A bacterial cellulose/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanometer conductive composite material and a preparing method thereof
A technology of ethylenedioxythiophene and bacterial cellulose, which is applied in the field of bacterial cellulose/poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene nano-conductive composite material and its preparation, can solve the problem of loss of three-dimensional network structure, difficult structural uniformity, and limitations Research and other issues to achieve the effect of uniform chemical structure, unique performance and good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
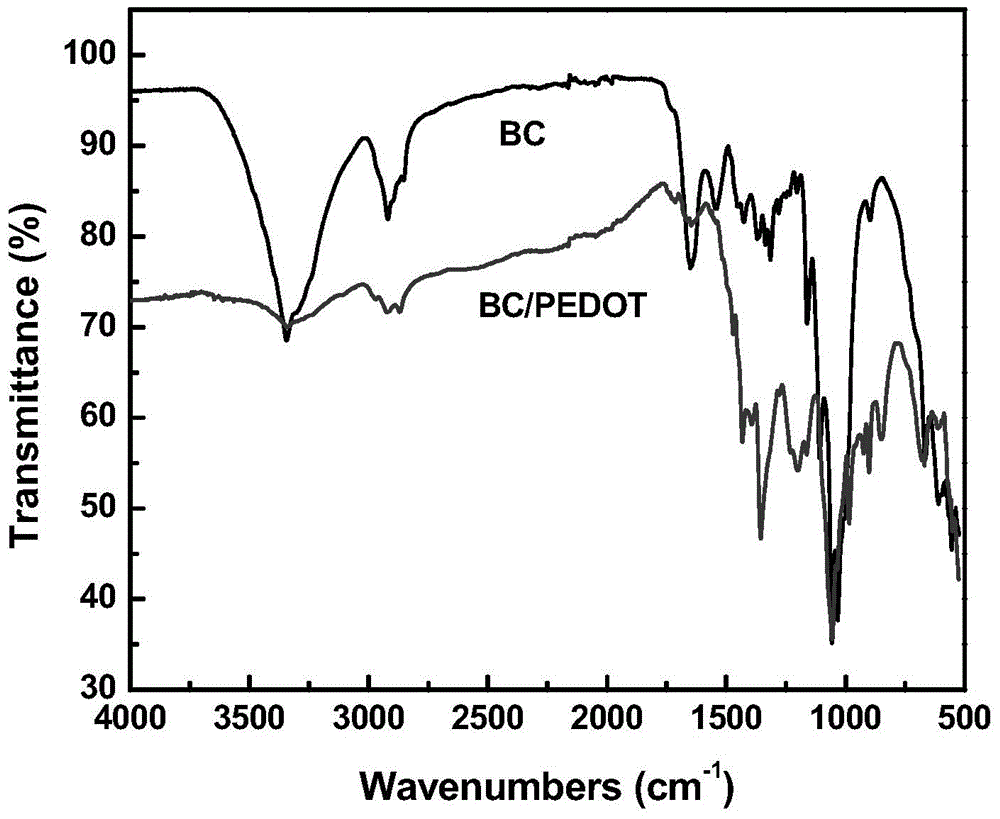
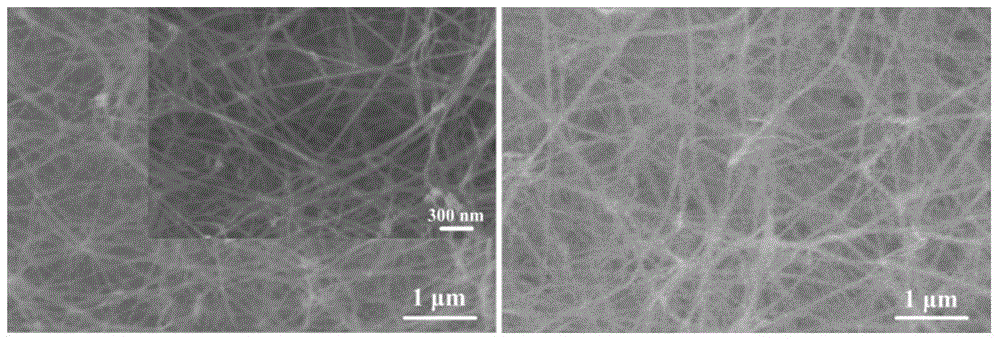
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
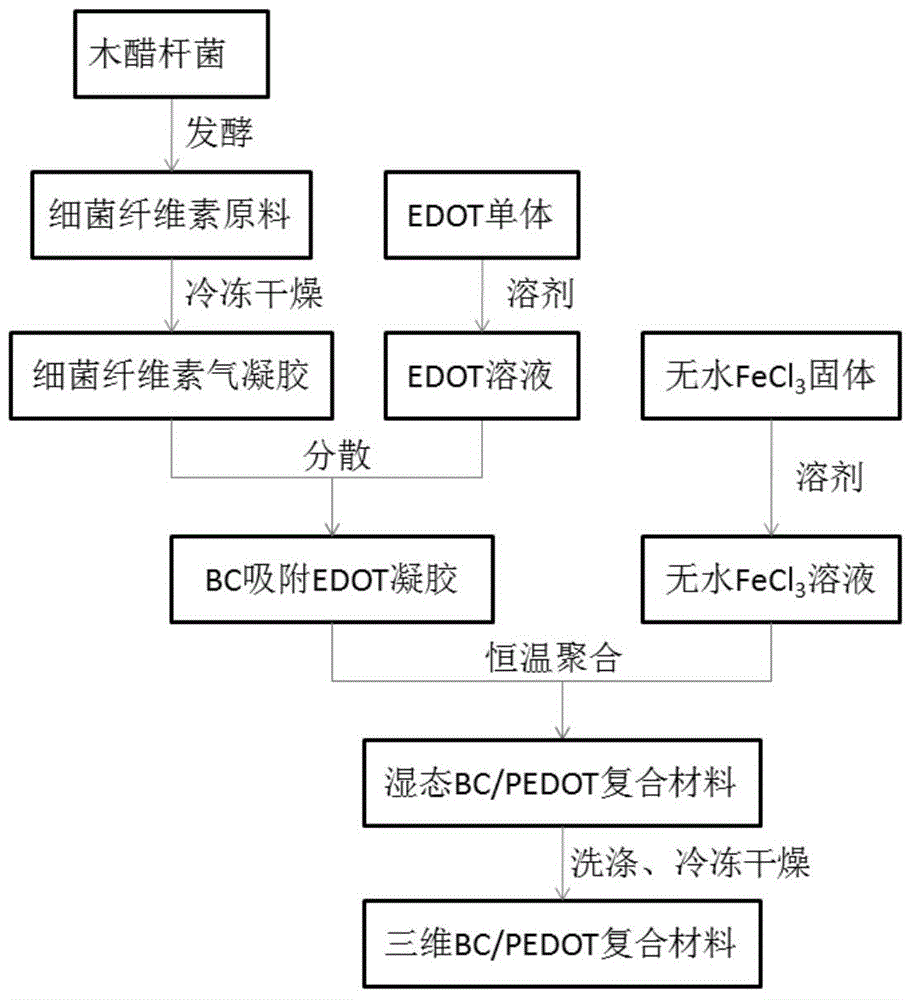
[0034] combine figure 1 , a preparation method of bacterial cellulose / poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene nano-conductive composite material, the steps are as follows:
[0035] The first step: get the bacterial cellulose membrane (film thickness 1mm~1cm) of Acetobacter xylinum dynamic fermentation, and the bacterial cellulose floc of static fermentation, use the NaOH of 0.1%~4% and 0.1%~4%H 2 o 2 Treat at 60-90°C for 1-5 hours. Rinse off with running tap water. (obtain pure bacterial cellulose raw material with three-dimensional network structure)
[0036] Step 2: Cut the cleaned bacterial cellulose wet film into small pieces of 1-3cm×1.5-4cm, and the bacterial cellulose flocs are dispersed in water with a mass concentration of 0.1%-5% and plasticized with containers of different shapes, placed in Freeze-dry in a freeze dryer for 10 to 24 hours, equipped with a vacuum bag. (Cellulosic material made into faceted small pieces)
[0037] Step 3: Prepare 0.01-0.5g / L EDOT and anhy...
Embodiment 1
[0046] The bacterial cellulose film obtained by the static fermentation of Acetobacter xylinum was treated with 0.1% NaOH and 0.1% H 2 o 2 Treat in a water bath at 80°C for 2 hours, take out tap water and rinse until neutral; cut into regular 2cm×2cm small pieces with scissors, place them in a freeze dryer for 24 hours, take out and place in 10mL of 0.05g / mLEDOT (3 , 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) ether solution, ultrasonic at 20°C for 30 minutes, then add an equal volume of 0.05 g / mL anhydrous ferric trichloride ether solution, quickly transfer to ultrasonic cleaning agent, and ultrasonically react at 20°C for 30 minutes , then take it out and wash it repeatedly three times with ethanol and deionized water successively, soak it overnight with deionized water for the last time, take it out and freeze-dry it to obtain the bacterial cellulose / poly-3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene composite material.
Embodiment 2
[0048] The bacterial cellulose film obtained by the static fermentation of Acetobacter xylinum was treated with 0.2% NaOH and 0.2% H 2 o 2 Treat in a water bath at 90°C for 2 hours, take out tap water and rinse until neutral; cut into regular pieces of 1cm×1cm with scissors, place them in a freeze dryer for 20 hours, take out and place in 10mL of 0.05g / mLEDOT (3 , 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) ethyl pure solution, 20 ℃ constant temperature ultrasonic 30min, then add an equal volume of 0.05g / mL anhydrous ferric trichloride ethyl ether solution, 20 ℃ constant temperature ultrasonic reaction 30min, then take out and transfer to 20 ℃ Place it in a constant temperature environment for 24 hours. When the ethanol is fully volatilized, the reaction is complete. After that, it is washed with ethanol and deionized water repeatedly three times, and the last time it is soaked in deionized water overnight, taken out and freeze-dried to obtain bacterial cellulose / poly 3,4- Ethylenedioxythiophe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com