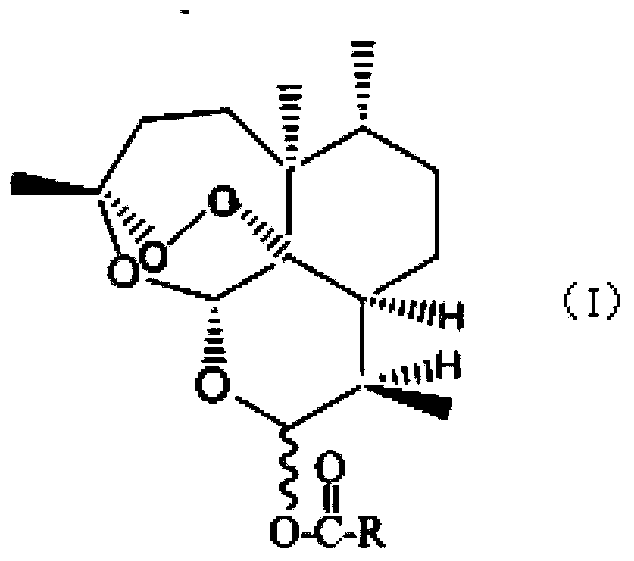
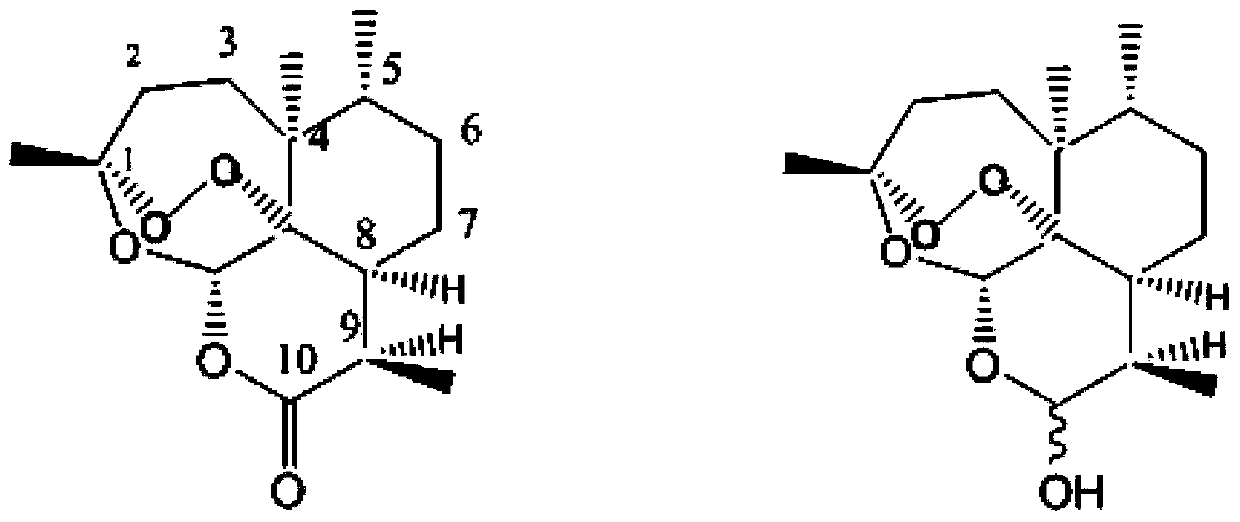
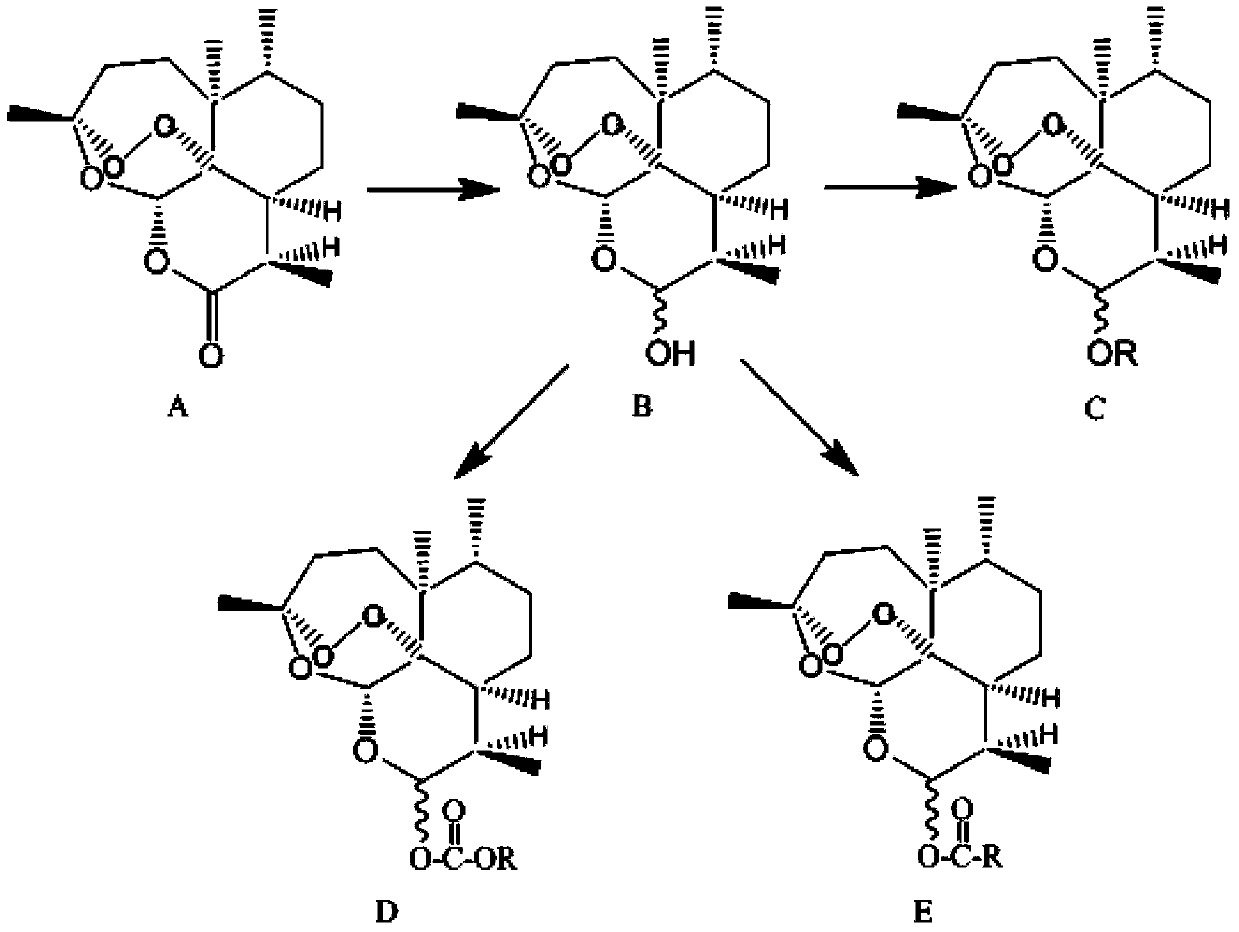
Dihydroartemisinin higher fatty acid ester and preparation method thereof
A technology of dihydroartemisinin and higher fatty acids, applied in organic chemistry, fermentation, antibacterial drugs, etc., can solve the problems of affecting enzyme selectivity and low reaction efficiency, and achieve improved solubility, high yield, and increased The effect of amphiphilicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1 prepares dihydroartemisinin stearate
[0046]
[0047]Dihydroartemisinin and stearic acid were dissolved in tert-butanol at a ratio of 1:6 (molar ratio), and the concentration of dihydroartemisinin in tert-butanol was 1 mg / ml. Add lipase Novozyme 435 at 60°C with a concentration of 4 mg / mL, place it in a shaker and shake at a speed of 60 rpm / min. After reacting for 5 hours, add 100 g of molecular sieve 4A to 1L of the reaction solution. Molecular sieve 4A was activated at 150° C. for 24 hours in advance. Molecular sieve 4A removed the water generated by the esterification reaction. After a total of 96 hours of reaction, the enzyme and molecular sieve were removed by filtration. Concentrate under reduced pressure to remove the solvent to obtain the reaction product substance. The reaction product was separated by column chromatography, and the mobile phase was ethyl acetate:petroleum ether 60-90°C=1:1.5. The yield of dihydroartemisinin stearate (F) obta...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2 prepares dihydroartemisinin laurate
[0049]
[0050] Dihydroartemisinin and lauric acid were dissolved in tert-butanol at a ratio of 1:6 (molar ratio), and the concentration of dihydroartemisinin in tert-butanol was 1 mg / ml. Add lipase Novozyme 435 at 60°C with a concentration of 4 mg / mL, place it in a shaker and shake at a speed of 60 rpm / min. After reacting for 5 hours, add molecular sieve 4A in an amount of 100 g to 1 L of liquid. Molecular sieve 4A is activated at 150°C for 24 hours in advance. Molecular sieve 4A removes the water generated by the esterification reaction. After 96 hours of reaction, the enzyme and molecular sieve are removed by filtration. Concentrate under reduced pressure to remove the solvent to obtain the product substance. The reaction product was separated by column chromatography, and the mobile phase was ethyl acetate:petroleum ether 60-90°C=1:2. The yield of dihydroartemisinin laurate (G) obtained by chromatographic separ...
Embodiment 3 2
[0051] Embodiment 3 The reaction of dihydroartemisinin and lauric acid in different ratios
[0052] Dihydroartemisinin and lauric acid are dissolved in tert-butanol at the ratio of 1:3, 1:4, 1:5, 1:7, 1:8 (molar ratio), dihydroartemisinin in tert-butanol The concentration in is 1mg / ml. At 60°C, lipase Novozyme 435 was added at a concentration of 4 mg / mL, and placed in a shaker to shake and stir. After reacting for 5 hours, add molecular sieve 4A in an amount of 100 g to 1 L of liquid. Molecular sieve 4A is activated at 150°C for 24 hours in advance. Molecular sieve 4A removes the water generated by the esterification reaction. After 96 hours of reaction, the enzyme and molecular sieve are removed by filtration. The solvent was removed by concentration under reduced pressure to obtain the product substance. The reaction product was separated by column chromatography, and the mobile phase was ethyl acetate:petroleum ether 60-90°C=1:2.
[0053] The yield of dihydroartemisinin ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com