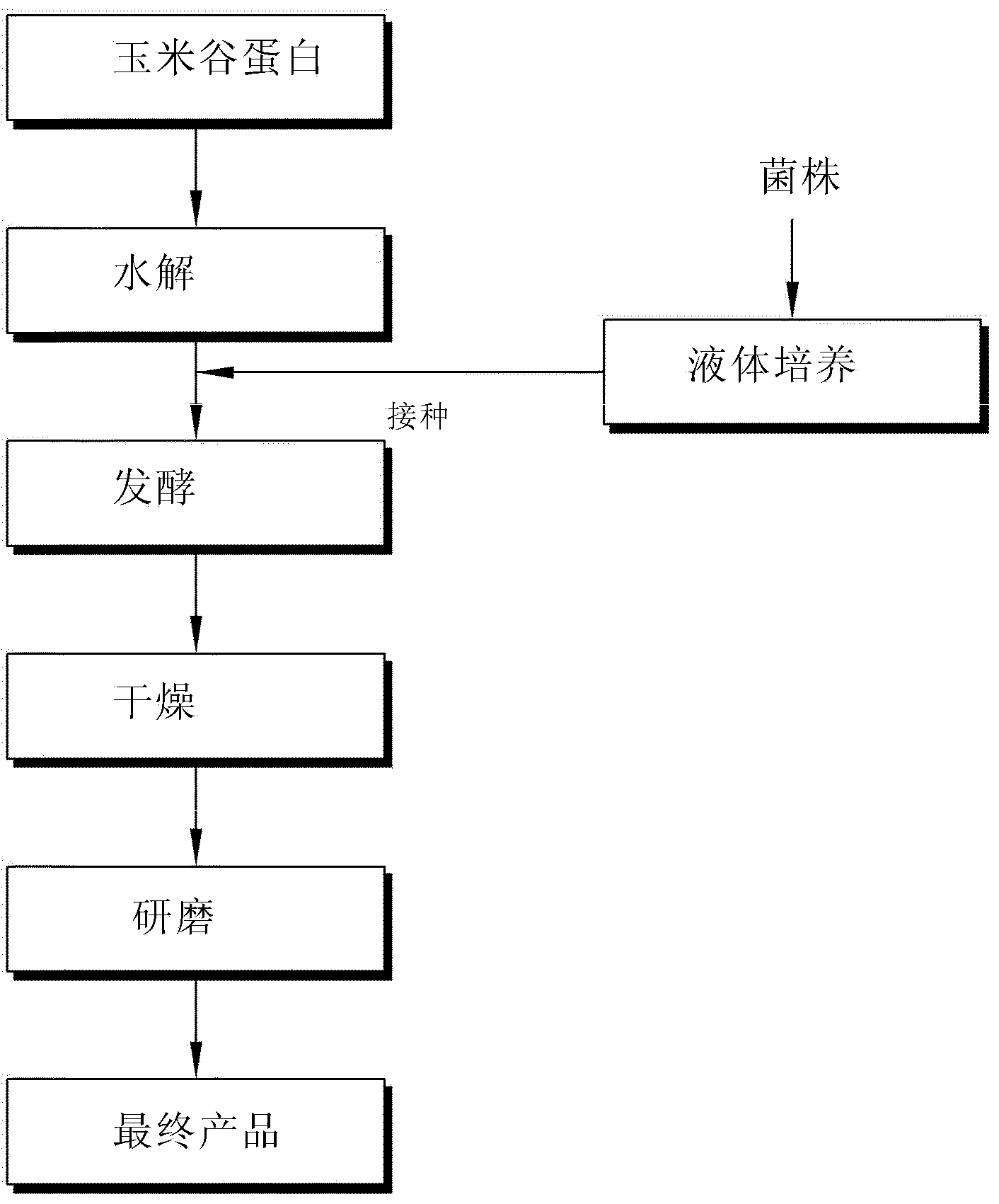
Preparation method for fermented corn gluten
一种谷蛋白、玉米的技术,应用在饲料添加剂领域,能够解决不能用饲料、没有提高玉米谷蛋白商业可用性、高昂生产成本等问题,达到低生产成本、优异商业可用性和价值、优异适用性和价值的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Embodiment 1 The influence of heat treatment on solid fermented corn gluten
[0067] Add an equal amount of water to the corn gluten, then heat the corn gluten at 60°C to 120°C, and cool to the optimum fermentation temperature of 37°C. Afterwards, Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) was inoculated in corn gluten with the same strain inoculation density in each experimental group.
[0068] Table 1 Solid state fermentation of heat-treated corn gluten
[0069]
[0070] As shown in Table 1, it can be seen that the growth of the inoculated strains has nothing to do with heat treatment. From the above results, it was confirmed that corn gluten was sufficiently fermented without performing the initial steaming (heat treatment) treatment.
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2 Confirmation of Fermentation Levels of Corn Gluten Based on Initial Content of Added Moisture
[0072] In order to determine the fermentation level of corn glutenin based on the initial moisture content, corn glutenin with moisture content adjusted to 30%, 40%, 50%, 60%, 70% and 80% after adding water was inoculated with Bacillus sp.) and lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus sp.) strains were fermented for 24 hours and counted. The results are shown in Table 2 below.
[0073] Table 2 Fermentation levels of corn gluten based on initial content of added moisture
[0074]
[0075] The results showed that when the moisture content of corn gluten was 30%, compared with the initial number of inoculated strains (1.0×10 7 cfu / g) compared to Bacillus strains (1.2×10 7 cfu / g) slight growth, lactic acid bacteria strains (8.2×10 6 cfu / g) did not grow. Furthermore, it can be seen that the Bacillus strain grows rapidly at a moisture content of 40% or more, indicating...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3 Determination of protein degradability based on corn gluten fermentation conditions
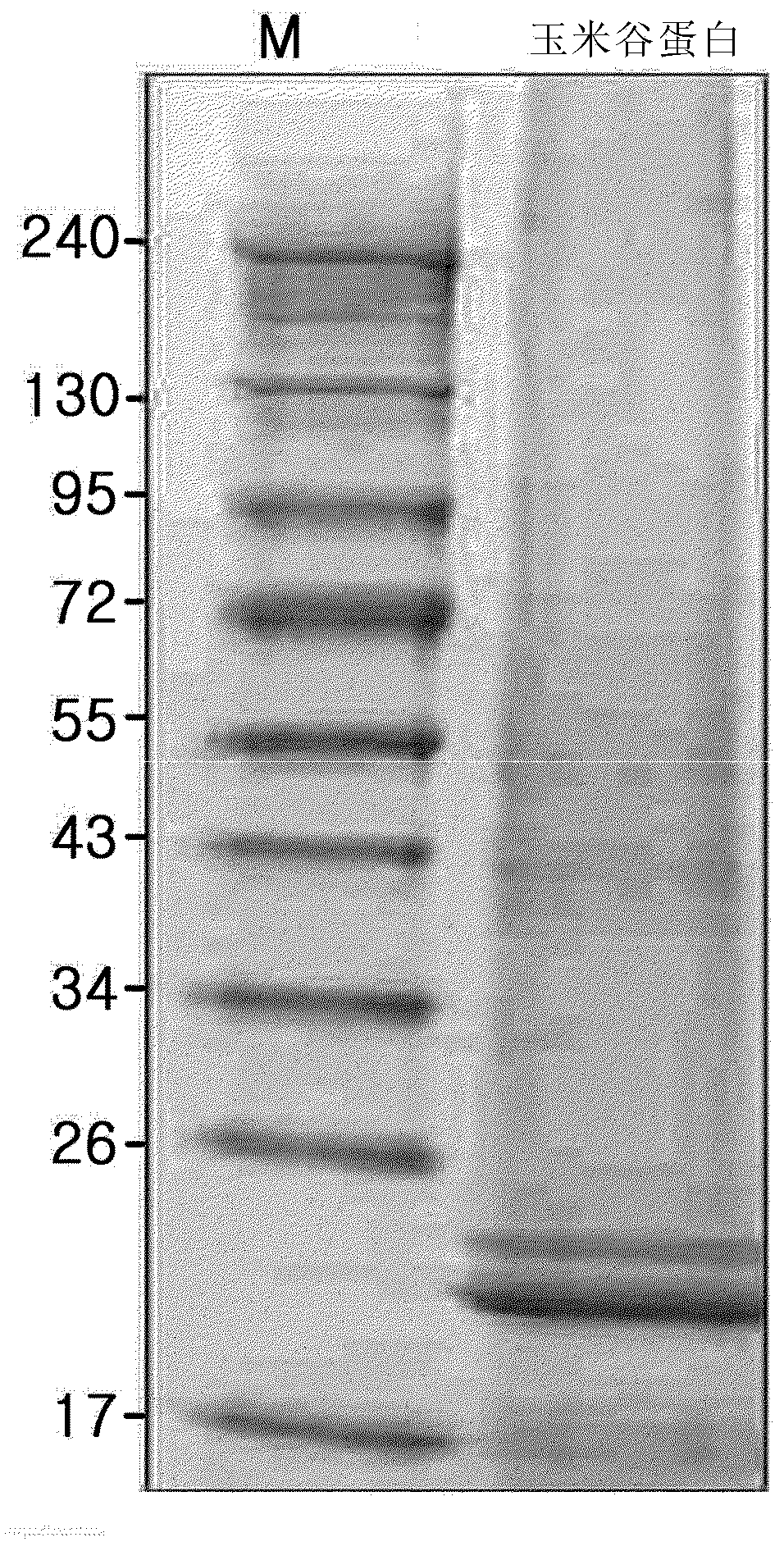
[0077] Protein species in maize glutenin were determined by SDS-PAGE. The results are shown in figure 2 . The results showed that corn glutenin was simply degraded into two proteins, such as figure 2 shown in .
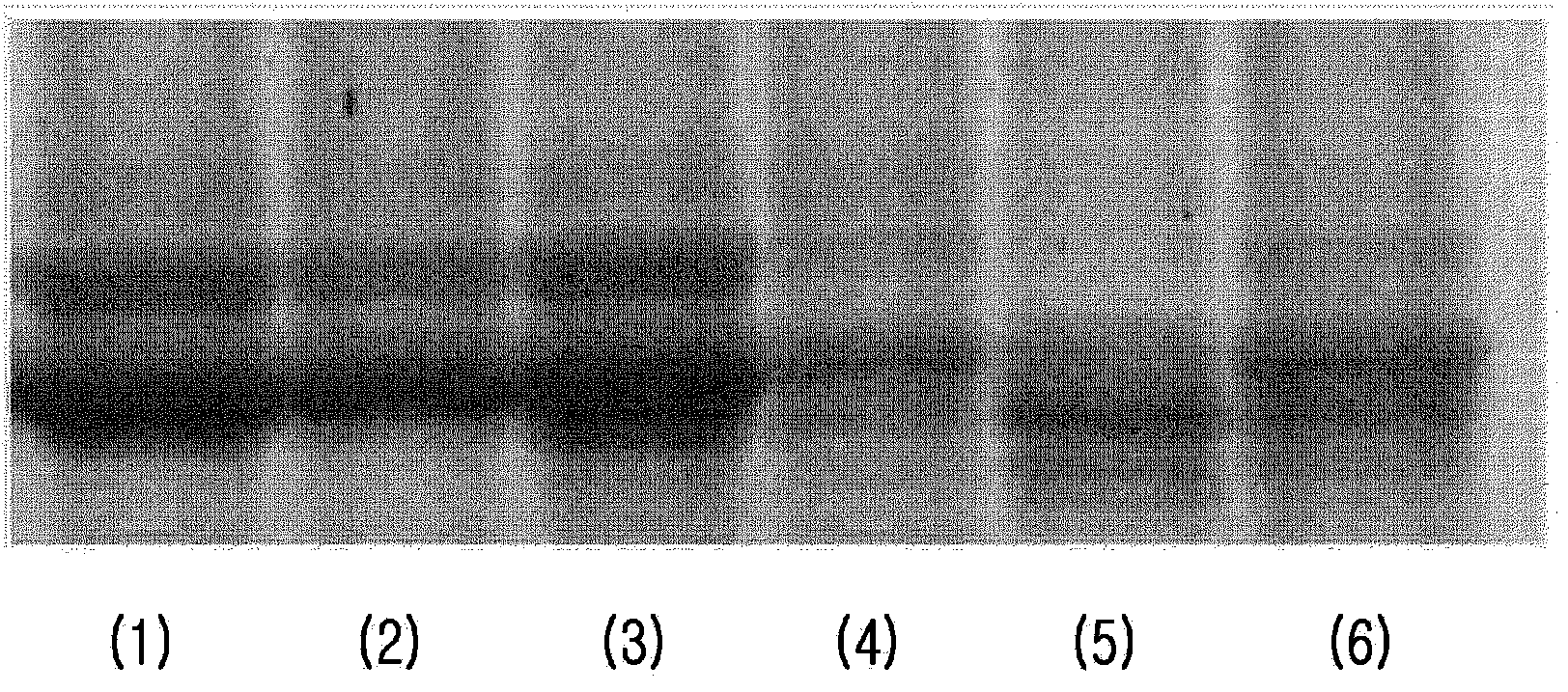
[0078] when figure 2 When the major proteins of corn glutenin shown in , were converted to low molecular weight molecules by fermentation, the digestion efficiency of the final product was improved, indicating protein degradation in corn glutenin under realistic fermentation conditions. image 3 After showing the corn glutenin with 50% moisture content after adding moisture was inoculated with plantarum lactobacillus and cultivated at 30°C for 48h, the degradation results (swimming lane 2) of the constituent proteins of corn glutenin; After the corn glutenin was inoculated with Bacillus subtilis and cultivated at 50°C for 48h, the degradation results of the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com