Heavy metal binding protein gene derived from radio-resistant bacterium and application of gene in heavy metal resistance
A technology that binds proteins and anti-radiation bacteria, applied in the field of genetics and breeding, can solve the problems of low efficiency, damage to soil structure and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Synthesis of Heavy Metal Binding Protein DrHMBP Gene of Radiation Resistant Bacteria
[0036] According to the gene sequence of the radioresistant bacteria DrHMBP registered in Genbank, the gene synthesis method [Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32, e98] was used to design the coding region of the synthetic gene according to the following principles without changing the amino acid sequence encoded by the gene : (1) Optimizing gene codons to improve gene translation efficiency. (2) Eliminate the recognition sites of commonly used restriction endonucleases inside the gene to facilitate the construction of expression cassettes. (3) Eliminate inverted repeat sequences, stem-loop structures and transcription termination signals, balance GC / AT within genes, and improve RNA stability. (4) Make the gene-encoded protein conform to the N-terminal principle (Tobias1991) to improve the stability of the translated protein. (5) The design increases the free energy at the 5' end of the...
Embodiment 2
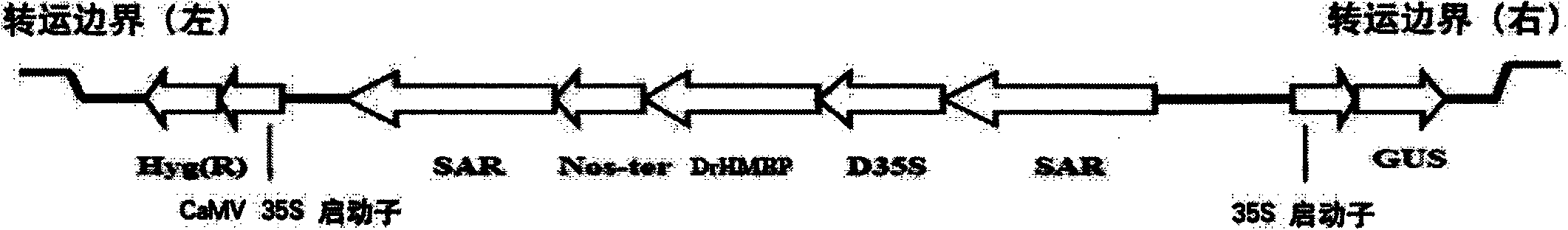
[0040] Construction of DrHMBP Agrobacterium Binary Vector
[0041] The positive clone of the artificially synthesized DrHMBP gene above was amplified by PCR with primers, then added Bam HI and Sac I cutting points at the head and tail respectively, and double-digested with Bam HI+Sac I, and the recovered DNA fragments were connected to the corresponding enzyme-cut vectors. The correct binary vector was obtained after cleavage identification and sequencing (see figure 1 ).
Embodiment 3
[0043] Transformation of Agrobacterium by electroporation
[0044]1) Preparation of Agrobacterium GV3101 competent, the method refers to MicroPulser TM Electroporation Apparatus Operating Instructions and Application Guide (BIO-RAD Company) ((Raineri et al., Bio. Tech., 1990, 8: 33-38).
[0045] 2) Take 50 μL of GV3101 competent cells, add 1 μL of DNA, and transfer to a 0.2 cm electric shock cup for transformation (400Ω, 2.5KV, 25 μf). Add 1 mL of LB medium containing 1% mannitol to recover the culture for 2 hours (28° C., 250 rpm). Take 10 μL and 100 μL respectively and apply on LB plates (rifampicin 50 μg / mL, gentamicin 50 μg / mL, chloramphenicol 100 μg / mL).
[0046] 3) Pick several clones, extract the Agrobacterium plasmid by alkaline method, identify by enzyme digestion, and detect by PCR.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com