Method of preparing microfibrillated cellulose from bamboo parenchyma cells
A technology of parenchyma cells and cellulose, which is applied in the fields of fiber raw material processing, pulping with organic solvents, textiles and papermaking, etc. It can solve the problems of cavitation fragmentation, high production energy consumption, and numerous operation steps, and the method is simple Easy to operate, reduce environmental pollution and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example
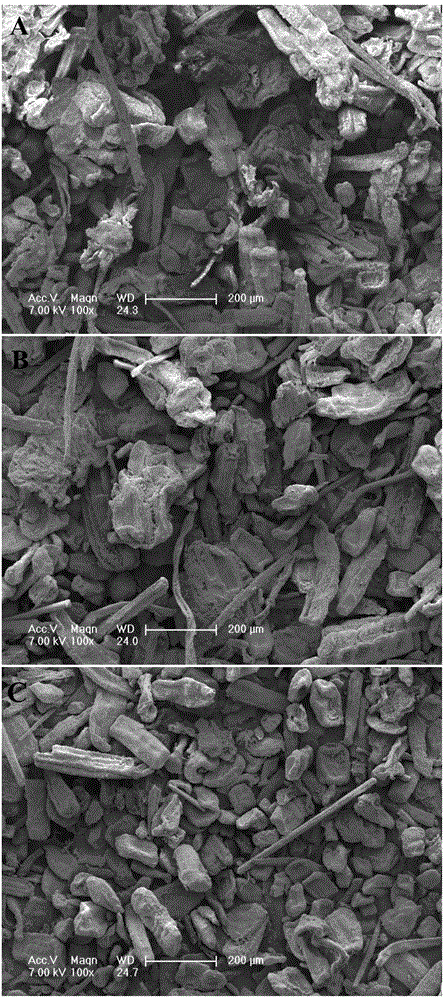
[0032] Spread the residues of bamboo floor processing evenly, dry naturally in a cool place for 10 hours, then place in a drying box, dry to absolute dryness at 103±1°C, crush in a plant grinder for 15 minutes, and then use 100 mesh, 120 mesh, 200 mesh respectively The objective sieve was sieved three times, and the particles passing through the sieve were collected and observed with a scanning electron microscope.
[0033] figure 1 It is the SEM picture of the raw material obtained through three mesh sieves (A: 100 mesh; B: 120 mesh; C: 200 mesh; magnification × 100); from figure 1It can be clearly seen that after 100 mesh and 120 mesh sieving, there are still a small amount of fibers in the raw material, while the raw material passing 200 mesh is basically parenchyma cells. Therefore, the following examples are all sieved with a 200-mesh sieve.
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Preparation of Microfibrillated Cellulose by High Frequency Ultrasound from Phyllostachys pubescens Parenchyma Cells
[0035] Moso bamboo is a kind of scattered bamboo.
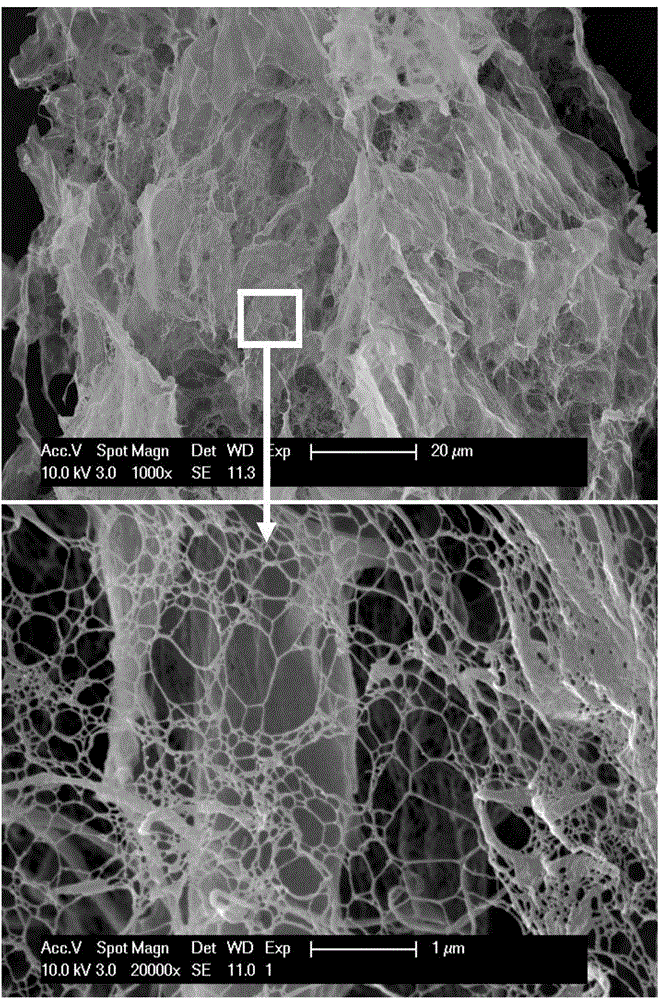
[0036] 1) First, split the moso bamboo into small bamboo stalks the size of a matchstick, then treat the small bamboo stalks in a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and glacial acetic acid (1:1 by volume) at 60°C for 18 hours; after the isolation treatment, Wash with deionized water several times until neutral, then place it in a container filled with a large amount of deionized water, and stir vigorously for 30 minutes to obtain a single-cell aqueous suspension; the aqueous suspension is filtered 3 times with a 200-mesh sieve, and the obtained After the filtrate is dried, parenchyma cells can be obtained;
[0037] 2) Chemical pretreatment: add the parenchyma cells obtained in step 1) into 1% (mass) sodium chlorite solution, place them in a water bath at 70° C. for 1 hour, and repeat this process ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Preparation of Microfibrillated Cellulose by High Pressure Homogenization of Phyllostachys pubescens Parenchyma Cells
[0041] 1) separation of parenchyma cells, same as in Example 1;
[0042] 2) chemical pretreatment, with embodiment 1;
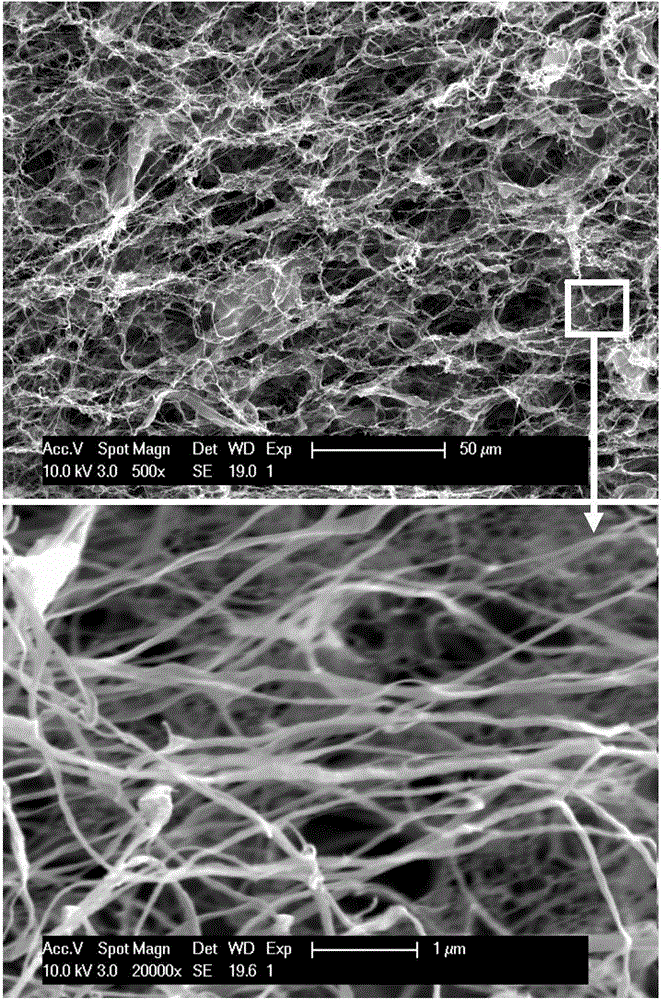
[0043] 3) Disperse the chemically treated parenchyma cells in step 2) into deionized water to form a 1% (mass) slurry. The working pressure of the high-pressure homogenizer is 150 MPa, and the diameter of the cavity is 100 μm. The slurry is repeatedly subjected to high pressure The number of times of the homogenizer cavity is 5; after the high-pressure homogenization is completed, the obtained transparent liquid is the microfibrillated cellulose sol.
[0044] After drying, observed by scanning electron microscope, see figure 2 . The diameter of the obtained microfibrillated cellulose is defined between 50-200nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com