Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for low protease A extra-cellular secretion under stress condition and construction method of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and protease, which is applied in the field of bioengineering to achieve the effect of improving foam retention
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
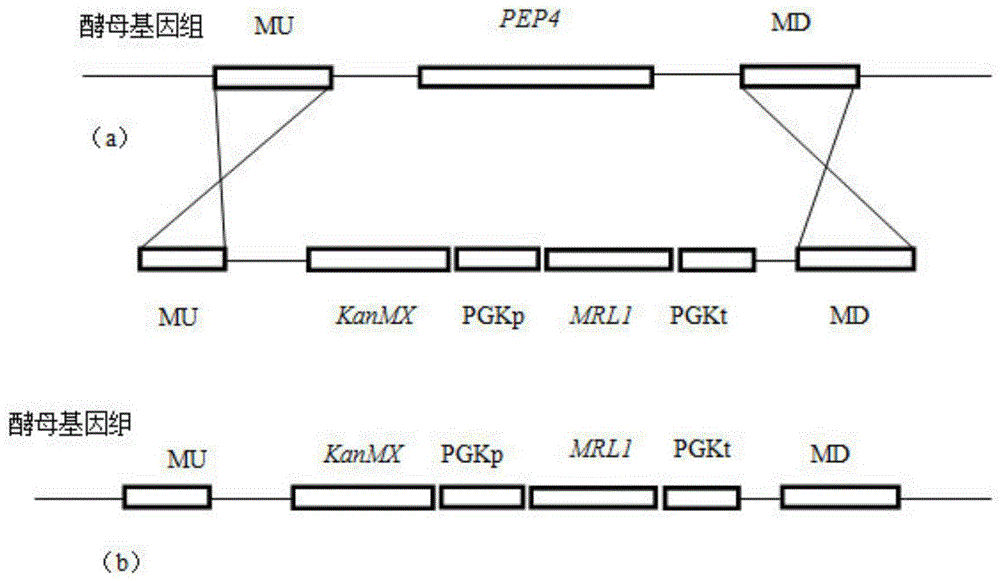
[0044] Example 1: Construction of PEP4 gene knockout and MRL1 gene overexpression strain
[0045] (1) Construction of Yep-PMKZ plasmid
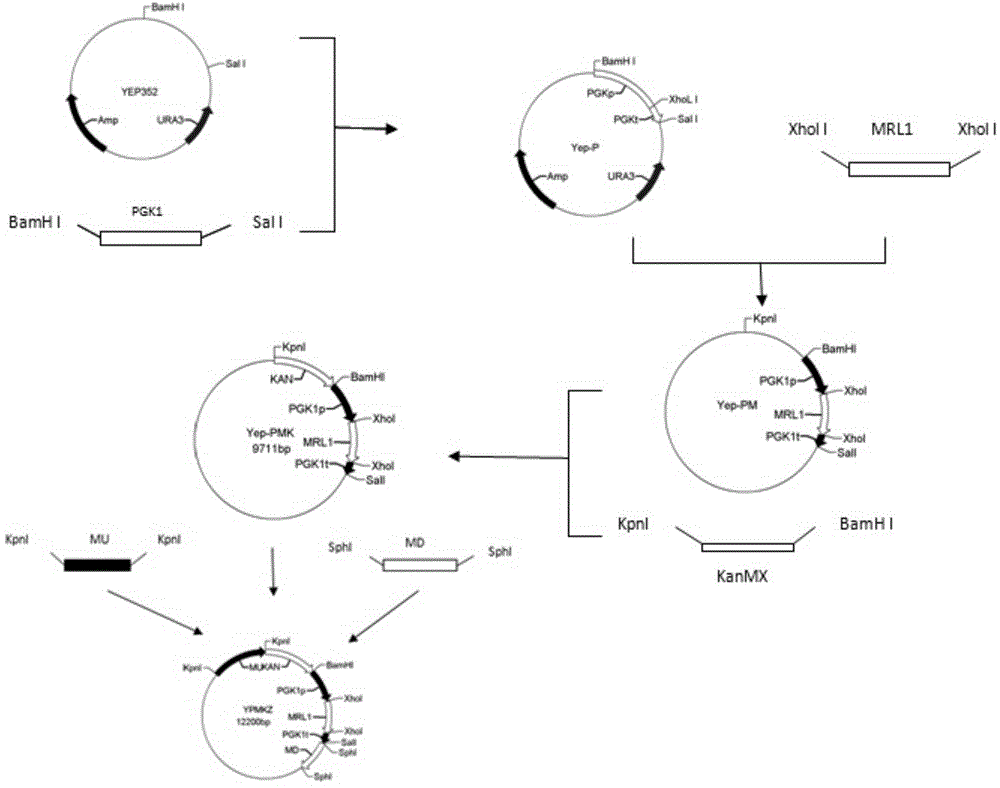
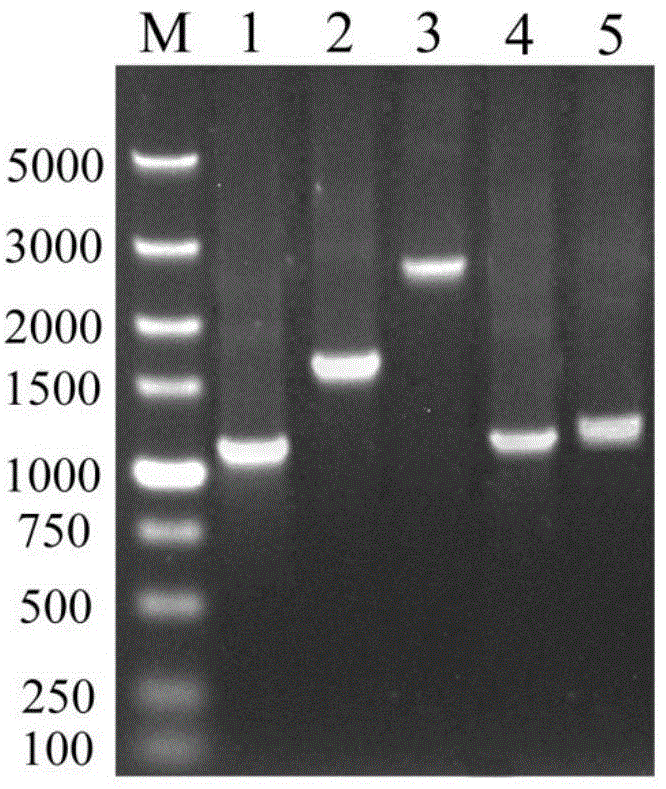
[0046] The construction process of recombinant plasmid Yep-PMKZ is as follows figure 1 Shown.
[0047] ① Using pPGK1 plasmid as a template, PCR amplified a strong promoter PGK1p-PGK1t gene fragment;
[0048] Upstream primer PGK-U: CGC GGATCC TCTAACTGAT CTATCCAAAACTGA (SEQ ID NO: 3)
[0049] Downstream primer PGK-D: CGC GTCGAC TAACGAACGCAGAATTTTC (SEQ ID NO: 4)
[0050] The underlined part is the restriction site
[0051] PCR reaction conditions: 95℃5min; 94℃45s; 61℃1min; 72℃100s, 30 cycles; 72℃10min, 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis to identify amplified products;
[0052] PCR reaction system (20μL)
[0053] PCR buffer
dNTP
Upstream and downstream primers
Template
Taq enzyme
DdH2O
total capacity
2.0μL
1.5μL
1.0μL each
1.0μL
0.5μL
13.0μL
20.0μL
[0054] The PCR product was ligated to the expression vector YEP352 to obtain the recombina...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2: Comparison of intracellular and extracellular protease A activity
[0089] Two strains of yeast strains RY1 and RPMKZ were used for beer fermentation experiments. After the fermentation, the fermentation broth was centrifuged to collect the bacteria. After the cell wall was broken, the intracellular protease A activity was measured, and the extracellular protease A activity of the fermentation broth was measured at the same time. The results are shown in Table 1. Through observation, it was found that the intracellular enzyme activity of the recombinant strain RPMKZ that overexpressed the MRL1 gene while a single PEP4 gene was deleted was not much different from that of the original strain, but the extracellular enzyme activity was reduced to 54% of the original strain. This is because although knocking out a copy of the PEP4 gene reduces the total expression of protease A, overexpression of the vacuolar sorting receptor gene MRL1 on the basis of knocking out PE...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Example 3: Fermentation performance-comparison of α-amino nitrogen changes
[0093] α-amino nitrogen is the main nitrogen source for yeast growth and metabolism. This study investigated the difference in the assimilation and metabolism of α-amino nitrogen between yeast strains RY1 and RPMKZ. Such as Figure 5 As shown, from the beginning of the main fermentation, the concentration of α-amino nitrogen in the fermentation broth showed an obvious decreasing trend, and at the end of fermentation, the change trend of α-amino nitrogen tended to be stable. This is because in the main fermentation period, yeast growth and metabolism use a large amount of α-amino nitrogen, so the rate of assimilation and absorption is very fast. At the end of fermentation, the number of yeast reached a stable value, and the assimilation rate of α-amino nitrogen also stabilized. Studies have shown that there is not much difference in the concentration of α-amino nitrogen between the two strains dur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com