Zirconium base alloy used for light-water reactors and preparation method thereof
A zirconium-based alloy and reactor technology, applied in the field of zirconium alloy materials, can solve the problems of decreased corrosion resistance, uneven growth, and inability to disperse and distribute, and achieve the effects of improving corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
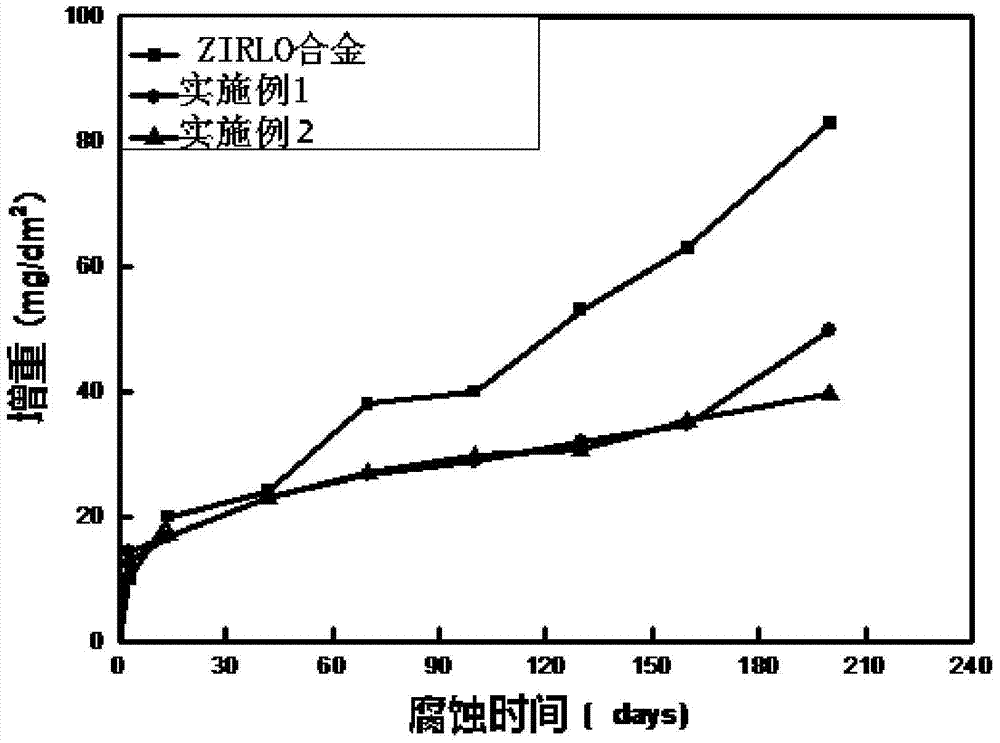
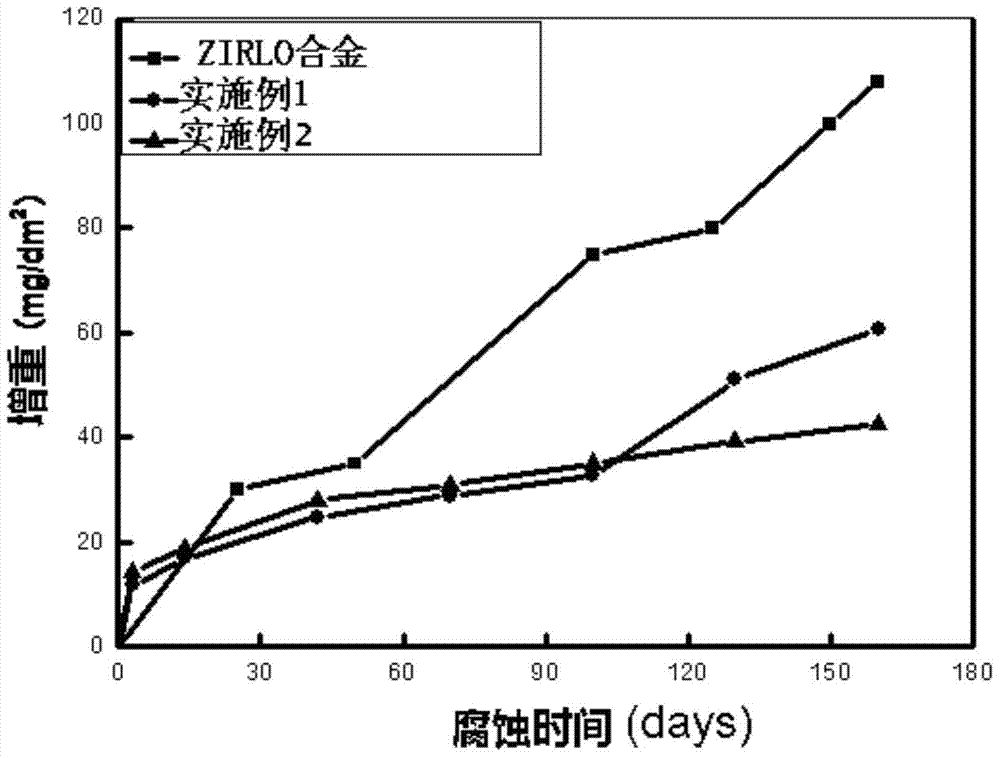
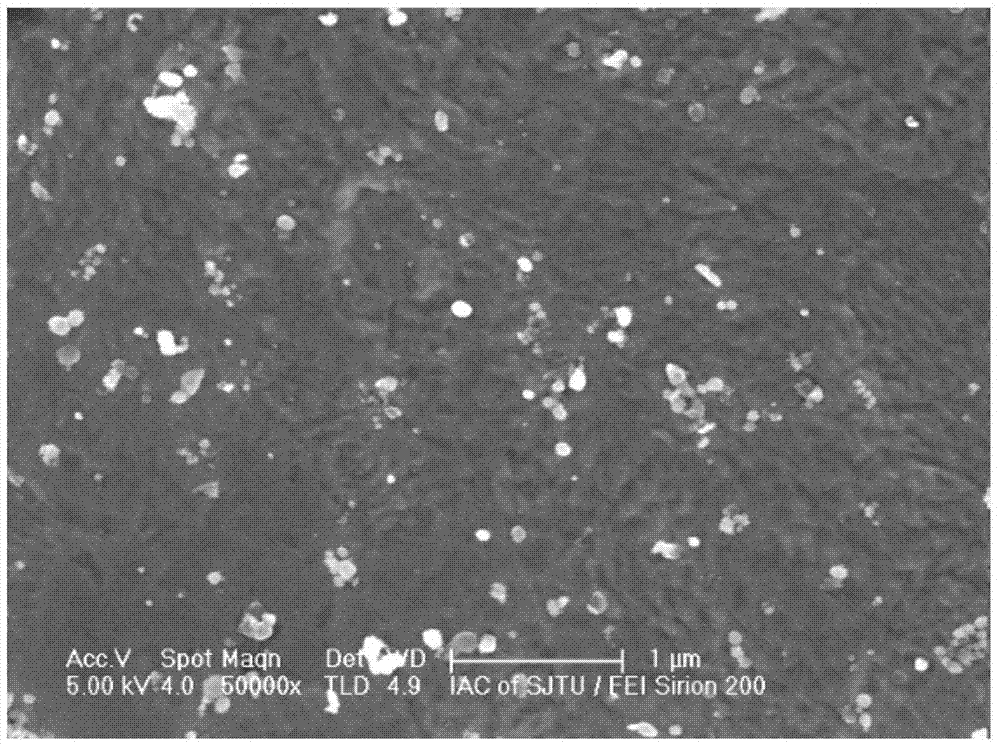
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0149] The first step, preparation of alloy ingot
[0150] The use of nuclear-grade sponge zirconium and nuclear-grade pure metal raw materials (Nb, Sn, Fe, Cu, Si) or master alloys is based on 0.35% by weight of niobium, 0.65% by weight of tin, 0.3% by weight of iron, and 0.05% by weight of Copper, 0.13% by weight of oxygen, 0.008% by weight of silicon and the balance of at least 98% by weight of zirconium containing impurities are smelted multiple times in a vacuum consumable electric arc furnace to produce an alloy ingot.
[0151] The second step, forging and β water quenching
[0152] The above alloy ingot is forged at 1000°C, processed into a billet, scaled, pickled to remove grease, and then subjected to β-phase homogenization treatment at 1050°C for 30 minutes and then water quenched. The quenching speed is greater than 30°C / s.
[0153] The third step, hot rolling treatment
[0154] After heating at 650°C for 50 minutes, hot rolling is carried out 5 to 6 times. During...
Embodiment 2
[0158] Implement this embodiment with the same zirconium alloy composition ratio as in Example 1, the difference is that the preparation method of the zirconium-based alloy is different, specifically as follows:
[0159] The first step is to prepare zirconium-based alloy ingots
[0160] Using nuclear-grade sponge zirconium and nuclear-grade pure metal raw materials (Nb, Sn, Fe, Cu, Si) or intermediate alloys according to the alloy composition of Example 1, respectively, using a vacuum consumable electric arc furnace for multiple melting, it is made alloy ingot.
[0161] The second step, forging and β water quenching
[0162] The alloy ingot is forged at 950-1050°C, processed into an alloy billet, after removing scale and pickling to remove grease, after 10-60 minutes of β-phase homogenization treatment at 1000-1100°C, water quenching, the quenching speed is greater than 30 °C / s.
[0163] The third step, hot rolling treatment
[0164] The alloy billet is heated at 580-700°C...
Embodiment 3
[0175] This example was carried out in the same preparation method as in Example 2, except that, in the components of the zirconium-based alloy, 0.44% by weight of niobium, 0.45% by weight of tin, 0.3% by weight of iron, 0.01% by weight of % copper, 0.13% by weight oxygen, 0.008% by weight silicon and the balance being a component batch of at least 98% by weight zirconium containing impurities.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com