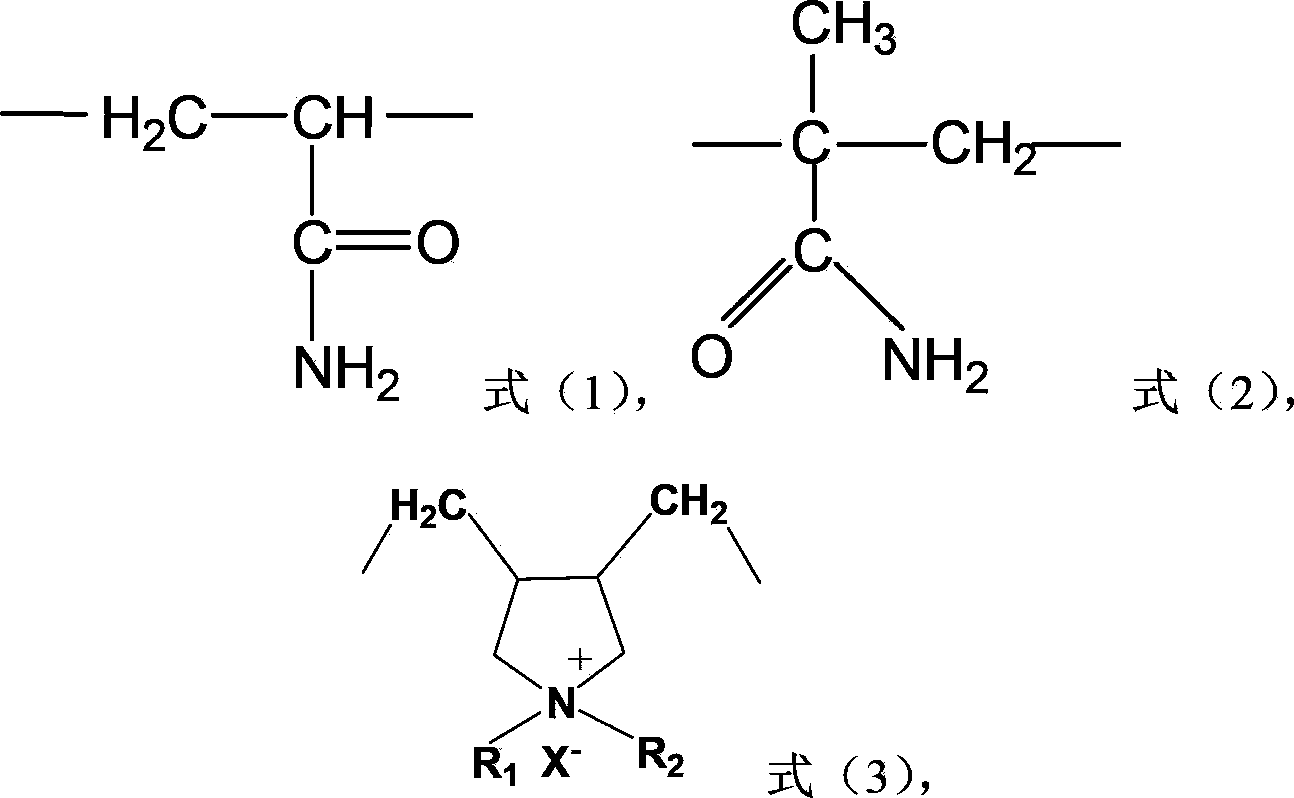
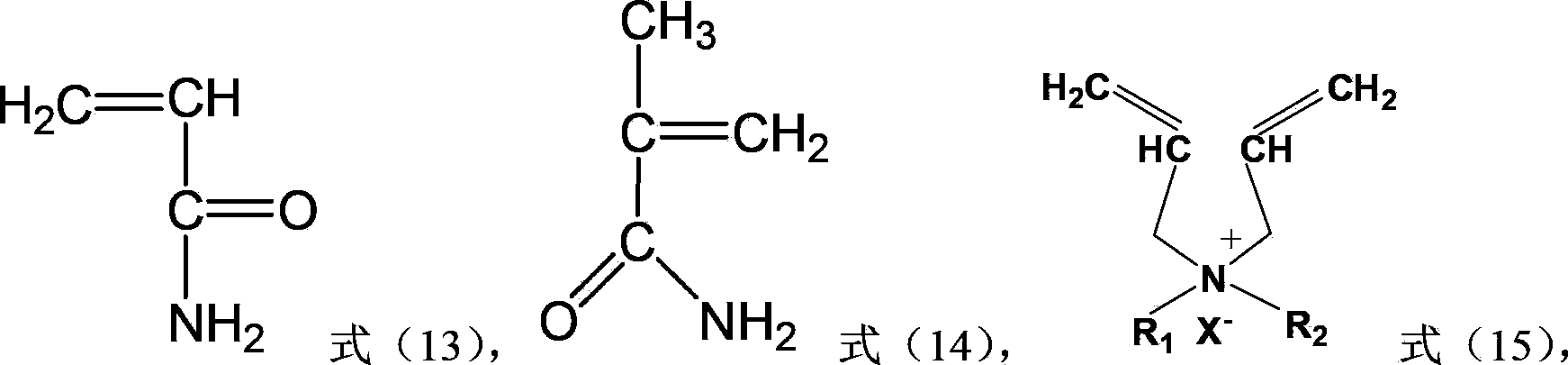
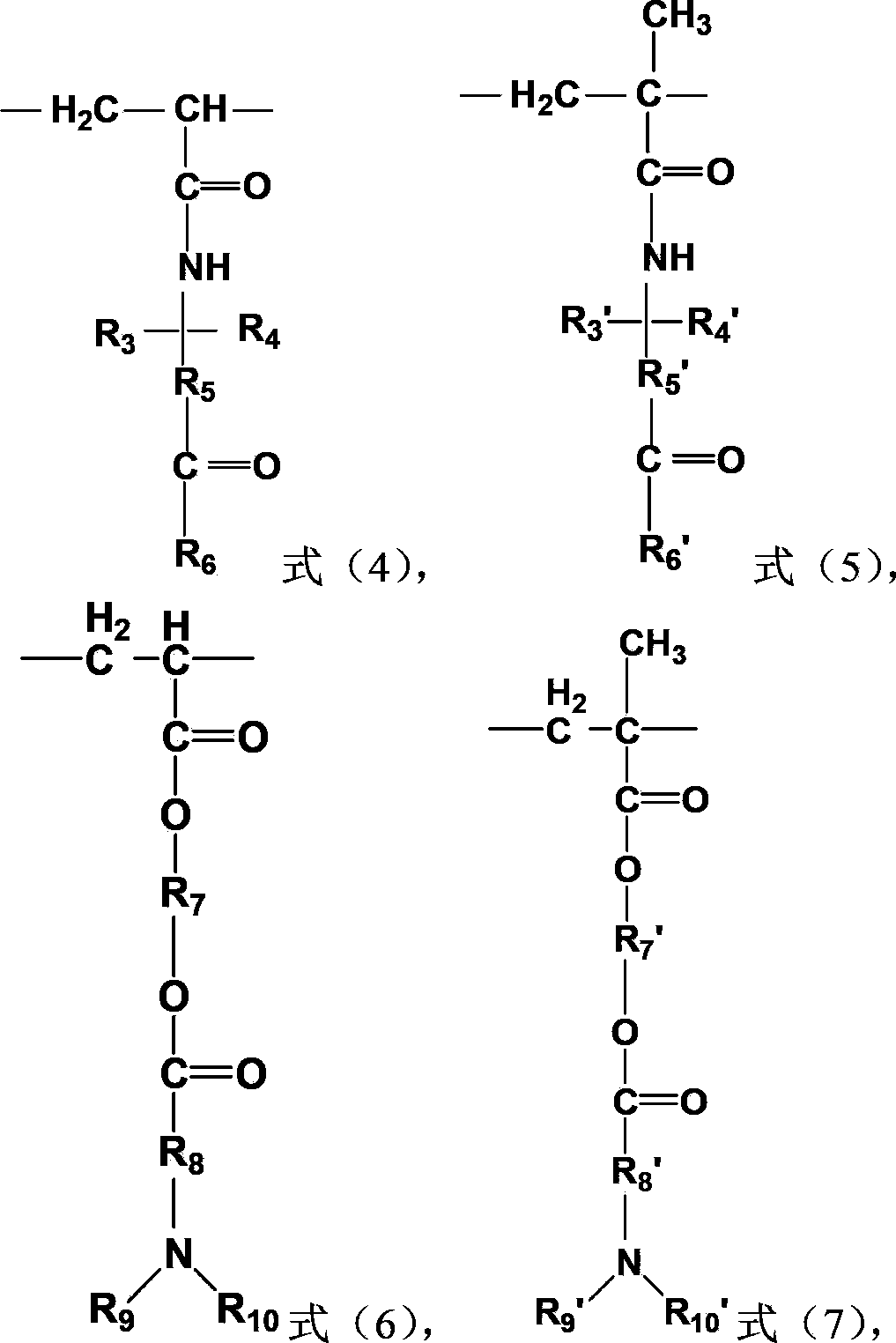Acrylamide copolymer, and preparation method and application thereof
An acrylamide-based and copolymer technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, mechanical equipment, piping systems, etc., can solve the problems of insignificant water sensitivity, poor fluid loss resistance, and limited resistance reduction performance, and achieve simple and simple Volume conversion rate, high drag reduction rate, and good compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of acrylamide copolymer by the solution polymerization method provided by the present invention.
[0085] At room temperature, 47.77g of acrylamide (AM), 39.6g of M1 monomer represented by formula (25), 7.90g of diacetone acrylamide (purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Company) and 0.5g of formula (26) The M2 monomer shown (prepared according to the method of the document Macromolecular Bioscience, 2006, 6(7), 540-554, the same below), was added to the reaction flask, 177.89g of deionized water was added, and stirred to completely dissolve the monomer , and stir well. 17.94 g of 1% by weight EDTA aqueous solution, 2.1 g of 1% by weight 2,2'-azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride aqueous solution, and 0.12 g of urea were respectively added to the flask, and stirred thoroughly to make them evenly mixed. Use 10% by weight of sodium hydroxide solution to pH 7.5, add 1.1 g of 0.5% by weight of sodium bisulfite solution, control the i...
Embodiment 2
[0093] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of acrylamide copolymer by the solution polymerization method provided by the present invention.
[0094] At room temperature, 39.4g of methacrylamide, 77.83g of M3 monomer represented by formula (28) (prepared according to the method of the document Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1991, 56(13), 4300-4304, the same below ), 15.6g of diacetone acrylamide and 0.01g of the M2 monomer represented by formula (26) were added to the reaction flask, 359.16g of deionized water was added, stirred to completely dissolve the monomer, and 0.1 Add 0.24 g of an aqueous solution of sodium citrate in % by weight, add 2.13 g of an aqueous solution of 1 % by weight 2,2'-azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride, add 0.08 g of urea, and stir well to make them evenly mixed. Use 25% by weight sodium hydroxide solution to pH 8, add 2.53g of 0.1% by weight sodium bisulfite solution, control the initial temperature of the system to 10°C, and add 3.0g o...
Embodiment 3
[0098] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of acrylamide copolymer by the solution polymerization method provided by the present invention.
[0099] At room temperature, 38.3g of acrylamide (AM), 45.52g of M4 monomer represented by formula (30) (according to the method of document Electrochimica Acta, 2003, 48(14-16), 1953-1959, the following The same), 30.46g of diacetone acrylamide and 0.21g of the M2 monomer represented by formula (26) were added to the reaction flask, and 457.96g of deionized water was added, stirred to completely dissolve the monomer, and stirred evenly. 10.03 g of a 1% by weight aqueous EDTA solution, 4.87 g of a 1% by weight azobisisobutylamidine hydrochloride aqueous solution, 0.03 g of urea, and 0.24 g of sodium formate were added to the flask, and stirred well to make them uniform. Use 1% by weight of sodium hydroxide solution to pH 7.5, add 1.1 g of 0.5% by weight of sodium bisulfite solution, control the initial temperature of the sy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com