Preparation method and application of RGD-modified ultra-small magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
An iron oxide nanometer and ultra-small magnetic technology, which is applied in the field of biomedical nanomaterials, can solve the problems of unfavorable nanoparticle surface ligand replacement reaction, complicated nanoparticle surface modification, and expensive reducing agent, so as to save preparation time and improve Excellent magnetic properties and monodispersity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0070] A preparation method of RGD-modified ultra-small magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, comprising the steps of:
[0071] Step 1. Preparation of Ultra-Small Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
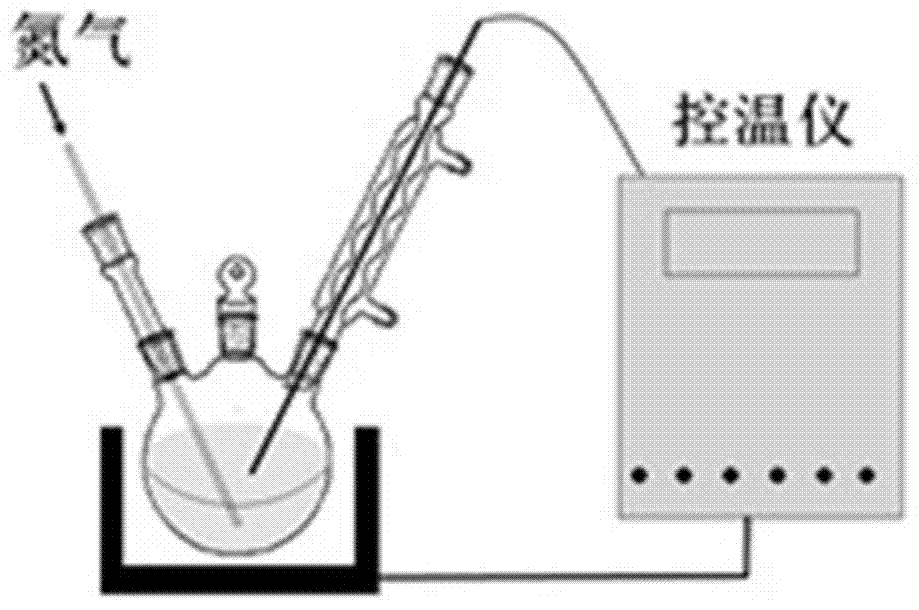
[0072] It is prepared by an improved high temperature pyrolysis method, and the reaction device is as follows figure 1 As shown, the reaction preparation process is as follows figure 2 As shown, wherein, iron acetylacetonate is a reaction raw material and a precursor, oleylamine is a surfactant and a reducing agent, and dibenzyl ether is a solvent. The specific preparation process is as follows:
[0073] Mix dibenzyl ether and oleylamine at a volume ratio of 1:9 to 9:1, continuously feed nitrogen to remove oxygen in the system, and then add iron acetylacetonate, the concentration of iron acetylacetonate in the reaction solution system is 0.125 to 0.175mol / L, heated at 2-6°C / min to 190-230°C (the temperature is the nucleation temperature of nanoparticles), preferably 220°C, and kep...
Embodiment 1
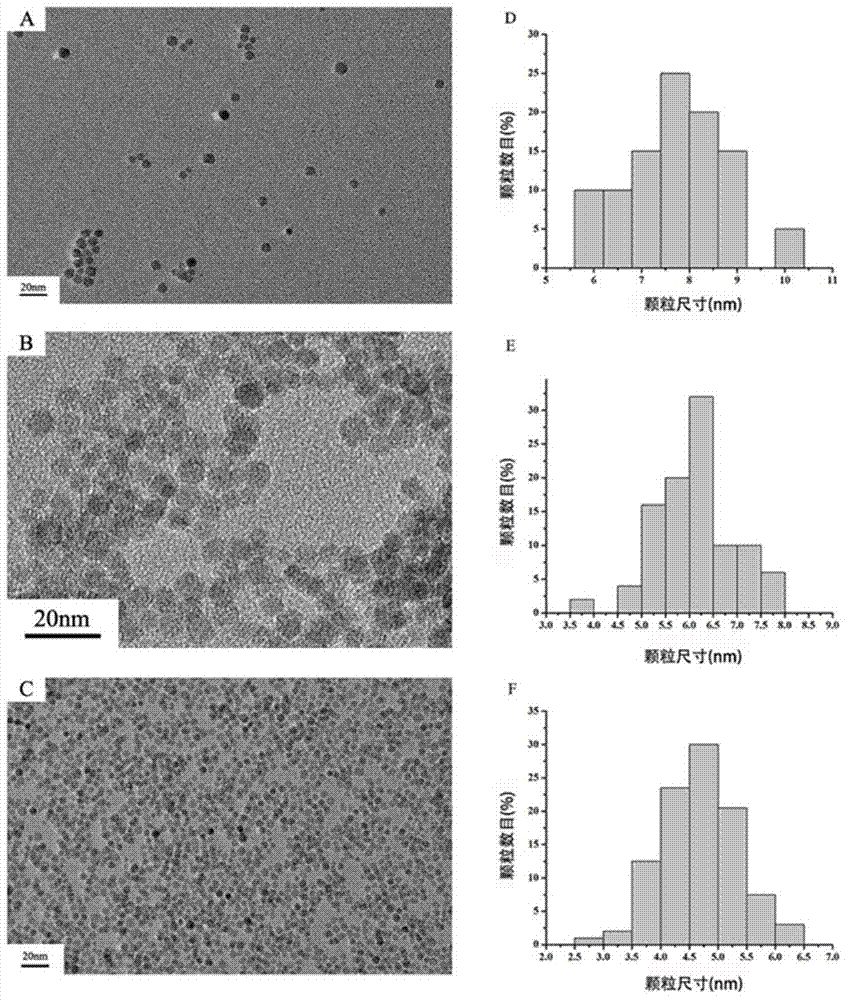
[0094] Preparation of ultrasmall magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles under different growth times.
[0095]Add 8mL of dibenzyl ether and 12mL of oleylamine to three 100mL three-necked flasks, continue to feed nitrogen to remove the oxygen in the system, then add 3mmol of iron acetylacetonate, and use the temperature control device at 3.3°C / min Heating rate Heat each reaction system to 220°C (nucleation temperature) and keep the temperature for 1h. This stage is the nucleation stage of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. During this process, the solution turns from brownish red to bright black. Next, each reaction system was heated to 290° C. (growth temperature) at a heating rate of 3.3° C. / min, and each reaction system was maintained at this temperature for 45 min, 35 min, and 15 min, respectively, so as to realize the preparation of nanoparticles with different growth times. After the reaction is over, remove the heat source, transfer the reactant to a beaker after naturally co...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Preparation of ultra-small magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles under different volume ratios of reaction materials.
[0098] Add 2mL dibenzyl ether and 18mL oleylamine, 8mL dibenzyl ether and 12mL oleylamine, 18mL dibenzyl ether and 2mL oleylamine respectively in three 100mL three-necked flasks, continuously feed nitrogen to remove the oxygen in the system, and then Add 3mmol of iron acetylacetonate, heat each reaction system to 220°C (nucleation temperature) at a heating rate of 3.3°C / min through a temperature program control device, and keep the temperature for 1h. This stage is the nucleation of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles stage, during which the solution turns from brown-red to bright black. Next, each reaction system was heated to 290° C. (growth temperature) at a heating rate of 3.3° C. / min, and each reaction system was maintained at this temperature for 15 minutes to realize the preparation of nanoparticles under different volume ratios of reaction raw materi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com