Preparation method of magnetic nanoparticle immobilized amino-acylase as well as product and application of preparation method
A technology of magnetic nanoparticles and aminoacylase, which is applied in the direction of immobilization on or in inorganic carriers, chemical industry, climate sustainability, etc., can solve the problems of poor practicability and high price, and achieves simple operation and low cost. , the effect of improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
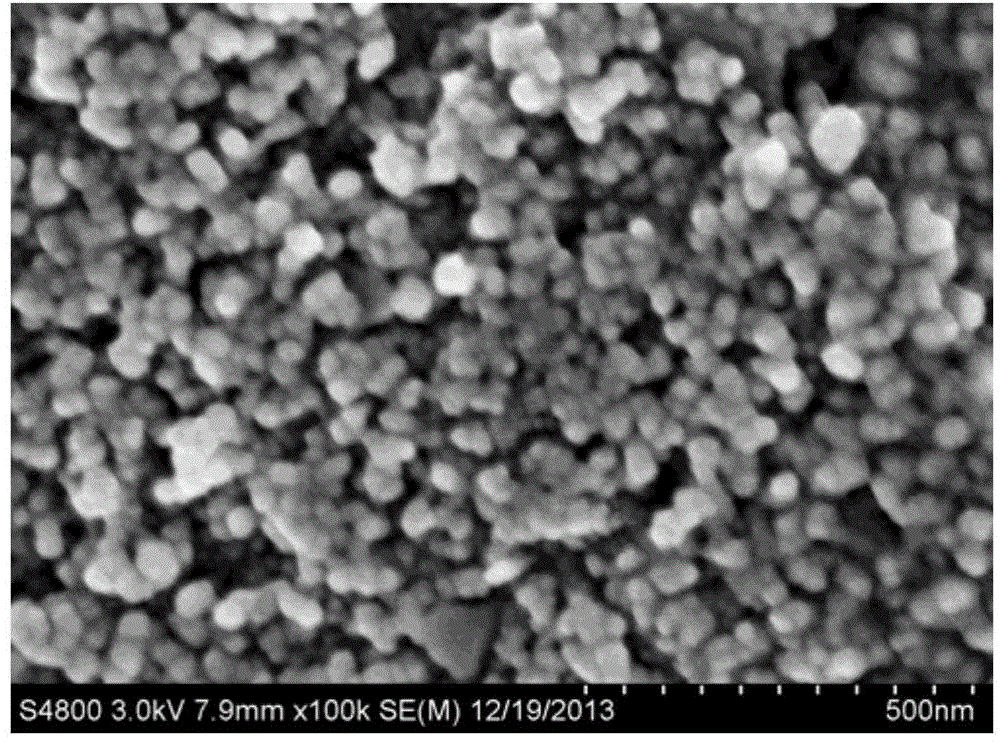
[0040] Preparation of Magnetic Ferric Oxide Nanoparticles Modified by Amino Surface
[0041] (1) Weigh 6.76g of ferric chloride hexahydrate and 3.48g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate and dissolve them in 100ml of deionized water so that the molar ratio of ferric ions to ferrous ions is equal to two to one. Nitrogen deoxygenation, add 5mol / L NaOH drop by drop while stirring mechanically until the solution pH = 10, to obtain a black iron ferric oxide nanoparticle solution, put this solution at 60°C for 30min, and the obtained iron ferric oxide nanoparticle Rinse 3 times with deionized water and ethanol, and redisperse in 50% (v / v) ethanol.
[0042] (2) Ultrasonic disperse 1.5g of magnetic iron ferric oxide nanoparticles into 150ml of 50% (v / v) ethanol, add 500μl of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES), nitrogen protection, 40 ℃ mechanical After stirring for 24 hours, the amino-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles were collected by a magnet, washed three times with deionized water and ab...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Amino-modified iron ferric oxide nanoparticles are mixed with an aminoacylase solution to obtain the magnetic nanoparticle-immobilized aminoacylase.
[0046] (1) Dissolve a certain amount of amino-modified magnetic ferric iron tetroxide nanoparticles in 0.1mol / L, pH 7.0 phosphate buffer to make the final concentration 8mg / ml, sonicate for 15min, add a certain amount of glutaraldehyde to make The final concentration was 1.0%, stirred at 30°C for 1 h, collected by a magnet, and washed with 0.1 mol / L, pH 7.0 phosphate buffer to remove residual glutaraldehyde.
[0047] (2) The collected nanoparticles were mixed with a certain concentration of aminoacylase solution for 1.5 h, collected by a magnet, washed with 0.1 mol / L, pH 7.0 phosphate buffer to remove residual free enzyme.
Embodiment 3
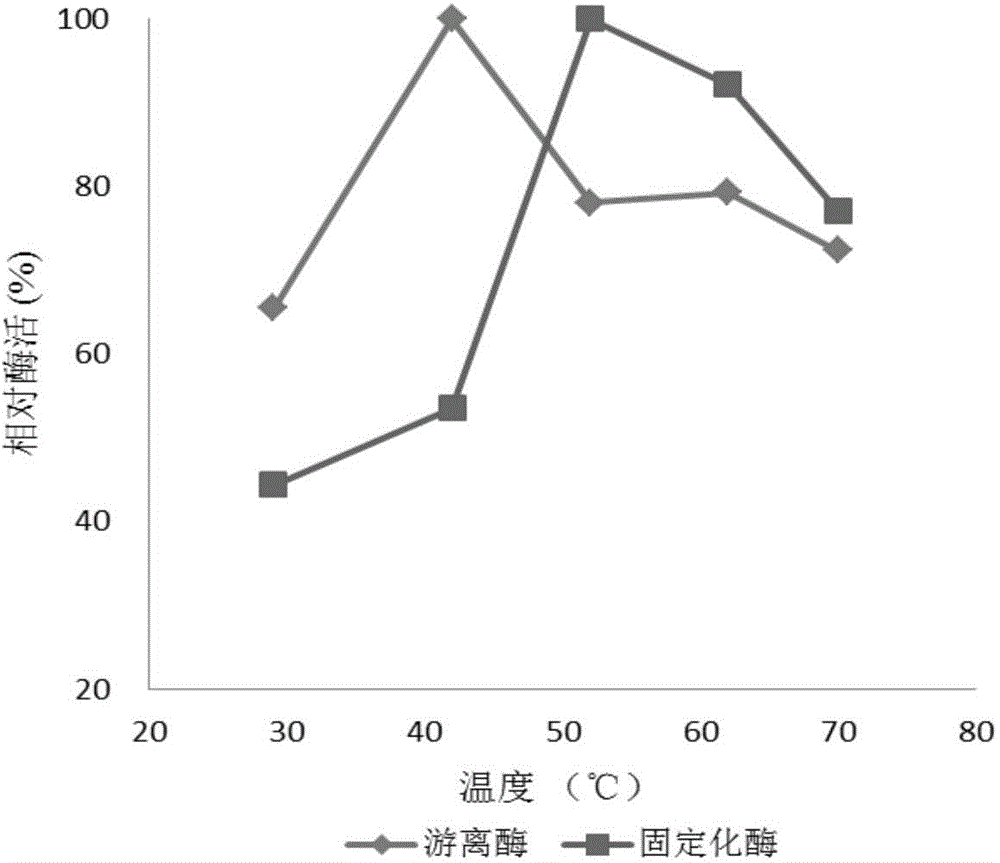
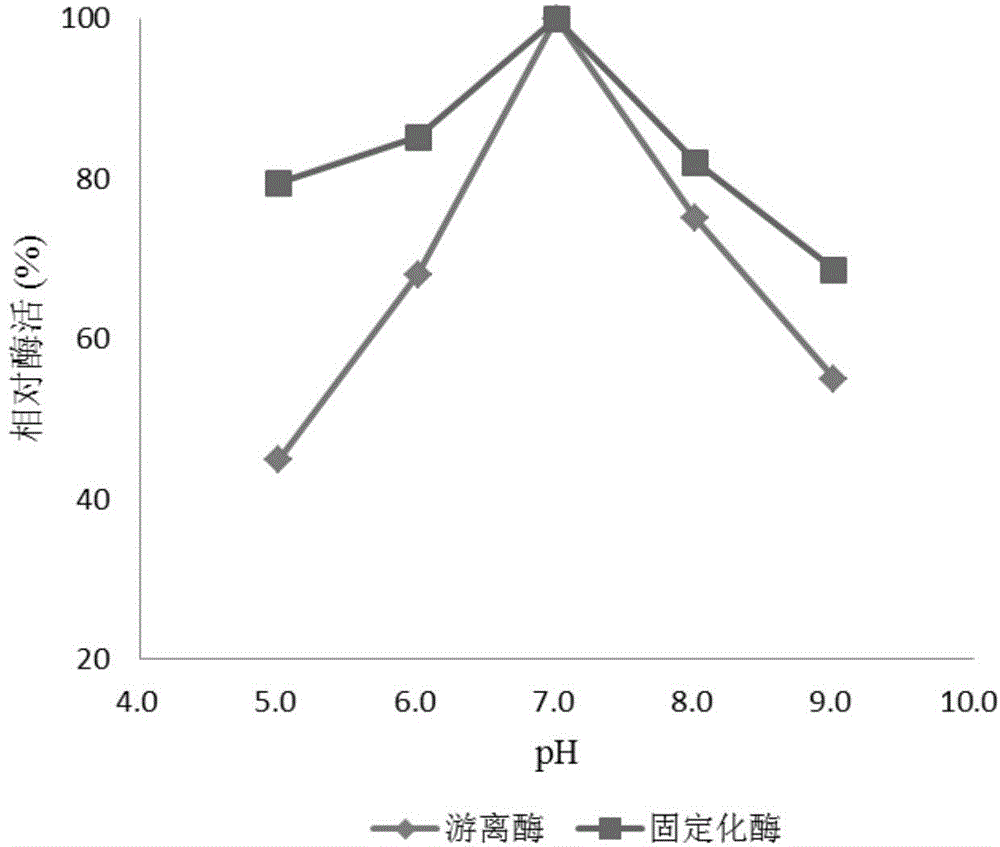
[0049] Determination of the enzyme activity and enzyme reaction temperature of the aminoacylase immobilized on the magnetic nanoparticles prepared in Example 2 and the free enzyme.
[0050] Measure 40mL 0.1mol / L pH7.0 phosphate buffer solution into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 5mL deionized water and 5mL 0.2mol / L N-acetyl-DL-theanine, respectively at 29°C, 42°C, and 52°C , 62°C, 72°C for 5 minutes, add 20 mg of free aminoacylase or the magnetic nanoparticle-immobilized aminoacylase obtained in Example 2, shake for 30 minutes, immediately stop the reaction by boiling water for 5 minutes, and dilute to a certain concentration after cooling , take 1mL of the sample to be tested for ninhydrin reaction, shake well, measure its OD570, and compare the standard curve to obtain the output of L-theanine. The enzyme activity unit is defined as: at pH 7.0, at 42°C, within 1 hour, the enzyme catalyzes the reaction to produce 1 μmol L-theanine, which is an activity unit (U). The relative ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com