Beta-glucosidase D mutant as well as expression plasmid and recombinant bacteria thereof
A technology of glucosidase and mutants, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of difficult enzyme purification and low catalytic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Construction of mutant expression plasmid and obtaining of recombinant E. coli mutant expression strain
[0028] 1. Construction of mutant expression plasmid
[0029] Gene in vitro cloning and site-directed mutation of D-type β-glucosidase by means of genetic engineering, with
[0030] The overall process is as follows:
[0031] RNA was extracted from the salivary glands and intestinal tissues of Taiwanese termites raised in the laboratory, and cDNA was obtained through reverse transcription.
[0032] The β-glucosidase gene of Taiwanese termite was found in the NCBI gene database ( JN565080 ), according to the sequence homology, design amplification primers, use the termite cDNA as a template for amplification, and add restriction enzymes Hin d III and Xho The restriction site of I, the PCR amplified product is inserted between the corresponding multiple cloning sites on the vector pET-28a (Novagen), and transformed into Ecoli .DH5α (Novagen company) in competent ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Determination of D-type β-glucosidase activity before and after mutation
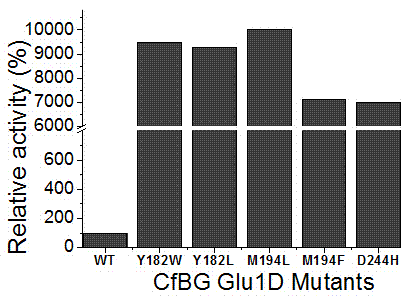
[0058] According to the method in Example 1, the original Escherichia coli pET-28a-Glu1D and other mutant strains were induced to express, and the enzyme activity was measured, and the results were as follows figure 2 Shown by the attached figure 2 It can be seen that the enzyme activity of the strain after the mutation is 94.6, 92.9, 100.3, 71.4, 69.9 times higher than that before the mutation, respectively.
[0059] The activity of the enzyme after the mutation of the present invention is greatly improved compared with that before the mutation. The results show that mutation of amino acids at key positions can change the activity and other properties of the enzyme. This strategy can be widely used to improve the properties of enzymes, accelerate the application of enzymes in industrial production, and has important social significance.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com