Method for carrying out protein enzymatic hydrolysis
A protein and protein solution technology, applied in the field of protein enzymatic hydrolysis, can solve the problems affecting the speed of large-scale identification of proteins and the lack of stable means for preparation, and achieve the effect of fast speed, simple steps, and improved enzymatic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
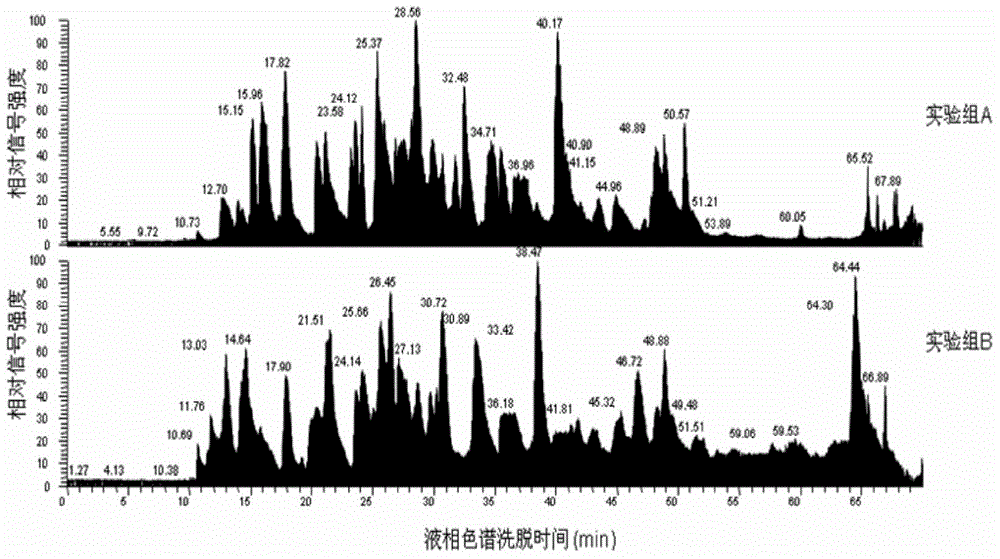
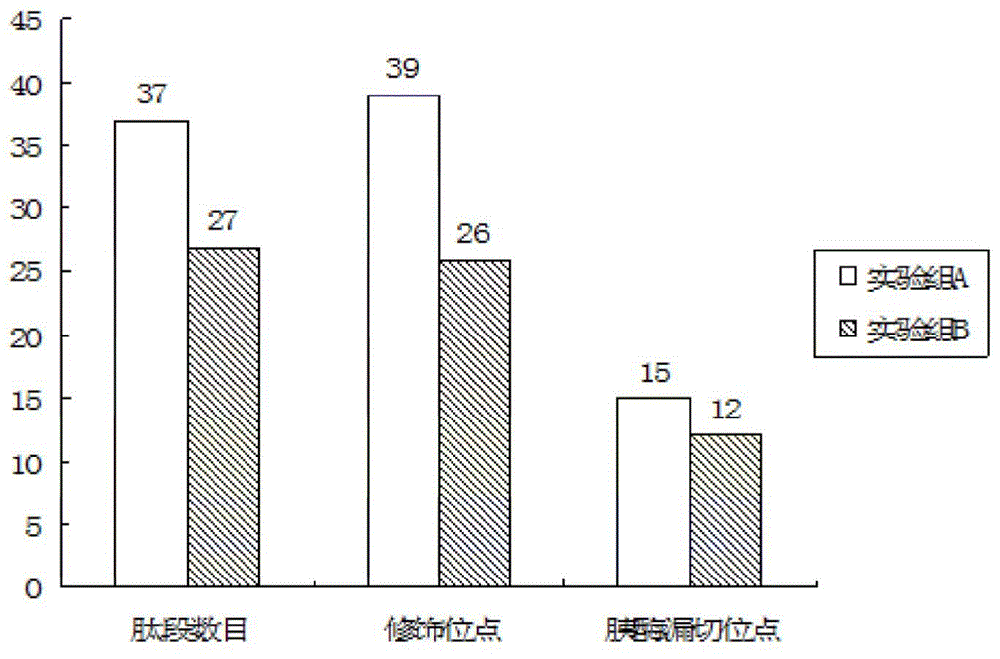
[0033] A method of enzymatically hydrolyzing protein, adding water to the protein and stirring it evenly, putting it into an electrophoresis tank, electrophoresis at 80V, collecting the protein solution after electrophoresis, dissolving the protein with an enzymolysis buffer solution containing trifluoroethanol, and then reducing the protein and alkylation treatment, adjusting the pH of the treated protein solution to 7.5, then adding trypsin accounting for 90% of the volume of the entire solution, and enzymatically hydrolyzing it to obtain a polypeptide product;
[0034] Wherein, the working electrode in the electrophoresis tank is an electrode modified by redox enzyme and zinc-aluminum layered double hydroxide.
[0035] Wherein, the enzymolysis buffer solution is composed of ammonium bicarbonate, trifluoroethanol and acetonitrile in a mass ratio of 2:40:8.
[0036] Wherein, the reagent for adjusting the pH value is ammonium bicarbonate solution with a mass fraction of 2%.
...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A method of enzymatically hydrolyzing protein, adding water to the protein and stirring it evenly, putting it into an electrophoresis tank, electrophoresis at 120V, collecting the protein solution after electrophoresis, dissolving the protein with an enzymolysis buffer solution containing trifluoroethanol, and then reducing the protein and alkylation treatment, adjusting the pH of the treated protein solution to 8.5, then adding trypsin accounting for 98% of the volume of the entire solution, and enzymatically hydrolyzing it to obtain a polypeptide product;
[0053] Wherein, the working electrode in the electrophoresis tank is an electrode modified by redox enzyme and zinc-aluminum layered double hydroxide.
[0054] Wherein, the enzymolysis buffer solution is composed of ammonium bicarbonate, trifluoroethanol and acetonitrile in a mass ratio of 2:60:15.
[0055] Wherein, the reagent for adjusting the pH value is ammonium bicarbonate solution with a mass fraction of 4%. ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] A method of enzymatically hydrolyzing protein, adding water to the protein and stirring it evenly, putting it into an electrophoresis tank, electrophoresis at a voltage of 100V, collecting the protein solution after electrophoresis, dissolving the protein with an enzymolysis buffer solution containing trifluoroethanol, and then reducing the protein and alkylation treatment, adjusting the pH of the treated protein solution to 8, then adding trypsin accounting for 96% of the volume of the entire solution, and enzymatically hydrolyzing it to obtain a polypeptide product;
[0072] Wherein, the working electrode in the electrophoresis tank is an electrode modified by redox enzyme and zinc-aluminum layered double hydroxide.
[0073] Wherein, the enzymolysis buffer solution is composed of ammonium bicarbonate, trifluoroethanol and acetonitrile in a mass ratio of 2 ∶ 50 ∶ 10 compositions.
[0074] Wherein, the reagent for adjusting the pH value is ammonium bicarbonate solutio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com