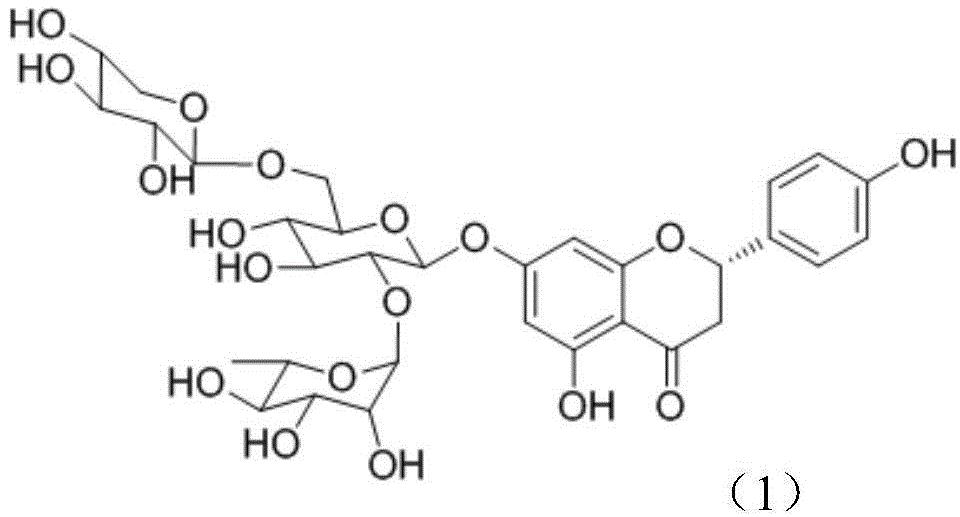
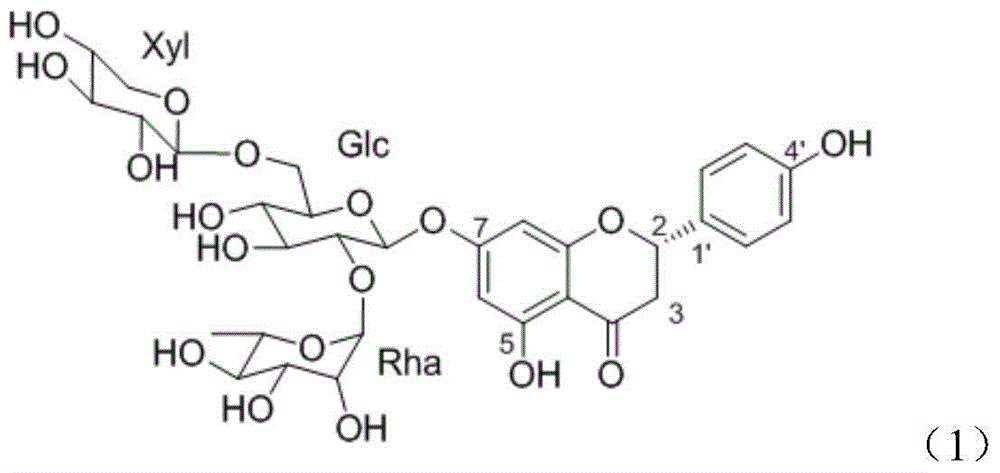
Application of flavonoid compound theaflavanoside II to prevention and treatment of plant nematode diseases
A technology of flavonoids and plant nematodes, applied in the application, nematicide, plant growth regulator and other directions, to achieve the effect of good compatibility and easy degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: the preparation of the flavonoid compound theaflavanoside II described in compound (1)
[0024] The residue (tea seed cake) of Camellia oleifera seed is pulverized with a plant pulverizer, passed through a 40-mesh sieve, soaked in 95% edible ethanol with 8 times the sample size (w / v), and placed in a cool place. Stir frequently. After 5-7 days, filter, add ethanol to the residue and soak, repeat twice, and combine the filtrate. The ethanol filtrate was decompressed on a rotary evaporator, concentrated below 45°C, and then extracted three times with petroleum ether to remove excess oil in the material. Add 3% hydrogen peroxide to the solution after extraction and degreasing, adjust the pH value to 10, put it in a water bath at 60° C., and decolorize it for 90 minutes. The decolorized solution was concentrated to a paste on a rotary evaporator, and dried in vacuo to obtain a crude extract. The crude extract is used as the material, and the components are ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: Determination of Egg Hatching Inhibitory Activity to Plant Nematodes
[0027] Bioassay of egg hatching inhibitory activity: use 24-well biological culture plate (draw a good line at the bottom), add 0.5mL of 1mg / mL medicinal solution to each hole (the final concentration of the solution is 0.83% after adding egg grains), then add 0.1 Egg fluid with a mL concentration of 1000 grains / mL was repeated 4 times for each treatment, and sterile water was used as a control, placed in a 25°C incubator, and the hatched second-instar larvae were recorded under an inverted microscope on the 3rd, 5th, and 7th day respectively Number, and calculate the egg hatch inhibition rate:
[0028]
[0029] The results of bioassay showed that the hatching inhibition rates of M. incognita eggs were 71%-90% when treated with 0.83 mg / ml concentration for 3, 5, 7, and 9 days. See Table 1 for details.
[0030] Table 1 Determination of the inhibitory activity of 0.83mg / mL theaflavanosid...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: Determination of poisonous activity to plant nematodes
[0035] Weigh 0.05g of compound (1) flavonoid compound theaflavanoside II, and dissolve it in 10mL of sterilized pure water (the sample is first dissolved with a small amount of sterilized water at about 50°C, and then adjusted to 10mL), to obtain a concentration of 5mg / mL concentration, and then diluted with sterilized pure water to the required gradient concentration. Use a 24-well biological culture plate, add 0.5mL of each concentration gradient drug solution to each well (the final concentration of the drug solution is 0.83mg / ml), and then add 0.1mL of nematode suspension (about 100-200), each treatment Set 4 repetitions, use sterile water as a control, put in a 25°C incubator, observe and count at 24h, 36h, 48h, 72h, and 96h (resuscitated with clean water for 24h), record the nematode life and death data under an inverted microscope, and calculate Adjusted mortality rate:
[0036]
[0037]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com