Driving method of gallium nitride transistor, driving circuit thereof, and fly-back converter using the circuit
A driving method and driving circuit technology, which are applied in the direction of high-efficiency power electronic conversion, adjustment of electrical variables, and output power conversion devices, can solve the problem of not reducing reverse conduction loss, etc. The effect of simple circuit structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
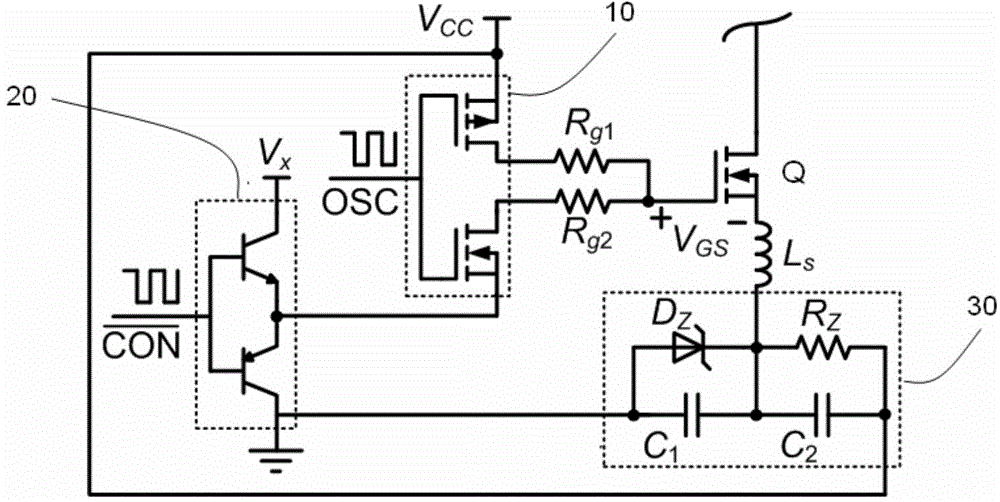
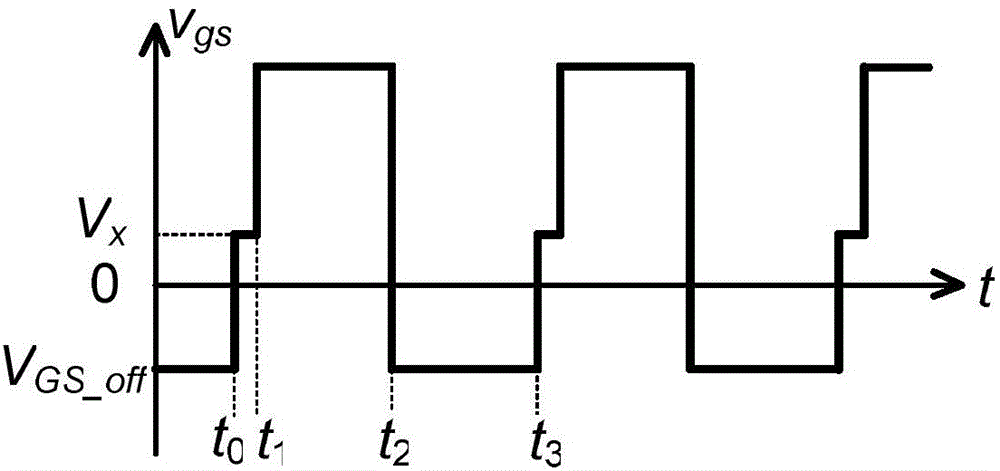
[0055] figure 1 The circuit diagram of the driving circuit of the gallium nitride transistor in the first embodiment of the present invention is given, wherein the inductance Ls represents the parasitic inductance in the circuit and the package, and this equivalent device is drawn for the convenience of explaining that the parasitic inductance will cause the turn-off time The oscillation problem of the driving voltage Vgs leads to the purpose of adding negative voltage to the driving.
[0056] A gallium nitride transistor driving circuit is composed of a switching tube Q, a driving pulse amplifying unit 10 , an intermediate level generating unit 20 and a negative voltage bias circuit 30 . Wherein, the switching tube Q is a gallium nitride transistor, the driving pulse amplifying unit 10 uses a single-channel low-side gate driver LM5114 of TI Company, and the intermediate level generating unit 20 is composed of an NPN triode and a PNP triode in the form of a totem pole. Negati...
Embodiment 2
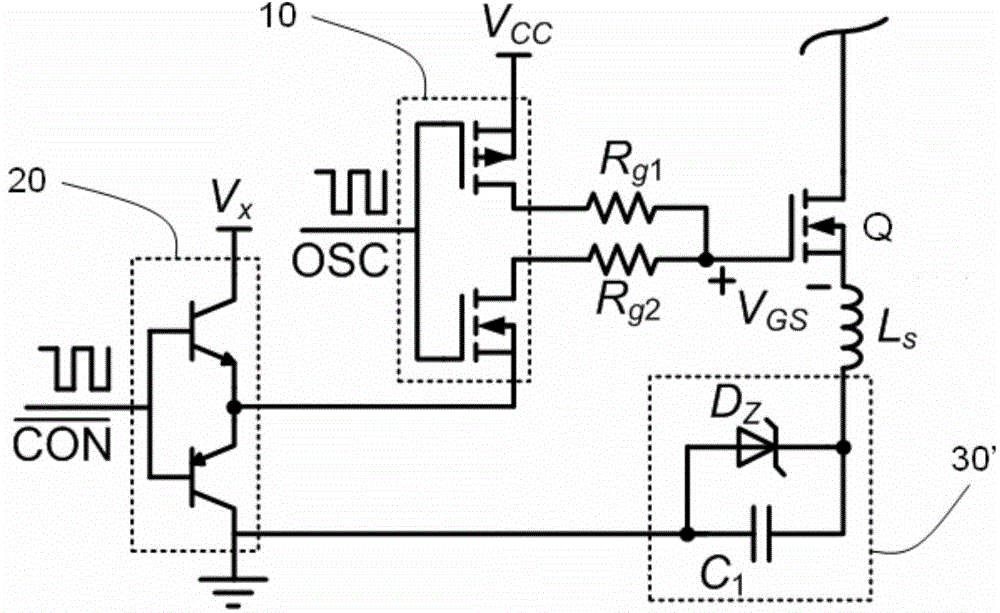
[0061] image 3 The driving circuit diagram of the gallium nitride transistor of the second embodiment of the present invention is given. The difference from the first embodiment is that the bias resistor R is omitted in the negative voltage bias circuit 30'. z and filter capacitor C 2 , using capacitance C 1 The charge stored in to ensure the Zener diode D z In Zener breakdown state, Zener diode D z The anode of the GaN transistor Q is connected to the source, and the Zener diode D z The cathode of the intermediate level generating unit is connected to the collector of the PNP transistor. The main advantage of this implementation is that two components are omitted and there is no longer a bias resistor R z on the loss. All the driving circuits using the gallium nitride transistor of the first embodiment in the following application examples can be replaced by the circuit of the embodiment.
Embodiment 3
[0063] Figure 4 It is the driving circuit diagram of the gallium nitride transistor of the third embodiment of the present invention. The difference from the second embodiment is that the connection position of the negative voltage bias circuit 30' has changed, and the source of the gallium nitride transistor and the Between the ground and the gate of the gallium nitride transistor, the specific connection relationship is that the Zener diode D z of the cathode and drive resistor R g1 connection, the Zener diode D z The anode of the GaN transistor Q is connected to the gate of the gallium nitride transistor Q. Compared with the previous two implementations, the advantage of this implementation is that the common ground of the driving circuit and the main circuit is realized. Similarly, all the driving circuits using the gallium nitride transistor of the first embodiment in the following application examples can be replaced by the circuits of the embodiment.
[0064] Figu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com