Extraction and content determination methods for natural astaxanthin of thick-wall microalgae
A technology of natural astaxanthin and an extraction method, which is applied in the field of extraction and content determination of natural astaxanthin from thick-walled microalgae, can solve the problems of limited sensitivity of thin-layer scanning, complicated operation, low accuracy, etc., and avoid high temperature decomposition. Or oxidative deterioration, high extraction efficiency, and complete wall-breaking effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
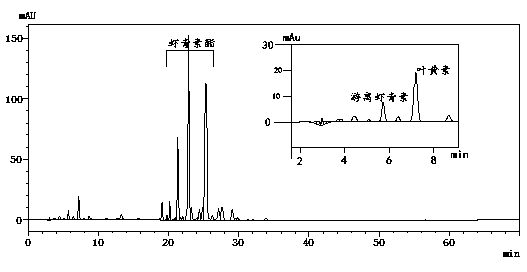
[0042] Example 1 Preparation and Content Detection of Haematococcus Pluvialls Fresh Algae Liquid Extract
[0043] (1) Extraction of Astaxanthin
[0044]1) Determination of dry weight of algae cells: take 50mL of fresh Haematococcus pluvialis algal liquid and filter it with qualitative filter paper (the qualitative filter paper has been baked in an oven at 80°C to constant weight), and then put the filtered filter paper in an oven at 80°C Baked to constant weight, weighed Haematococcus pluvialis dry weight 31.5mg, 31.3mg (parallel test).
[0045] 2) Astaxanthin extraction: take another 50mL of fresh algae liquid and centrifuge at a speed of 8000r / min, remove the supernatant, transfer the centrifuged Haematococcus pluvialis algal cells into a mortar, add appropriate amount of quartz sand in turn, and Pour liquid nitrogen into the mortar and freeze. After the algal cells are fully frozen, add 0.5 mL of extraction solvent (dichloromethane-methanol (v:v=1:3)) and grind thoroughly...
Embodiment 2
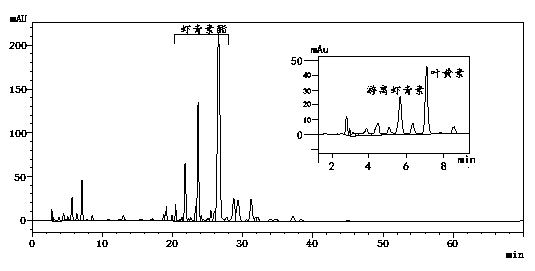
[0056] Example 2 Preparation and Content Detection of Haematococcus Pluvialls Dry Algae Powder Extract
[0057] (1) Extraction of Astaxanthin
[0058] 1) Astaxanthin extraction: Take 50.0 mg of dried Haematococcus pluvialis powder in a mortar, add appropriate amount of quartz sand in turn, and pour liquid nitrogen into the mortar to freeze. After the algal cells are fully frozen, add 1 mL of extraction solvent (dichloromethane-methanol (v:v=1:1)) and grind thoroughly, transfer the algal cells together with the extraction solvent to a centrifuge tube, and rinse the mortar with the extraction solvent , wash until there is no residue, centrifuge the residue and supernatant at a speed of 3000r / min, and collect the supernatant. Then repeat the above liquid nitrogen grinding and extraction steps until the centrifuged supernatant is colorless, and combine the supernatants.
[0059] 2) Preparation of astaxanthin test solution: Concentrate the above-mentioned astaxanthin sample by pu...
Embodiment 3
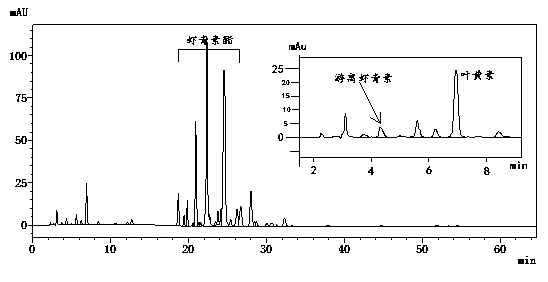
[0064] Example 3 Preparation and Content Detection of Haematococcus Pluvialls Fresh Algae Liquid Extract
[0065] (1) Extraction of Astaxanthin
[0066] 1) Determination of dry weight of algae cells: take 100mL of fresh Haematococcus pluvialis algae liquid and filter it with qualitative filter paper (the qualitative filter paper has been baked in an oven at 80°C to constant weight), and then put the filtered filter paper in an oven at 80°C Baked to constant weight, weighed Haematococcus pluvialis dry weight 62.9mg, 62.7mg (parallel samples).
[0067] 2) Astaxanthin extraction: Take another 100mL of fresh algae liquid and filter it with qualitative filter paper, then use the extraction solvent (chloroform-methanol (v:v=1:5)) to wash the algae cells on the filter paper into the mortar, Until no algal cells remain on the filter paper, add appropriate amount of quartz sand in turn, and pour liquid nitrogen into the mortar to freeze. After the algae cells are fully frozen, add 0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com