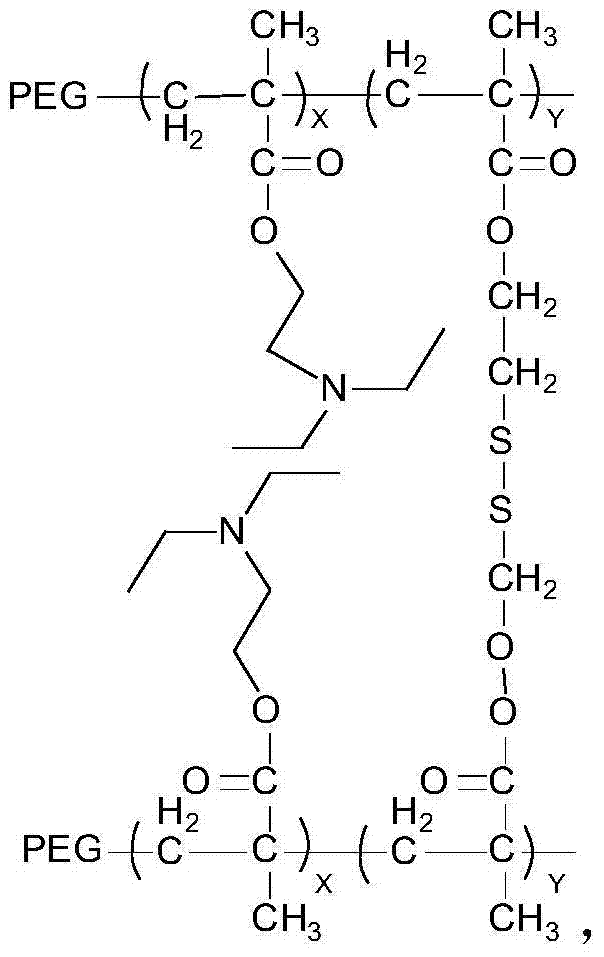
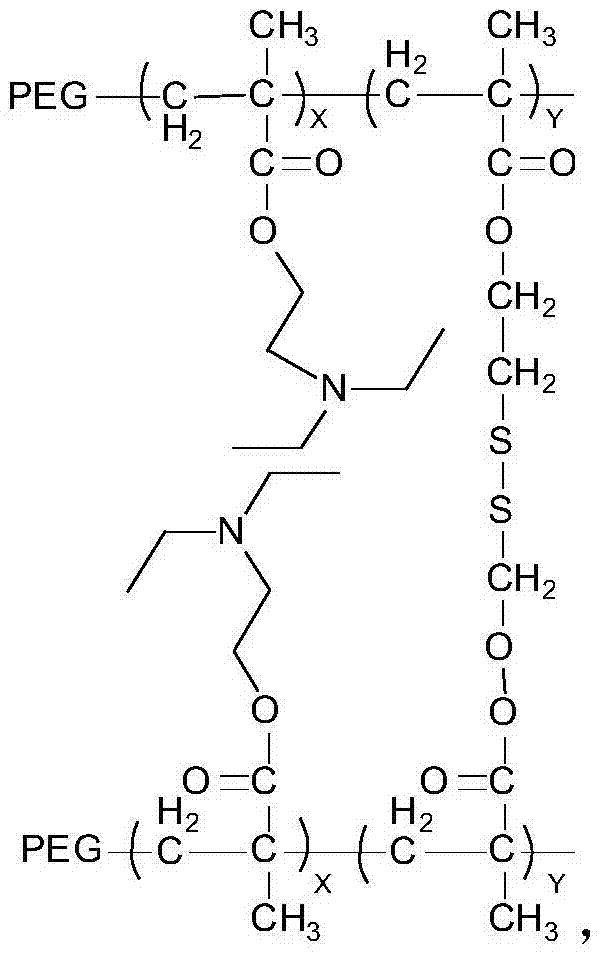
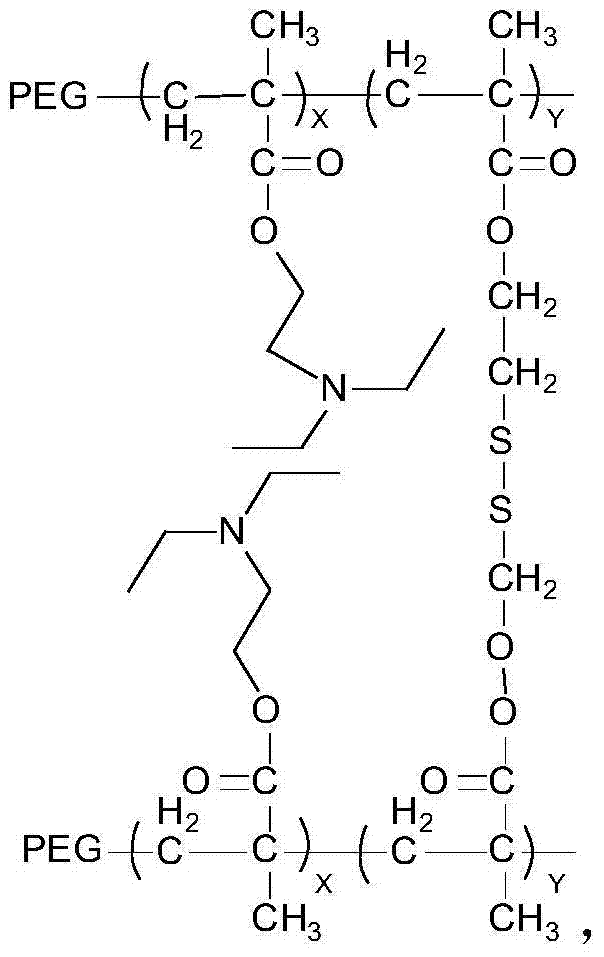
Ph-redox double sensitive amphiphilic polymer and preparation method thereof
An amphiphilic polymer and sensitive technology, applied in the field of polymers, can solve the problems of poor delivery stability, poor targeting, and poor controllability, and achieve good redox sensitivity and enrichment effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] The preparation method of the above-mentioned pH-redox double-sensitive amphiphilic polymer, the specific steps are as follows:
[0033] Step 1, add bis(2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide to a round bottom flask, add dichloromethane, triethylamine and methacryloyl chloride under ice bath conditions, then seal the system and place it under magnetic force at 0°C After stirring for 3 to 5 hours, washing and extraction were carried out in sequence, and the organic extract was washed with anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 After drying for 8-14 hours, filter with absorbent cotton, pass the filtrate through a silica gel chromatography column, and finally elute and spin dry to obtain a cross-linking agent;
[0034] The structural formula of the crosslinking agent is: The molecular weight is 290.
[0035] Among them, the proportions of all raw materials for the synthesis of crosslinking agents in the total weight are: bis(2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide 5-8%, dichloromethane 67-70%, triethylamine 12-15%...
Embodiment 1
[0047] Step 1, add 5% of bis(2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide into a round bottom flask, add 70% dichloromethane, 12% triethylamine in turn under ice bath conditions, and slowly add 13% methacrylic acid Acyl chloride, the system is sealed and reacted for 3 hours at 0°C with magnetic stirring;
[0048] Transfer to a separatory funnel, add 17% NaHCO of the total weight of raw materials used for synthesis 3 (concentration 5%) solution washing, extracting 3 times with dichloromethane of 33% of the total weight of raw materials to remove unreacted bis(2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide; add anhydrous Na to the organic layer extract 2 SO 4 After drying for 8 hours, filter with absorbent cotton, pass the filtrate through a silica gel chromatography column, elute with petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (volume ratio 8:1) eluent, combine the eluent and spin dry to obtain a crosslinking agent;
[0049] Step 2: Add 0.5% polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether (n=1000) into a round bottom flask, add 29% te...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Step 1, add 8% bis(2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide into a round bottom flask, add 67% dichloromethane, 14% triethylamine in turn under ice bath conditions, and slowly add 11% methacrylic acid Acyl chloride, the system is sealed and reacted for 4 hours at 0°C with magnetic stirring;
[0054] Transfer to a separatory funnel, add 24% NaHCO of the total weight of raw materials used for synthesis 3 (concentration 5%) solution washing, extracting 3 times with dichloromethane of 35% of the total weight of raw materials to remove unreacted bis(2-hydroxyethyl) disulfide; add anhydrous Na to the organic layer extract 2 SO 4 After drying for 12 hours, filter with absorbent cotton, pass the filtrate through a silica gel chromatography column, elute with petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (volume ratio 10:1) eluent, and spin dry the combined eluent to obtain a crosslinking agent;
[0055] Step 2: Add 0.7% polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether (n=2000) into a round bottom flask, add 27% te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com