyl methacrylate
[0093] MMA: methyl methacrylate
[0094] LMA: lauryl methacrylate
[0095] nBA: n-butyl acrylate
[0096] nBMA: n-butyl methacrylate
[0097] iBA: Isobutyl Acrylate
[0098] iBMA: Isobutyl methacrylate
[0099] tBMA: tert-butyl methacrylate
[0100] CHMA: Cyclohexyl methacrylate
[0101] 2HEA: 2-Hydroxyethyl Acrylate
[0102]
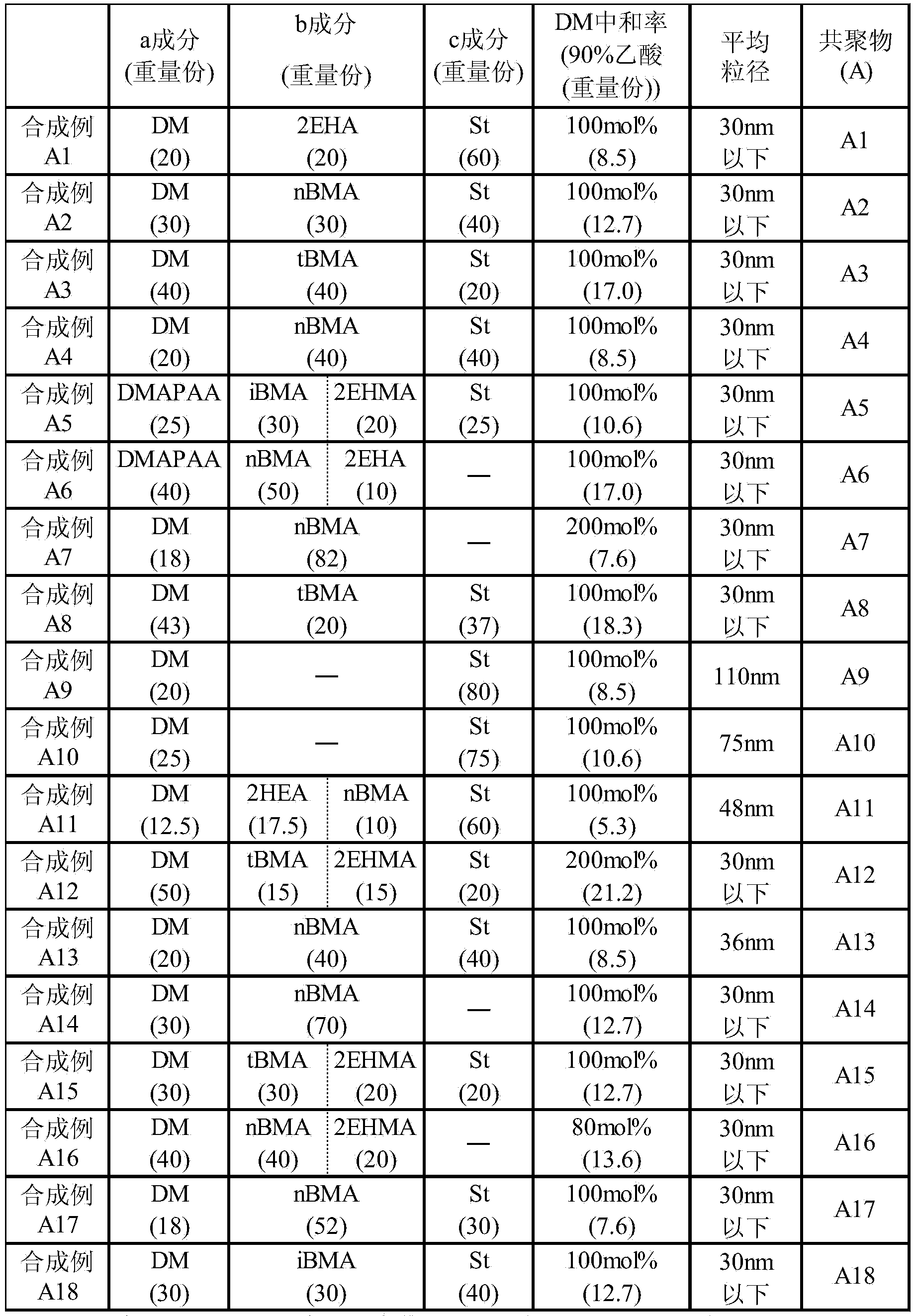
Synthetic example A1
[0104] 20 parts by weight of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (DM), 20 parts by weight of 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (2EHA), styrene (St) of 60 parts by weight, 0.7 parts by weight of 32 parts by weight of n-dodecylmercaptan as a chain transfer agent, and 32 parts by weight of toluene as a solvent, and stirred. Then, it heated to about 105 degreeC, 1 weight part of tert-butylperoxyisopropyl monocarbonate was added as an initiator, and it was made to react at about 110 degreeC for 3 hours. Then, 8.5 parts by weight of 90% by weight acetic acid and 300 parts by weight of water were charged into the four-necked flask in order to neutralize the tertiary amino group portion of the obtained copolymer and a trace amount of DM remaining. Then, after distilling off toluene by heating, it diluted with water so that the solid content concentration might become 25 weight%, and the copolymer (A1) was obtained.
Synthetic example A2
[0106] In the four-necked flask, drop into 30 parts by weight of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (DM), 30 parts by weight of n-butyl methacrylate (nBMA), 40 parts by weight of styrene (St), 0.5 parts by weight tert-dodecylmercaptan as a chain transfer agent, and 32 parts by weight of isopropanol as a solvent, and stirred. Thereafter, it was heated to about 85°C, 1 part by weight of 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile was added as an initiator, and the mixture was reacted at about 90°C for 3 hours. Then, 12.7 parts by weight of 90% by weight acetic acid and 300 parts by weight of water were charged into the four-necked flask in order to neutralize the tertiary amino group portion of the obtained copolymer and a trace amount of DM remaining. Then, after distilling off isopropanol by heating, it diluted with water so that the solid content concentration might become 25 weight%, and obtained the copolymer (A2).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water absorption | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com