Polyimide layer-containing flexible substrate, polyimide layer-containing substrate for flexible solar cell, flexible solar cell, and method for producing same
A polyimide layer, solar cell technology, applied in the direction of final product manufacturing, chemical instruments and methods, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient heat resistance, adverse effects of photoelectric efficiency, and lack of flexibility of substrates , to achieve the effect of preventing penetration and diffusion and good photoelectric efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
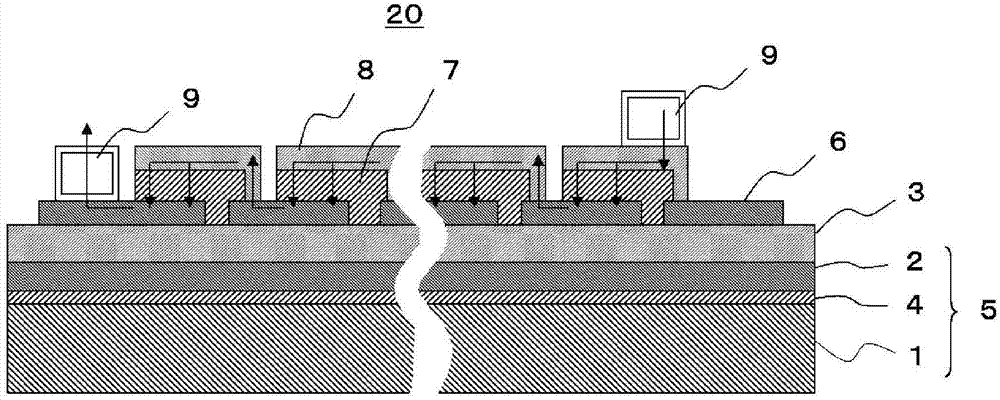
[0045] use figure 1 Embodiments of the present invention will be described.
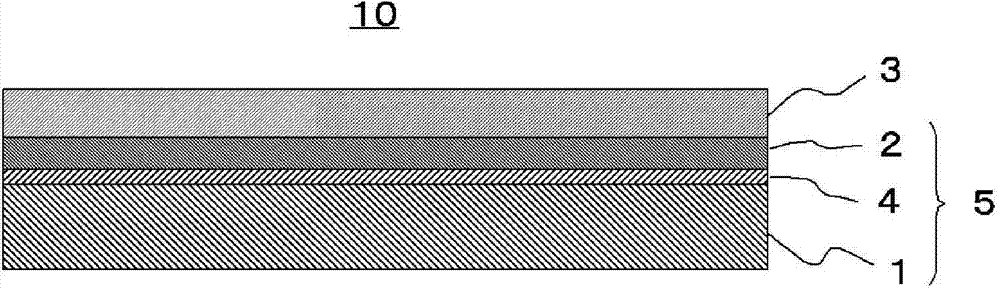
[0046] The first embodiment of the present invention is a flexible substrate 10 containing a polyimide layer having a metal substrate and a polyimide layer 3, the metal substrate is made of ordinary steel or stainless steel ( Hereinafter, it is composed of a metal foil 1 abbreviated as SUS, and the polyimide layer 3 is formed on a metal substrate with a layer thickness of 1.5 to 100 μm and a glass transition temperature of 300 to 450° C.
[0047] For polyimide monomers, barrier properties, especially to gaseous components such as moisture and oxygen, cannot be ensured. Therefore, if no additional barrier film is provided, the intrusion of other components from the outside such as gas components will lead to poor performance. Reduced, so as the substrate of the device, its suitability is insufficient. In addition, the strength of the polyimide monomer is not necessarily sufficient, and due to the ad...
no. 2 approach
[0054] In CIGS solar cells, if metal elements, especially Fe atoms, diffuse into the power generation layer, the conversion efficiency will decrease, and if metal is used instead of glass as the base material, it will prevent F e The diffusion of atoms becomes particularly important. In order to solve this problem, there may be a flexible substrate containing a polyimide layer as the second embodiment of the present invention, which has a metal substrate and a polyimide layer 3, and the metal substrate is not a metal foil made of ordinary steel or SUS. 1 is directly laminated with heat-resistant polyimide, but on the surface of metal foil 1 of ordinary steel or SUS, there is a metal layer composed of one of copper, nickel, zinc or aluminum or an alloy layer thereof (hereinafter referred to as It is a metal layer or alloy layer 2), the polyimide layer 3 is formed on the metal layer or alloy layer 2, the layer thickness is 1.5-100 μm, and the glass transition temperature is 300-...
no. 3 approach
[0062] Metal foils with metal layers containing aluminum (hereinafter, sometimes abbreviated as "Al") produced by conventional techniques tend to be less flexible than metal foils with metal layers containing Cu, Ni, or Zn. This is because, in general, when aluminum or aluminum-based plating is performed on an ordinary steel layer or a SUS layer to form a metal layer or an alloy layer 2, the metal foil 1 composed of an ordinary steel layer or SUS and the metal containing Al layer or the interface of the alloy layer 2, a Fe-Al alloy layer 4 (for example, FeAl 3 , Fe 2 al 8 Si, FeAl 5 Si and other intermetallic compounds), the Fe-Al alloy layer 4 is very hard and brittle, and if the coated steel or SUS undergoes extreme elastic-plastic deformation during processing, the Fe-Al alloy layer 4 cannot follow the Deformation of the metal foil layer 1 eventually causes peeling of the metal foil 1 and the metal layer or alloy layer 2 containing Al and cracking of the metal layer or a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com