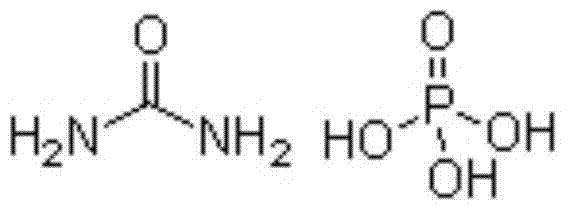Method for preparing sodium dihydrogen phosphate by utilizing phosphoric acid by wet process
A technology of sodium dihydrogen phosphate and wet-process phosphoric acid, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., and can solve problems such as difficult to handle by-products, unfavorable environmental protection, and unstable product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
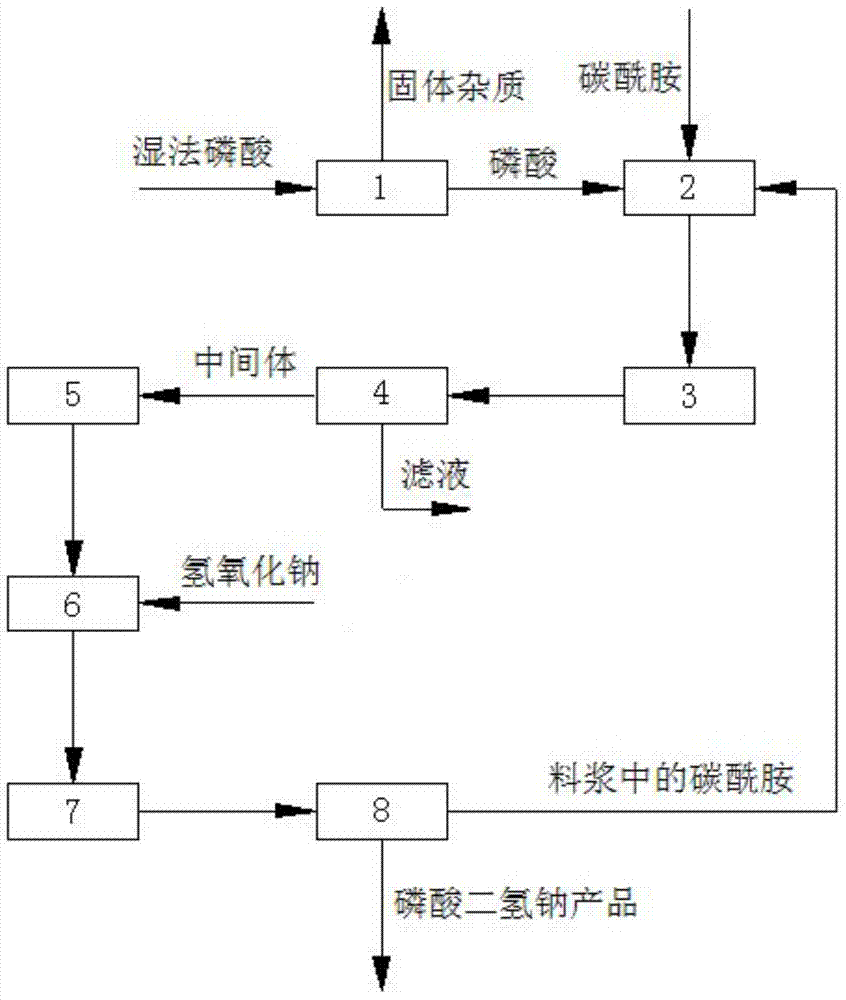
[0046] (1) Impurity removal of wet-process phosphoric acid:
[0047] The solid impurities contained in the wet-process phosphoric acid with a concentration of 15% are removed by centrifugation or press filtration to obtain phosphoric acid for subsequent use;
[0048] (2) Synthesis reaction of intermediates:
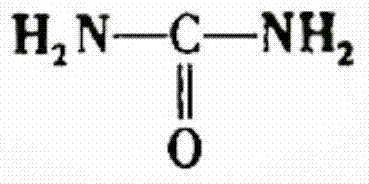
[0049] Put the phosphoric acid obtained in step (1) into the intermediate synthesis tank, adjust the concentration of phosphoric acid, heat up to 60°C, and add carbonamide and phosphoric acid under stirring conditions to carry out the synthesis reaction. The amount of carbonamide added is based on the mole of phosphoric acid The ratio is 1.0:1 to determine, stirring to dissolve and heat preservation reaction, the reaction time is 80min;
[0050] (3) Cooling and crystallization to obtain the intermediate:
[0051] After the synthesis reaction is completed, put the obtained intermediate slurry into the cooling crystallization tank and cool it to a temperature of 20°C to c...
Embodiment 2
[0055] (1) Impurity removal of wet-process phosphoric acid:
[0056] The solid impurities contained in the wet-process phosphoric acid with a concentration of 40% are removed by centrifugation or press filtration to obtain phosphoric acid for subsequent use;
[0057] (2) Synthesis reaction of intermediates:
[0058] Put the phosphoric acid obtained in step (1) into the intermediate synthesis tank, adjust the concentration of phosphoric acid, heat up to 70°C, and add carbonamide and phosphoric acid under stirring conditions to carry out the synthesis reaction. The amount of carbonamide added is based on the mole of phosphoric acid The ratio is 1.05:1 to determine, stirring to dissolve and heat preservation reaction, the reaction time is 100min;
[0059] (3) Cooling and crystallization to obtain the intermediate:
[0060] After the synthesis reaction is completed, put the obtained intermediate slurry into the cooling crystallization tank to cool to a temperature of 30°C, centr...
Embodiment 3
[0064] (1) Impurity removal of wet-process phosphoric acid:
[0065] The solid impurities contained in the wet-process phosphoric acid with a concentration of 50% are removed by centrifugation or press filtration to obtain phosphoric acid for subsequent use;
[0066] (2) Synthesis reaction of intermediates:
[0067] Put the phosphoric acid obtained in step (1) into the intermediate synthesis tank, adjust the concentration of phosphoric acid, heat up to 80°C, and add carbonamide and phosphoric acid under stirring conditions to carry out the synthesis reaction. The amount of carbonamide added is based on the mole of phosphoric acid The ratio is 0.95:1 to determine, stirring to dissolve and heat preservation reaction, the reaction time is 60min;
[0068] (3) Cooling and crystallization to obtain the intermediate:
[0069] After the synthesis reaction is finished, put the obtained intermediate slurry into a cooling crystallization tank to cool to a temperature of 10°C, centrifug...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com