Method for pretreating lignocellulose by using carboxyl functionalized ionic liquid solution
A carboxyl-functionalized, lignocellulose technology, applied in bulk chemical production, fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of high price of ionic liquids and high regeneration costs, and achieve the effects of low cost, reduced pretreatment costs, and mild conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
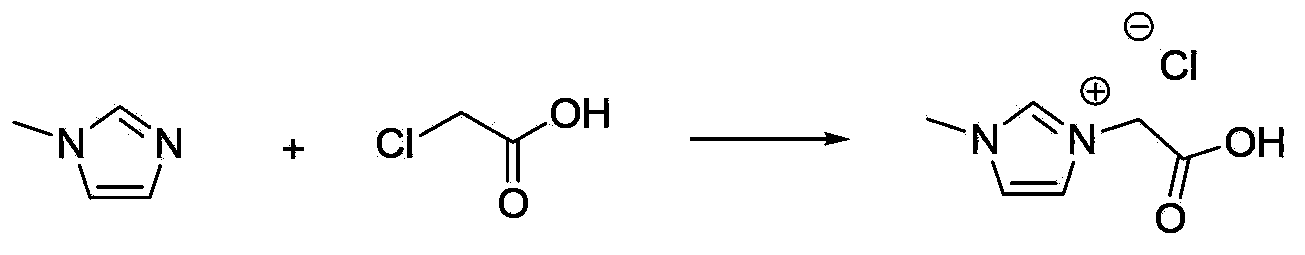
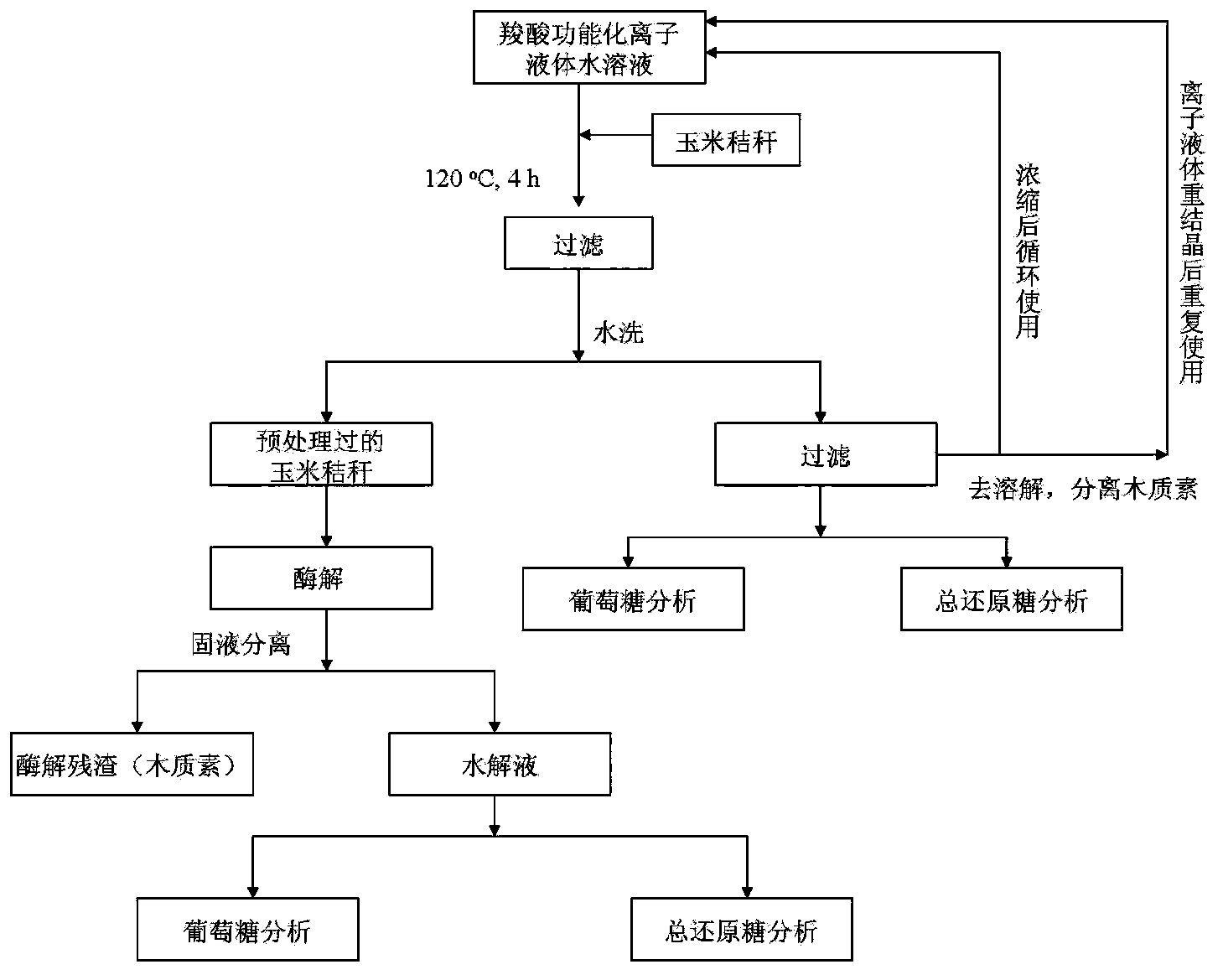
[0073] Put 3g of corn stalk or spruce thermomechanical pulp, 12g of 1-methyl-3-carboxymethylimidazolium chloride salt, 18g of water into a 100ml round bottom flask, install a condensing device, heat and stir at 120°C for pretreatment After 12 or 24 hours, cool down to room temperature, filter, and collect the filtrate for recycling. The filter residue is washed with 100 ml of water to remove the solid matter separated by filtration, and the residual ionic liquid is removed. After the solid sample is dried, it is ready to use. For the convenience of comparison, the main component contents of original corn straw and spruce thermomechanical pulp are shown in Table 1. After the cellulose-rich sample is dried, the component analysis structure is shown in Table 1. The filtrate was concentrated to 30g and directly recycled.
[0074] Table 1 Composition of raw materials without pretreatment
[0075]
[0076] Table 2 Composition of raw materials after pretreatment under different...
Embodiment 2
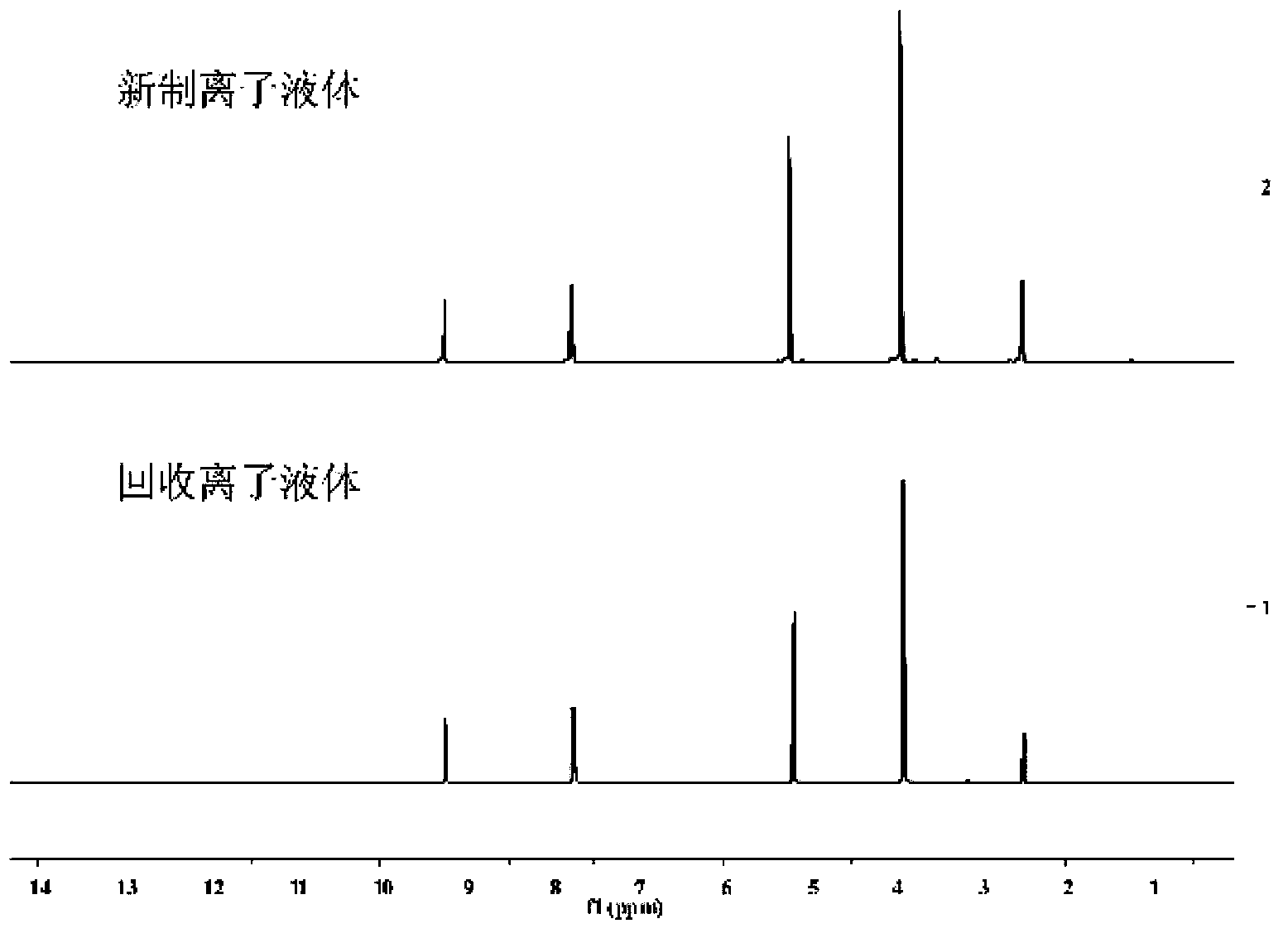
[0080] Add 3g of corn stalks, 6g of 1-methyl-3-carboxymethylimidazolium chloride salt, and 24g of ethanol into a 100ml autoclave, cover the autoclave, heat and stir at 120°C for 24h, and then cool down to room temperature. The reactor was opened, filtered, and the filtrate was collected for recycling, and the filter residue (cellulose-rich sample) was washed with 200 ml of water to remove residual ionic liquid. For convenience of comparison, the composition analysis structures of the original corn stalks and pretreated corn stalks (cellulose-rich samples) are shown in Table 3 after drying. Rotary evaporation to remove ethanol, recycling, adding 50ml of water to the system, the separated lignin precipitated, separated by filtration, washed to remove the ionic liquid, dried for later use. After the water was removed by rotary evaporation, the ionic liquid was recrystallized from methanol-ethyl acetate to realize the purification and recycling of the ionic liquid. NMR analysis s...
Embodiment 3
[0086] The drying of biomass raw materials is a very energy-consuming process, and this patent has good tolerance to water. We illustrate the wet biomass material claimed in the present invention by using corn stover with a moisture content of up to 20 wt % as raw material. details as follows:
[0087] The corn stalks are crushed before use, and the moisture content is 20.4wt%. Weigh 10g of corn stalks, 3g of 1-methyl-3-carboxymethyl chloride, 27g of butanol, add them into a 100ml autoclave, cover the autoclave, heat and stir at 160°C for 0.5 hours, and drop to At room temperature, open the reaction kettle, filter, collect the filtrate for recycling, and wash the filter residue (cellulose-rich sample) with 300 ml of water to remove residual ionic liquid. After the cellulose-rich sample is dried, the component analysis structure is shown in Table 4. Rotary evaporation removes butanol, recycles it, adds 50ml of water to the system, and the separated lignin precipitates out, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com