Method for preparing zirconium phosphate particles coated by antibiotic, and zirconium phosphate particles prepared thereby
An antibacterial ingredient, zirconium phosphate technology, applied in the field of thermal decomposition, can solve the problems of limited content of antibacterial substances, low amount of antibacterial substances, complicated processes, etc., and achieve the effect of excellent antibacterial power and stability, and free expression of color.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
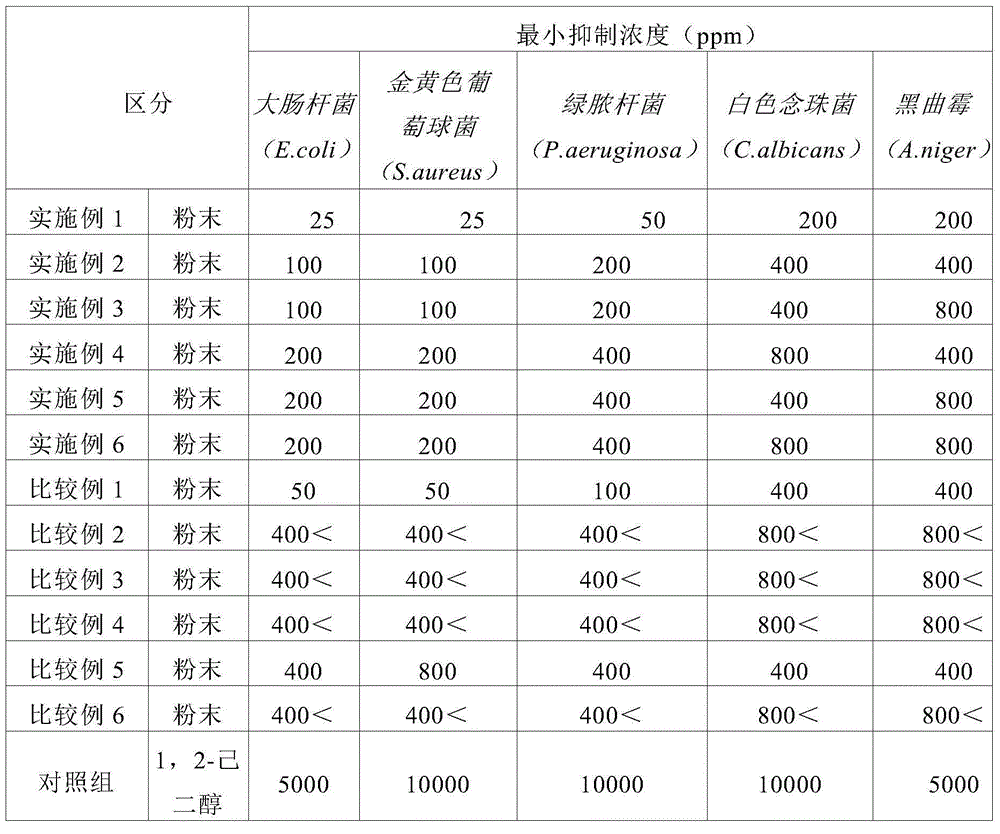
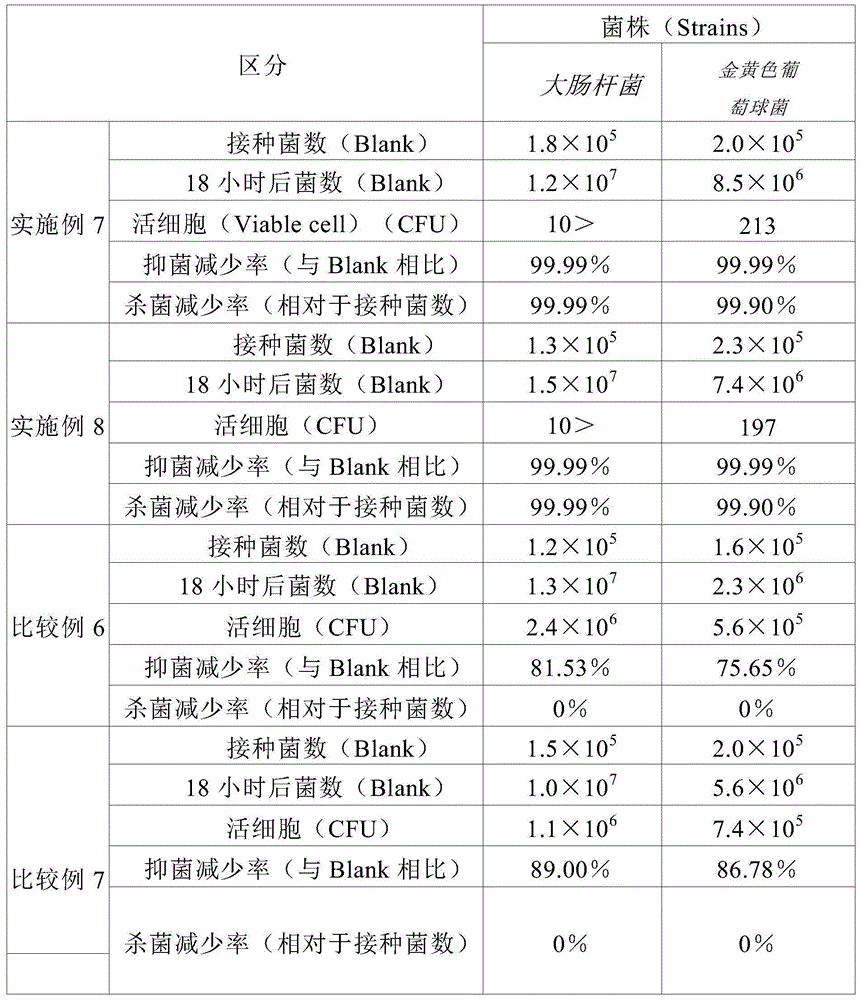
[0036] In the preparation process of inorganic antibacterial agents, a long-term thermal decomposition process under high temperature conditions is required in the prior art. For example, it is necessary to maintain a thermal decomposition process time of 1 to 36 hours at a temperature of 850 to 950°C, but the inorganic antibacterial agent zirconium phosphate powder prepared by the present invention only needs to be thermally decomposed at a temperature of 250 to 300°C for 0.5 to 1 hour. After thermal decomposition at 450-500°C for 1-2 hours, it can exhibit sufficient antibacterial properties.
[0037] The zirconium phosphate powder coated with an antibacterial component of the present invention has strong antibacterial activity, excellent heat resistance, chemical resistance, and processability, and is in the form of a white powder applicable to various dosage forms. Even when a small amount of expensive silver ion substance is used, it exhibits excellent antibacterial power ...
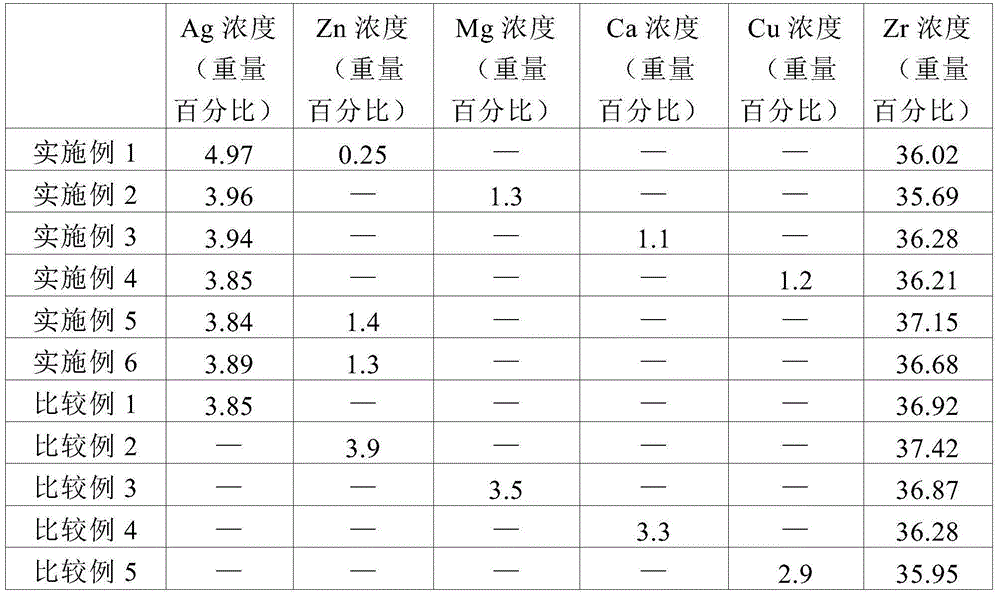
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1: the preparation of the zirconium phosphate powder that contains silver and zinc coating layer
[0042] To 50g of zirconium phosphate (Zr(HPO 4 ) 2 ·H 2 O) Add 1L of deionized water, disperse it to a particle size below 500nm by a basket mill, put it into a 2.5L four-port reactor, and stir at 40°C for 1 hour to disperse. Dissolve 3 g of silver nitrate (AgNO 3 ) and 14.9g of zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 )·6H 2 O) to prepare an aqueous solution, thereby adding dropwise to the above reaction liquid for 1 hour, stirring at 150 rpm at a temperature of 40° C. for 24 hours, and reacting in a light-shielded state. Thereafter, the reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, filtered through a separatory funnel, and washed twice with 250 g of deionized water to fully remove water. At a temperature of 45°C, a far-infrared dryer was used to dry the filter cake with hot air for 12 hours, and a jet mill was used to pulverize it. The pulverized powd...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: Preparation of zirconium phosphate powder containing silver and magnesium coating layer
[0044] In the step of reacting the zirconium phosphate of Example 1 above with silver and zinc, the zirconium phosphate dispersion was prepared by dissolving 3 g of silver nitrate and 12.8 g of magnesium nitrate in 80 g of purified water 95.8 g. A metal nitrate salt solution was used to form a silver and magnesium coating layer. In the same manner as in Example 1 above, 47.4 g of zirconium phosphate powder containing a silver and magnesium coating layer was obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com