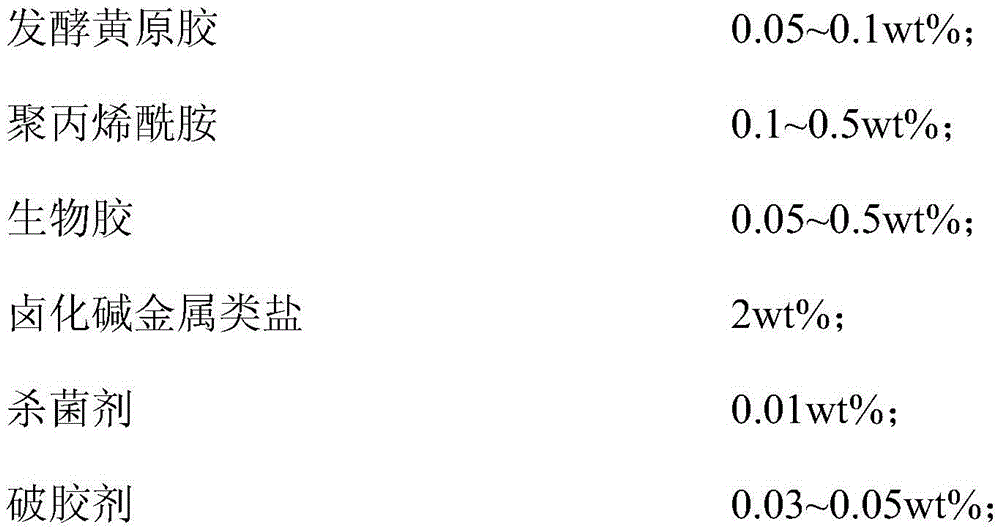supramolecular biopolymer fracturing fluid
A technology of molecular biology and polymers, applied in the direction of microorganisms, drilling compositions, methods based on microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as long time required, complex foam fracturing fluid construction equipment, and tight supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
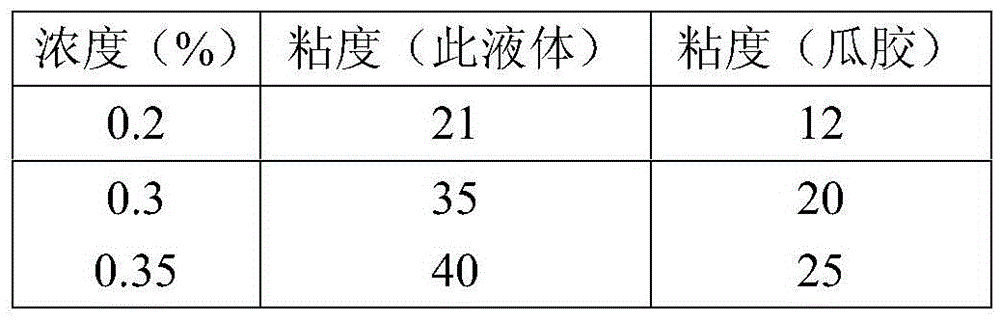
[0023] Dissolve 2.0g of KCl and 0.03g of ammonium persulfate in 100mL of distilled water, then add 0.01g of fungicide octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide, then add 0.05g of fermented xanthan gum, 0.1g of polyacrylamide and 0.05 g xanthan gum, stirring to fully dissolve various components, and the supramolecular biopolymer fracturing fluid is obtained when the solution is uniformly mixed into a viscous solution.
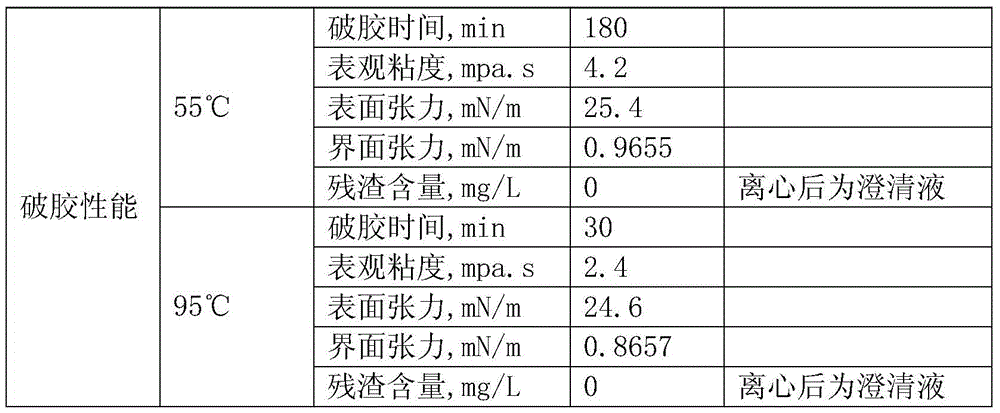
[0024] The supramolecular biopolymer fracturing fluid prepared in this embodiment is suitable for medium and low temperature coalbed gas wells, tight gas wells or oil wells at temperatures below 100°C.
Embodiment 2
[0026] Dissolve 2.0g KCl and 0.04g ammonium persulfate in 100mL distilled water, then add 0.01g bactericide cetyltrimethylammonium chloride, then add 0.08g fermented xanthan gum, 0.2g polyacrylamide and 0.5 g carboxymethyl cellulose, stirring to fully dissolve various components, and the supramolecular biopolymer fracturing fluid is obtained when the solution is uniformly mixed into a viscous solution.
[0027] The supramolecular biopolymer fracturing fluid prepared in this embodiment is suitable for medium and high temperature carbonate rock or sandstone oil wells at 100°C to 120°C.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Dissolve 2.0g KCl and 0.04g sodium persulfate in 100mL distilled water, then add 0.01g bactericide cetyltrimethylammonium chloride, then add 0.08g fermented xanthan gum, 0.2g polyacrylamide and 0.5 g guar gum, stirring to fully dissolve various components, and the supramolecular biopolymer fracturing fluid is obtained when the solution is uniformly mixed into a viscous solution.
[0030] The supramolecular biopolymer fracturing fluid prepared in this example is suitable for medium and high temperature carbonate rock oil wells at 100-120°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| shear viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| interfacial tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com