Method for carrying out electrochemical treatment on surface of biomedical magnesium or magnesium alloy with high biological activity and low degradation rate
A bioactive and biomedical technology, applied in anodizing, electrolytic inorganic material coating, etc., can solve the problems of fast corrosion rate and low biological activity, and achieve the improvement of corrosion resistance, increase corrosion resistance, and reduce corrosion current density. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
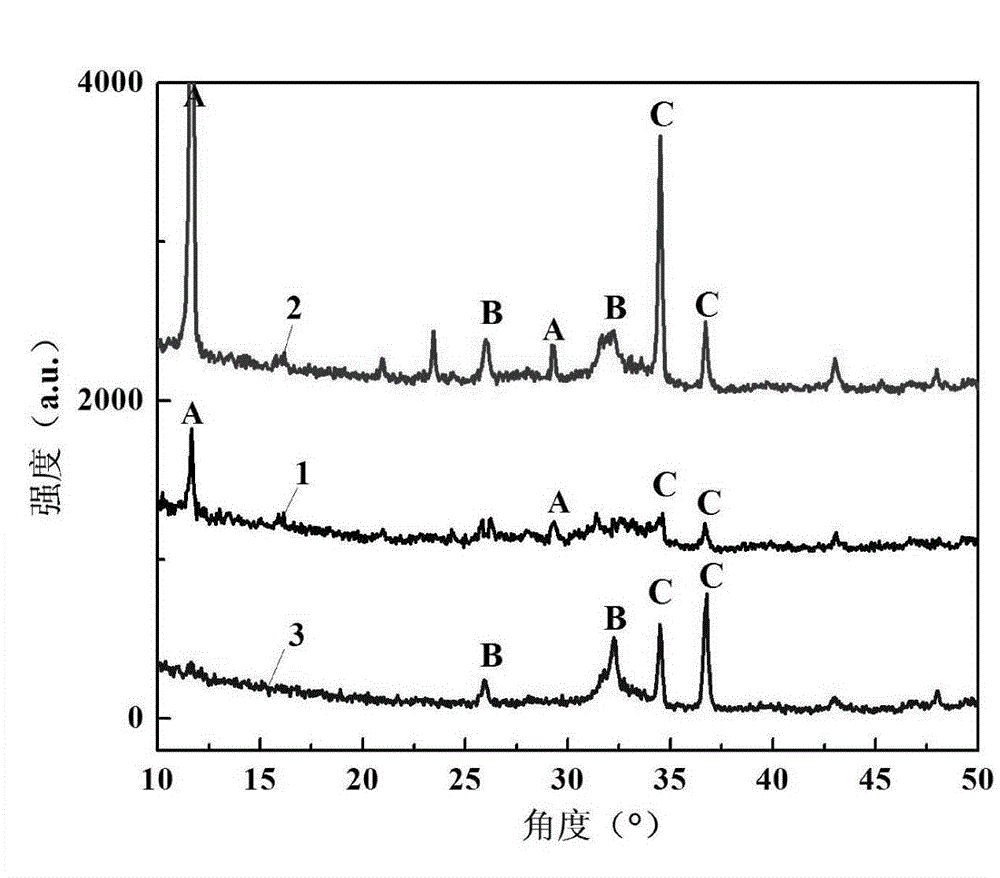
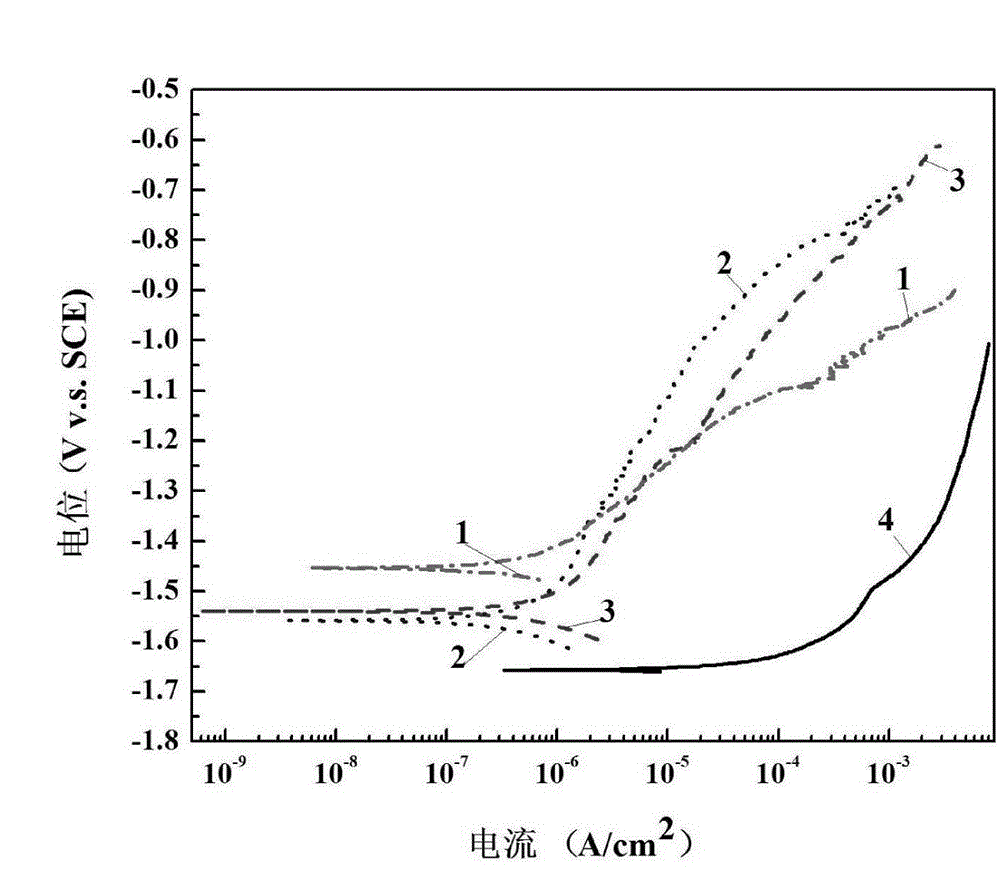
[0015] Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, a method for electrochemically treating the surface of biomedical magnesium or magnesium alloy with high biological activity and low degradation rate is carried out through the following steps:
[0016] 1. Preparation of micro-arc oxidation film on the surface of magnesium or magnesium alloy: place the magnesium or magnesium alloy with the oxide film removed in the electrolyte as the anode, and titanium as the cathode, and perform micro-arc oxidation for 2 minutes at a voltage of 300V to 450V. ~20min, then the magnesium or magnesium alloy is taken out, rinsed and dried to obtain magnesium or magnesium alloy with a micro-arc oxidation film on the surface; wherein, the electrolyte contains Na with a concentration of 10g / L-20g / L 2 SiO 4 , NaOH with a concentration of 5g / L to 20g / L and KF with a concentration of 5g / L to 10g / L, the temperature of the electrolyte is 15°C to 40°C, and the solvent of the electrolyte is water;
[0017] Two, the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0018] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in Step 1, the micro-arc oxidation is carried out for 10 minutes under the condition of a voltage of 400V. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
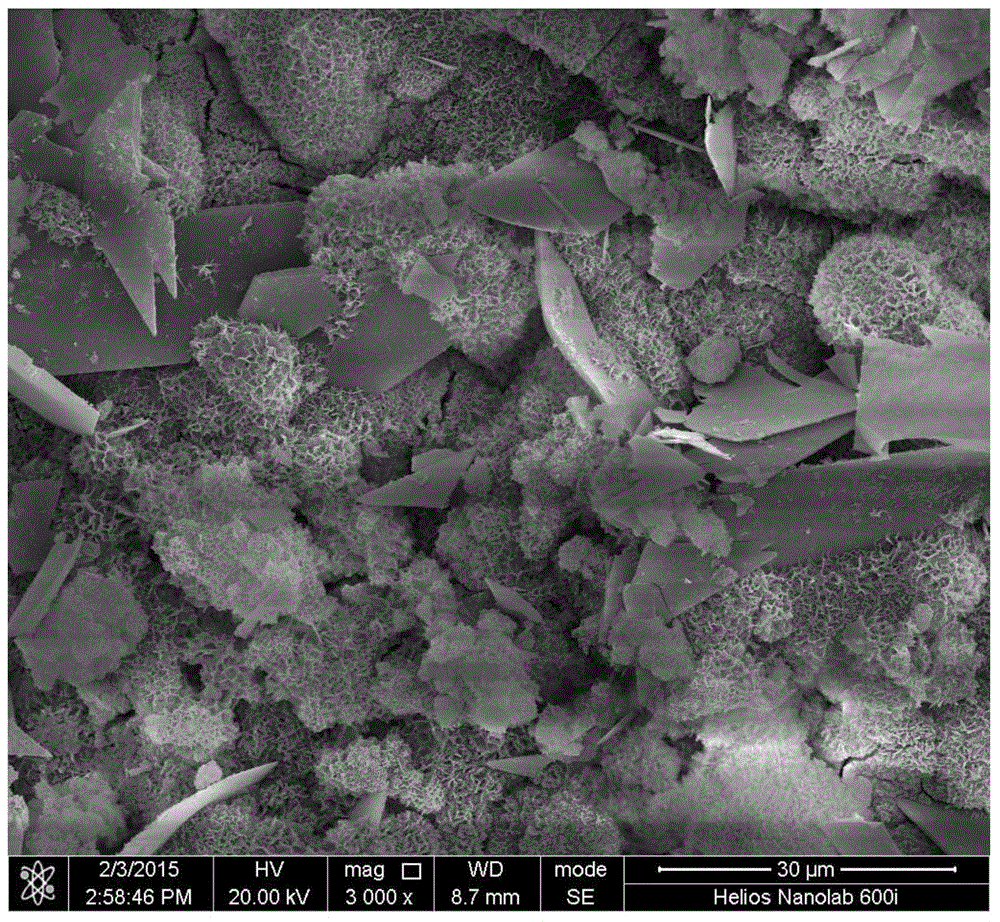
[0019] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the surface coating deposition in step 2 is divided into the following three types: ① When the deposition voltage is 3V-5V and the temperature is 25°C-45°C Add dipotassium hydrogen phosphate solution with a concentration of 0.05 mol / L dropwise to a calcium nitrate solution with a concentration of 0.0835 mol / L at a rate of 5 mL / min to 30 mL / min to obtain a surface covered with dihydrogen phosphate Calcium-coated magnesium or magnesium alloy; ② When the deposition voltage is 3V ~ 5V, the temperature is 45 ℃ ~ 65 ℃, the rate is 5mL / min ~ 30mL / min into the calcium nitrate solution with a concentration of 0.835mol / L Add dropwise dipotassium hydrogen phosphate solution with a concentration of 0.05mol / L to obtain magnesium or magnesium alloy with a mixed coating of calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate and hydroxyapatite on the surface; Add dipotassium hydrogen phosphate solution with a concentra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com