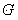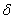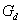Method for testing mechanical property of braze welding connector
A technology of brazing joints and testing methods, applied in the direction of applying stable tension/pressure to test the strength of materials, can solve the problems of lack of testing methods for mechanical properties of brazed plate-fin structures, inaccurate test results, etc. Reliable test results, simple and clear results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] see figure 1 . A method for testing the mechanical properties of a brazed joint, comprising the following steps:
[0063] (1) Preparation of T-shaped tensile specimen 8
[0064] Adopting the base material of metal materials including carbon steel, aluminum alloy, copper alloy and titanium alloy with a thickness of h=0.9mm, cutting the base material into profiles with a length of 150 mm and a width of 160 mm, and bending them at 90°, Bending the 150mm short side of the profile into an L-shaped structure that is 105mm long and 45mm short.
[0065] Then align the two L-shaped structural parts at the level of 45mm on the short side (back to back), and place a high-temperature resistant nickel-based solder BNi in the middle 2 , Nickel-based solder BNi 2 The thickness is h c =70μm; then brazed with a clamp to obtain a T-shaped welded piece.
[0066] During the implementation, it was found that when the bending angle of the base metal is greater than 90°, the tightness o...
Embodiment 2
[0089] A method for testing the mechanical properties of a brazed joint, the basic content of which is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
[0090] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is:
[0091] The loading rate for testing the mechanical properties of the T-shaped tensile specimen 8 joint at room temperature is 2mm / min, and the preload is 200N.
[0092] The load-displacement curve figure of embodiment 2 test is referring to Figure 4 .
Embodiment 3
[0094] A method for testing the mechanical properties of a brazed joint, the basic content of which is the same as in Example 1.
[0095] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is:
[0096] Austenitic stainless steel with thickness h=0.5mm; nickel-based brazing material BNi 2 The thickness is h c =40μm.
[0097] T-shaped tensile test specimen 8 Welding section 1 has a length of 30mm and a width of 15mm; tensile section 2 has a length of 60mm and a width of 15mm; clamping end 3 has a width of 25mm and a length of 30mm, and the pin on the clamping end 3 The hole 4 has a diameter of 6mm.
[0098] The testing temperature of the heating furnace 9 is 200° C.; the holding time of the testing temperature is 10 minutes.
[0099] The loading rate is 3mm / min and the preload is 200N.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com