Pichia pastoris expression vector taking chloramphenicol as screening marker and application thereof
An expression vector, Pichia pastoris technology, applied in the direction of using the vector to introduce foreign genetic material, recombinant DNA technology, fungi, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing experimental or production costs, facilitating preparation and related operations, and avoiding cumbersome medium configuration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Preparation of Pichia pastoris GS115 electroporation competent
[0024] The present invention requires a special preparation method for electrotransformation competence. This method is different from the classic electrotransformation competent preparation method. The main difference lies in the culture medium and some reagents used. The specific steps are as follows:
[0025] 1) Cultivate Pichia pastoris in a 50ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 5ml of YPG medium (peptone 2g / 100ml, yeast extract 1g / 100ml, glycerol 3g / 100ml), overnight at 30°C;
[0026] 2) Take 1-5ml of the overnight culture, inoculate it into a 2L shake flask containing 500ml of fresh YPG medium, and grow to OD overnight 600 Between 1.3-1.5;
[0027] 3) Collect the cells by centrifugation at 1500g for 5 minutes at 4°C, and suspend the cells with 500ml pre-cooled sterile water;
[0028] 4) Collect the cells by centrifugation at 1500g for 5 minutes at 4°C, and suspend the cells with 250ml pre-c...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Sensitivity detection of Pichia pastoris to chloramphenicol
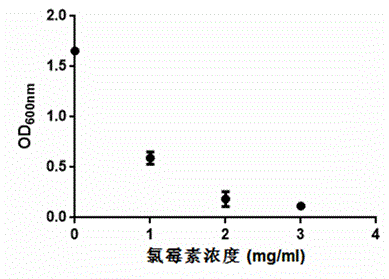
[0033]The present invention finds for the first time that chloramphenicol has an inhibitory effect on Pichia pastoris. On YPG solid medium (peptone 2 g / 100ml, yeast extract 1 g / 100ml, glycerin 3g / 100ml, Agar 2g / 100ml), chlorine Pichia pastoris could not grow on the resistant plate solid medium of Mycin (purchased from Sangon Biotechnology Company, 0692C503), but it grew normally on the non-resistant plate solid medium ( image 3 ). The present invention further explored the optimal resistance concentration of Pichia pastoris GS115 (purchased from Novagen, K1750-01), added different concentrations of chloramphenicol to the YPG medium, and found that the inhibitory effect of chloramphenicol on GS115 has a dosage dependency ( Figure 4 ), and at a concentration of 2 mg / ml and above, Pichia GS115 was basically unable to grow.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: Transformation of the chloramphenicol resistance gene and verification of its release from the inhibitory effect of chloramphenicol
[0035] In order to verify that the inhibitory effect of chloramphenicol on Pichia can be relieved by degrading chloramphenicol through gene expression in the presence of a chloramphenicol resistance gene (CAT), the present invention obtained from the pACYC184 plasmid (purchased from New England
[0036]
[0037] 0.25pm / μL of swimming primers, 0.4mmol / μL of dNTP, 2 ng / μL of DNA template, 5 U / 100 μL of taq DNA polymerase, 1×taq buffer, the total volume is 25 μL. Perform the reaction as follows: 93°C, 3min pre-denaturation; 93°C, 30s; 50°C, 40s; 72°C, 1min reaction for 30 cycles; finally 72°C extension for 10min) to obtain the chloramphenicol resistance gene CAT, by Bam HI (purchased from TAKARA, 1001A), not Ⅰ (purchased from TAKARA, 1166A) was connected to Pichia pastoris expression vector pPIC3.5K (purchased from Novagen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com