Infrared photoelectric detector and preparation method thereof
An electrical detector, infrared light technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems affecting the detection efficiency and detection limit of devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
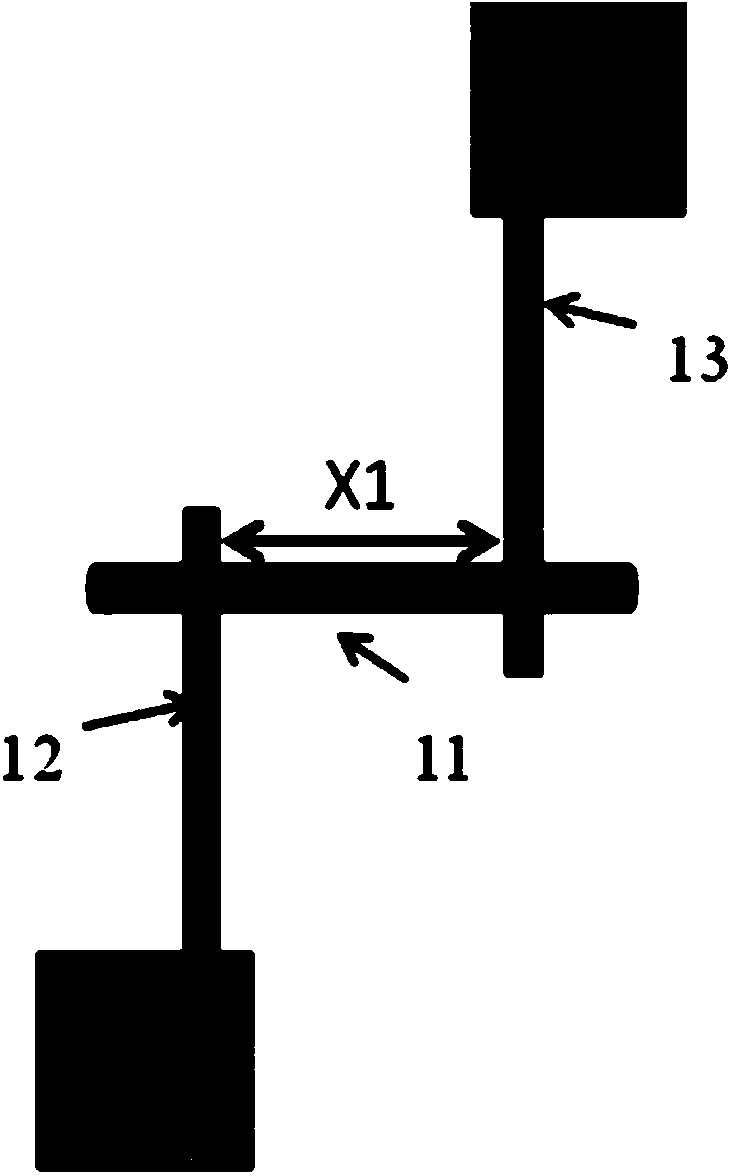
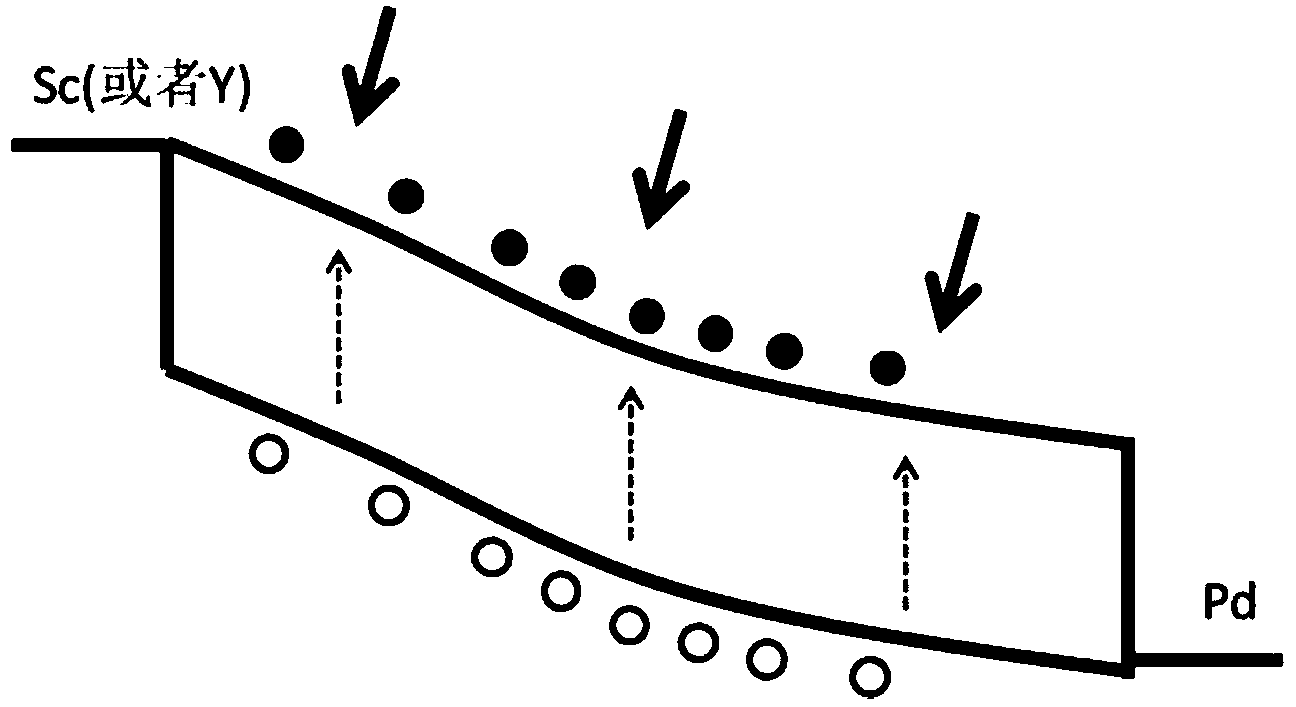
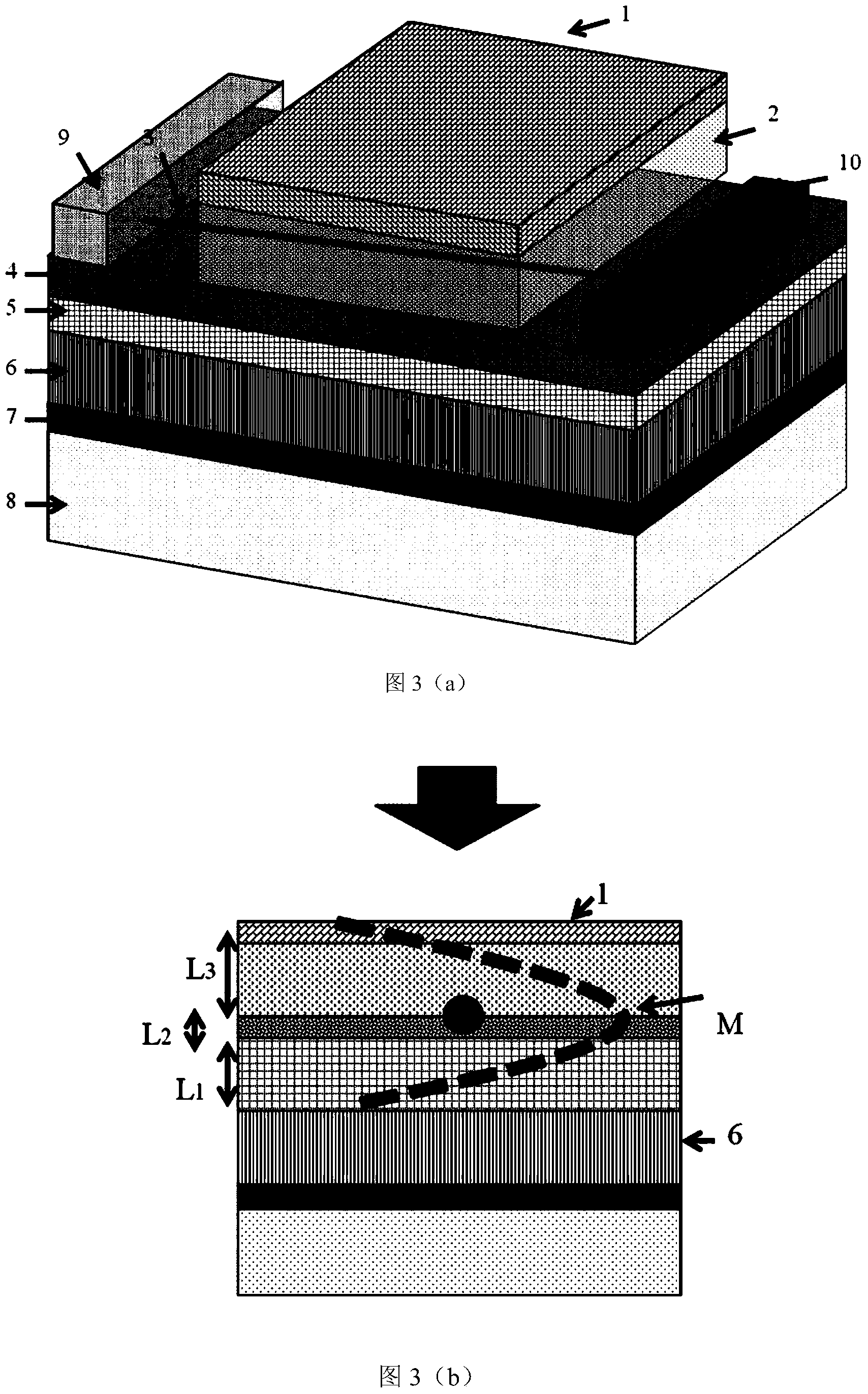
[0053] image 3 (a) shows the basic form of the infrared photodetector integrated semiconductor carbon nanotube diode and Fabry-Perot optical microcavity of the present invention. The semiconductor carbon nanotube 3 is entirely located on the hafnium oxide 4 substrate, and its two asymmetric electrodes are respectively between the palladium electrode 9 and the scandium electrode 10, with a distance of 1.5 microns. Wherein the electrode 9 is a palladium electrode with a width of about 1 micron, and the electrode 10 is a scandium (or yttrium) electrode with a width of about 1 micron. In the following example, we will illustrate the specific preparation steps for on-chip integration of the commonly used 1500 nm waveband, as follows:
[0054] 1. On the silicon substrates 7 & 8, an electron beam coater is used to deposit a silver reflective layer 6 of 130 nanometers and a silicon dioxide layer 5 of 165 nanometers respectively. Considering the easy oxidation of silver, the two are ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Image 6 It is based on the schematic diagram of the diode structure of multiple semiconducting carbon nanotubes. Figure 7 (a) Infrared photodetector integrated with semiconducting carbon nanotubes based on carbon nanotube film and Fabry-Perot optical microcavity shown in (a), the structural cross-sectional schematic diagram of the infrared photodetector is shown in Figure 7 (b) shown. The semiconducting carbon nanotube 3 is integrally located on the hafnium oxide 4 substrate, and its two asymmetric electrodes are respectively between the palladium electrode 9 and the yttrium electrode 21, with a difference X2 of 1 micron. Wherein the electrode 9 is a palladium electrode with a width of about 1.5 microns, and the electrode 21 is a yttrium electrode with a width of about 1.5 microns. In the following example, we will specifically describe the preparation of the on-chip integrated 1300nm waveband, as follows:
[0064] 1. On the silicon substrate 7 & 8, a 100-nm silve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com