Method for treating ammonia-nitrogen containing p-aminodiphenyl amine production wastewater
A technology for the production of p-aminodiphenylamine and waste water, which is applied in natural water treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. It can solve the problem that the COD content does not meet the national discharge standard and lacks complete and effective means , Chlorine leakage in the air and other problems, to achieve stable treatment effect, high ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency, and reduce treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
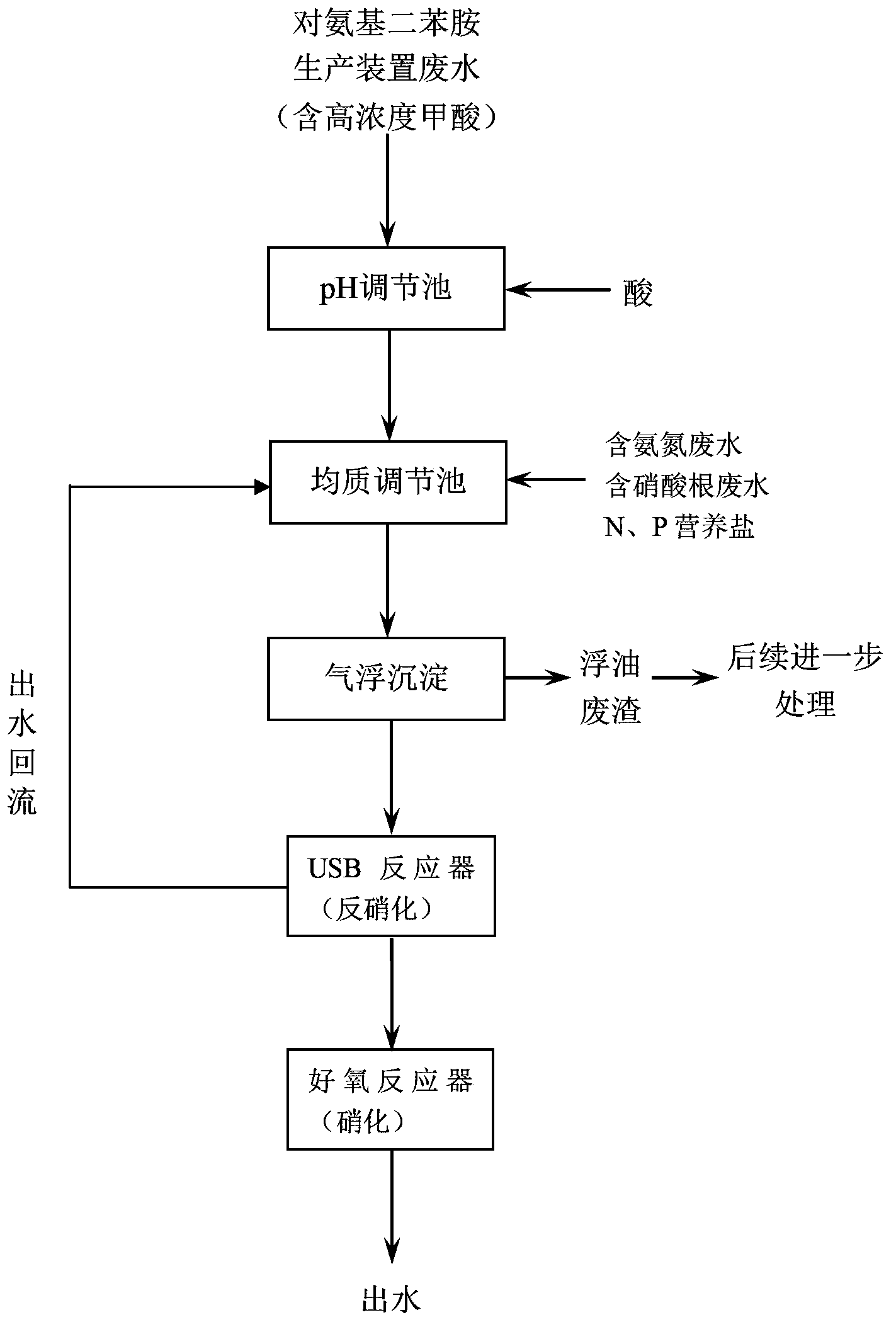
[0070] The wastewater flow rate of a p-aminodiphenylamine production plant in a chemical plant is 100t / d, and the pollutant indicators in the wastewater are: COD of wastewater is 50130mg / L, TOC is 30320mg / L, concentration of formic acid is 116300mg / L, pH is 10.8; wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen The concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the medium is 212mg / L.
[0071] In the first step, in the pH adjustment pool, dilute HCl is used to adjust the pH of p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater to 4.5.
[0072] In the second step, in the homogeneous adjustment tank, p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater (wastewater from the production of p-aminodiphenylamine containing formic acid) is mixed with wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen (wastewater from the production of aniline containing ammonia nitrogen), and the tail magnesium water containing nitrate is added. , and add part of the reflux water from the USB reactor and a small amount of dilution water to dilute the wastewater. The pH of...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The waste water flow rate of a p-aminodiphenylamine production plant in a chemical plant is 110t / d, and the pollutant indicators in the waste water are: waste water COD is 62400mg / L, TOC is 41700mg / L, formic acid concentration is 162600mg / L, pH is 11.4; The concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater is 276mg / L.
[0080] In the first step, in the pH adjustment pool, dilute HCl is used to adjust the pH of p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater to 4.8.
[0081] In the second step, in the homogeneous adjustment tank, p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater is mixed with wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen, ammonium nitrate wastewater containing nitrate is added, and part of the reflux water from the USB reactor and a small amount of dilution water are added to dilute the wastewater. The pH of the effluent in the homogeneous adjustment tank is 7.1, the COD is 1248.0mg / L, the TOC is 834.0mg / L, the formic acid is 3252.0mg / L, the nitrate is 1273.6mg / L, and the ammonia nitrogen con...
Embodiment 3
[0088] The wastewater flow rate of a p-aminodiphenylamine production plant in a chemical plant is 120t / d, and the pollutant indicators in the wastewater are: wastewater COD is 71500mg / L, TOC is 52620mg / L, formic acid concentration is 228700mg / L, pH is 12.5; The concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater is 325mg / L.
[0089] In the first step, in the pH adjustment tank, use dilute HNO 3 Adjust the pH of p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater to 5.4.
[0090] In the second step, in the homogeneous adjustment tank, p-aminodiphenylamine wastewater is mixed with ammonia nitrogen-containing wastewater, sodium nitrate solution is added, and part of the reflux water from the USB reactor and a small amount of dilution water are added to dilute the wastewater. The pH of the effluent in the homogeneous adjustment tank is 7.2, the COD is 1430.0mg / L, the TOC is 1052.4mg / L, the formic acid is 4574.0mg / L, the nitrate is 1259.6mg / L, and the ammonia nitrogen concentration is 162.5mg / L. TOC...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| chemical oxygen demand (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com