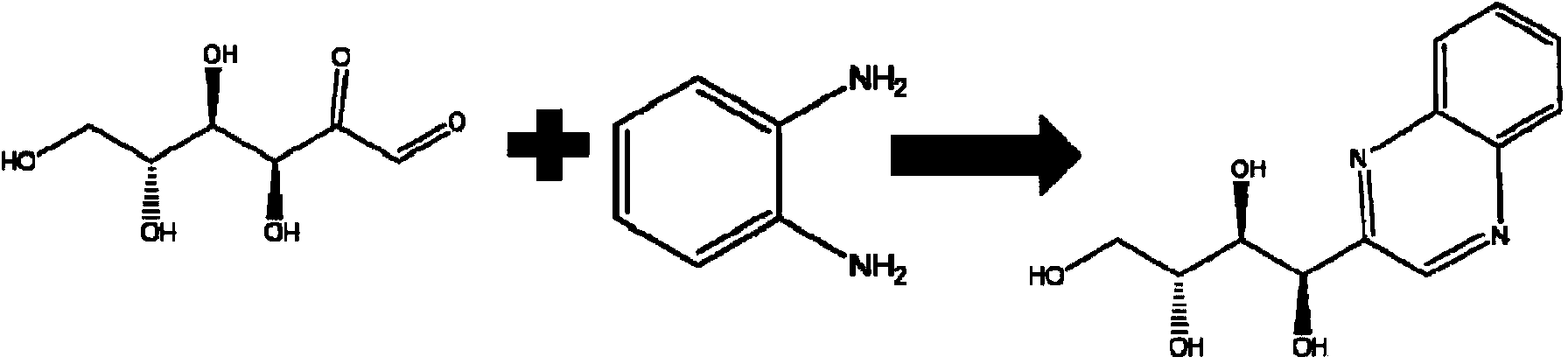
Detection method of peptide-advanced glycation end product
A technology for advanced glycosylation and end products, applied in measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable quantification of dicarbonyl compounds in reaction intermediates, affecting the qualitative and quantitative properties of pyrrolidine, and low content of dicarbonyl compounds, etc. , to achieve good detection limit, qualitative accuracy and readability, and quantitative accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
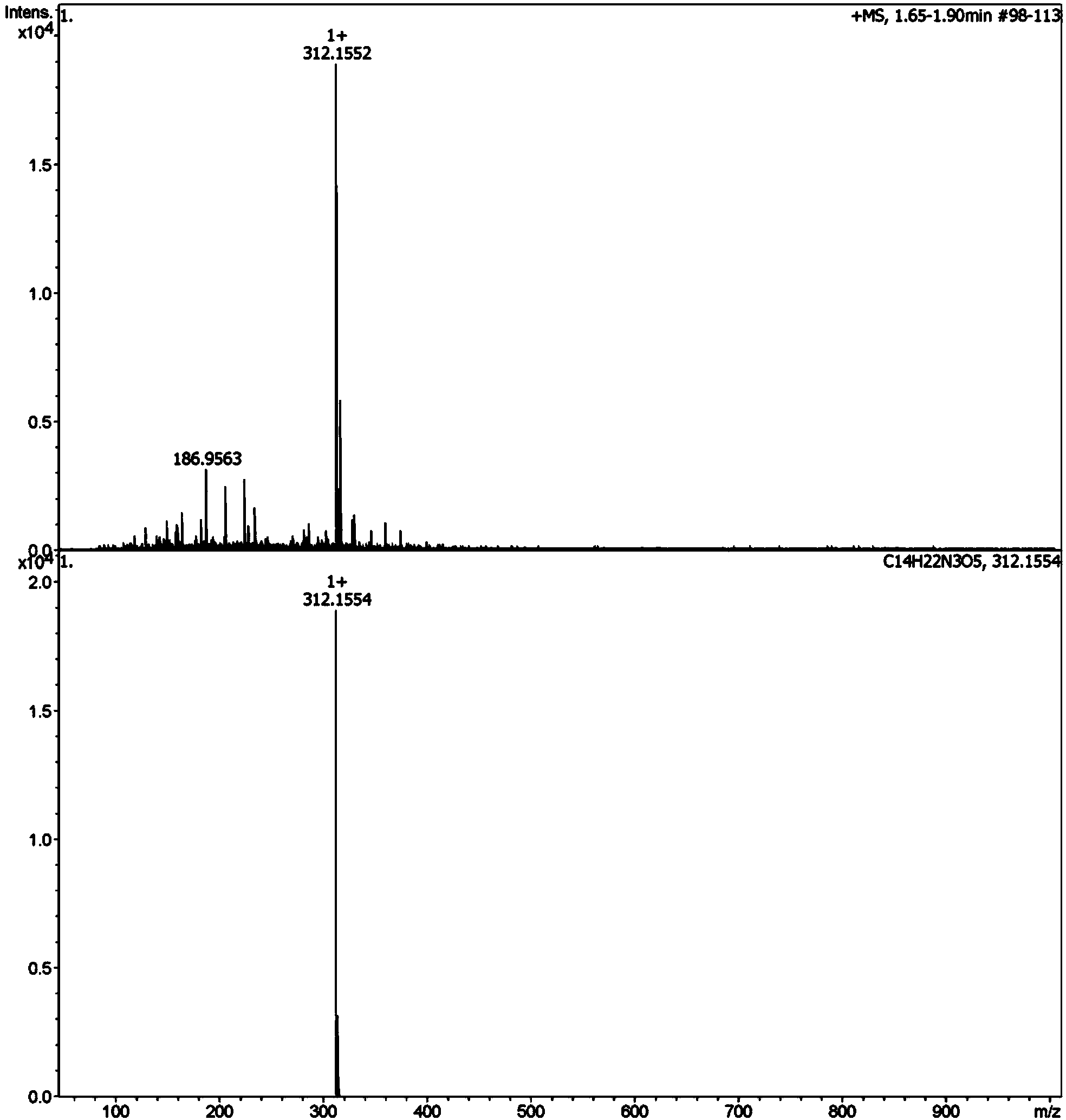
[0051] Use dipeptide (N)Lys-Ala(C) to react with glucose, (N)Lys-Ala(C) and glucose are mixed in 0.2M PBS (phosphate buffer, pH=6.8) medium, dipeptide concentration 10 -3 mol / L, glucose concentration 5×10 -3 mol / L, with a total volume of 15mL, heated at 140°C for 20min in a microwave digestion tank. After reaching the designated heating time, immediately add o-phenylenediamine whose molar mass is 2 times of the reducing sugar molar mass in the sample, so that the reaction is terminated immediately. After 3 hours, solid-phase extraction was used for enrichment, and the steps were as follows: select functionalized polystyrene / divinylbenzene as the extraction column, activate the extraction column with 4mL methanol and 4mL water respectively, load the sample with 1mL, rinse with 2mL water, and negatively Elute with 4 mL of pure methanol after being pumped dry under pressure for 4 min. Blow the eluate to dryness with nitrogen at 50 ° C. The mobile phase is fixed to 1 mL, filtered...
Embodiment 2
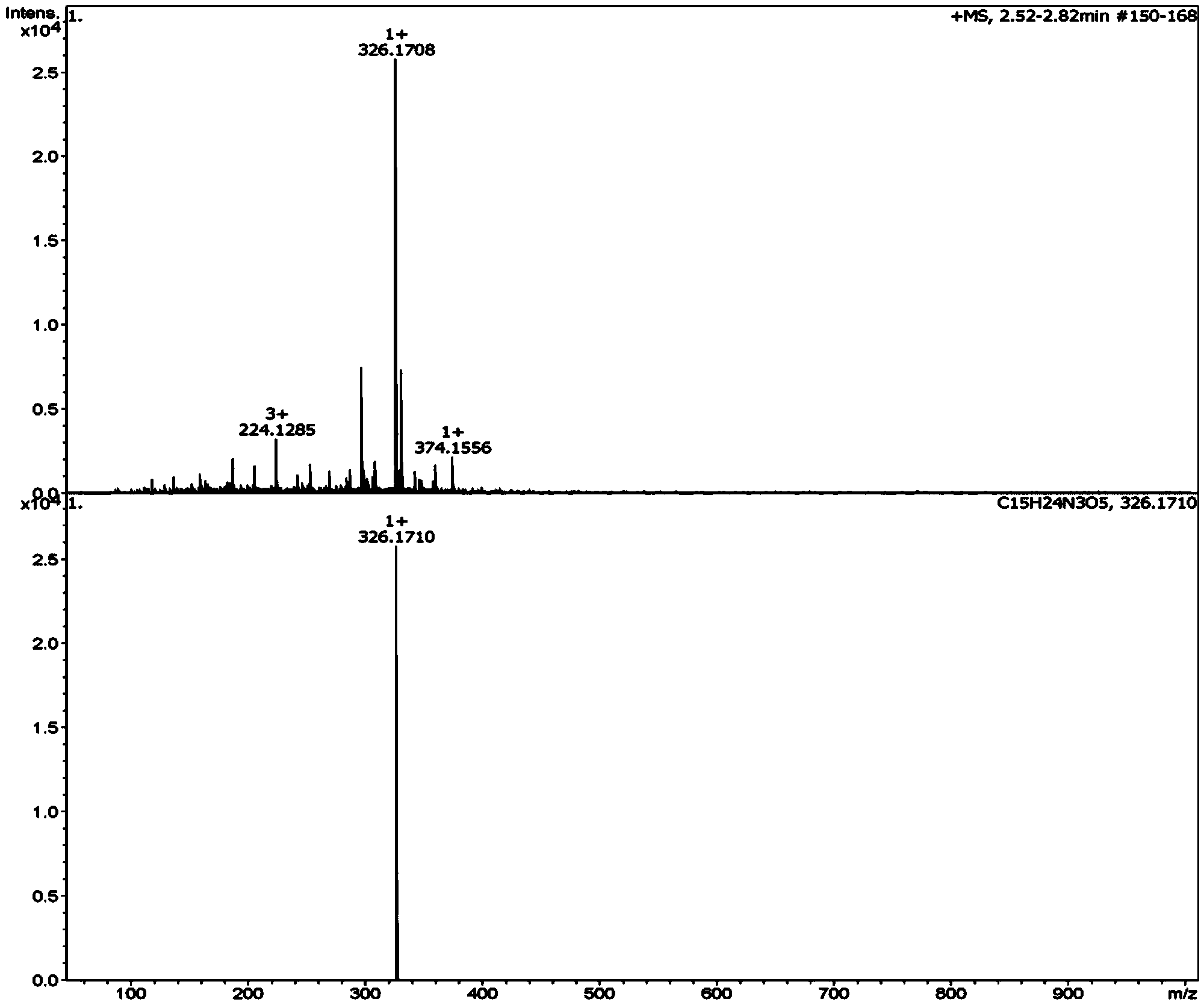
[0053] Use dipeptide (N)Lys-Gly(C) to react with glucose, mix (N)Lys-Gly(C) and glucose in 0.2M PBS (phosphate buffer, pH=6.8) medium, dipeptide concentration 10 -3 mol / L, glucose concentration 5×10 -3 mol / L, with a total volume of 15mL, heated at 140°C for 20min in a microwave digestion tank. After reaching the designated heating time, immediately add o-phenylenediamine whose molar mass is 5 times of the reducing sugar molar mass in the sample, so that the reaction is terminated immediately. After 3 hours, use solid-phase extraction technology for enrichment, the steps are as follows: use 4mL methanol and 4mL water to activate the extraction column respectively, load the sample with 1mL, rinse with 2mL water, dry it under negative pressure for 4min, and elute with 4mL pure methanol. The liquid was removed and blown to dryness with nitrogen at 50°C, the mobile phase was adjusted to 1 mL, filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane, and then analyzed by high-resolution mass spectromet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com