Rotary hearth furnace bottom and rotary hearth furnace with same
A technology for the bottom and base of a rotary hearth furnace, which is applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of damage to the bottom structure, easy bonding between slag and the bottom of the furnace, and failure to tap iron and slag smoothly, so as to reduce erosion, ensure safe operation, and enhance Antioxidant effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
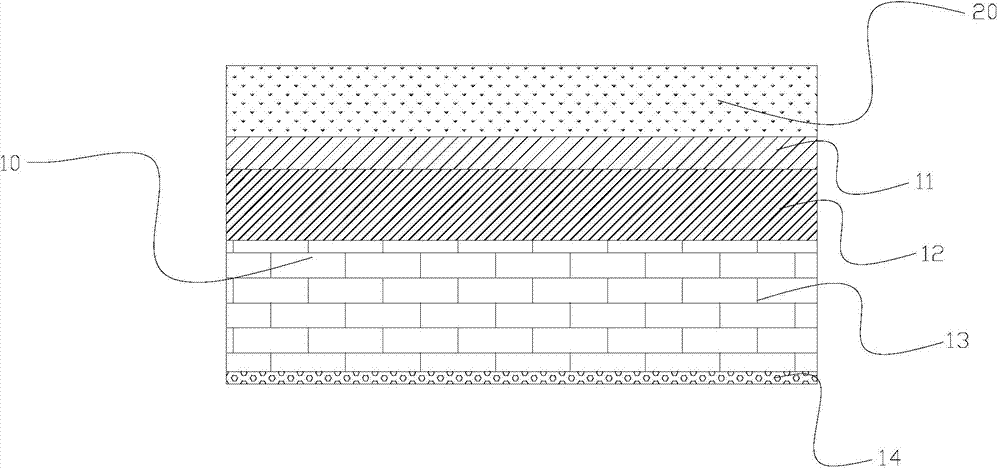
[0039] Bottom of rotary hearth furnace: 6 layers in total, with a total thickness of 650mm. Such as figure 2 Shown from top to bottom are: the first layer is the poured slag-resistant casting layer (including two equal-thickness slag-resistant casting sub-layers), the thickness is 154mm; the second layer is the standard high-alumina brick Lz- 55; the third layer is a standard clay brick N-3a with a thickness of 136mm; the fourth layer is a standard lightweight clay brick with a thickness of 272mm (the thickness of the standard light clay brick is 136); the fifth layer is a refractory fiberboard with a thickness of 20mm.
[0040] The slag-resistant casting layer is formed by the following materials: alumina accounts for 55% by weight of the mixture, brown corundum accounts for 20% by weight of the mixture, silicon carbide accounts for 15% by weight of the mixture, and silicon nitride accounts for 4% by weight of the mixture. Metal silicon powder accounts for 2% by weight of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com