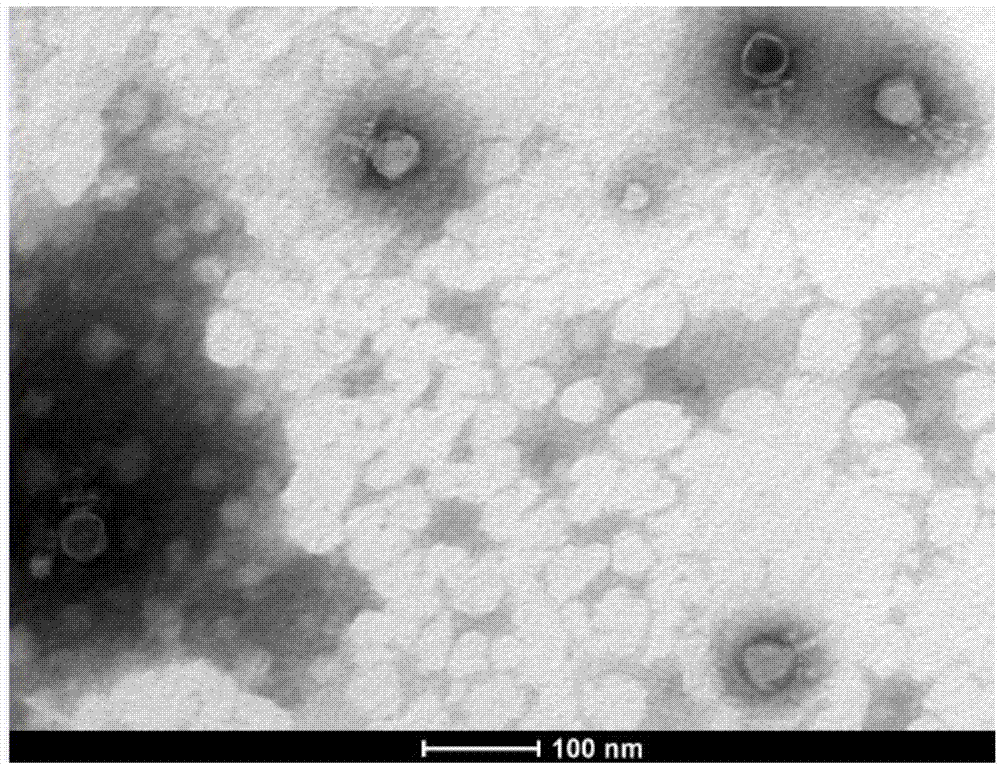
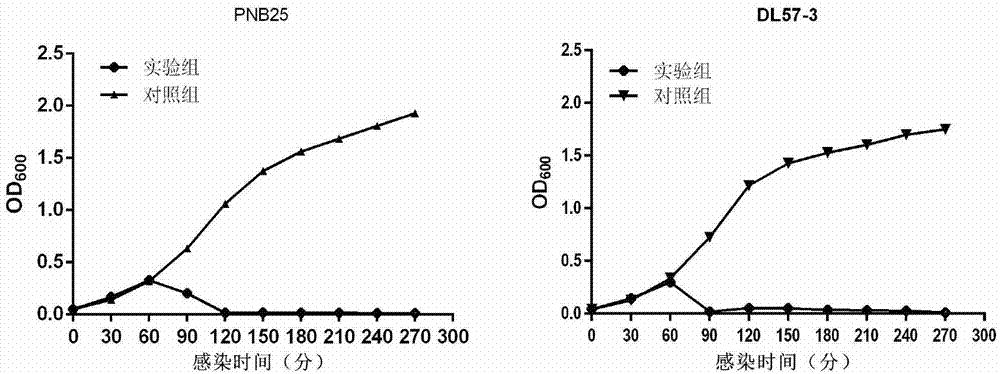
Bacteriophage able to split multiple resistant staphylococcus aureus, separation method and application thereof
A staphylococcus, separation method technology, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of limited number of bacteriophages, narrow bacteriostasis spectrum, and low bacteriostasis efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1, the processing of sample
[0043] Fully dissolve the collected soil, feces and nasal swab samples in sterilized 50mL PBS solution, centrifuge at 5000rpm at 4°C for 20min to remove bacteria and other impurities, filter the supernatant with a 0.22μm filter membrane, and place the filtrate in a sterile Shake culture in the bottle at 37°C and 150rpm for 18h, check for sterility, and store the filtrate without bacterial growth at 4°C for enrichment and isolation of phage.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2, enrichment of phage stock solution
[0045] Three enrichment methods were used; the specific operations were as follows:
[0046] After getting the filtrate 30mL of embodiment 1 and the BHI substratum of equal volume and mixing, add and be in logarithmic growth phase (OD 600 =0.5~0.7) of the phage host bacteria Staphylococcus aureus 3mL, shake culture at 165rpm at 37°C overnight. The next day, centrifuge at 12000rpm at 4°C for 15min, take 30mL of the supernatant, add equal volumes of BHI medium and 1mL of host bacteria enrichment solution, stand at 37°C for 30min, shake at 165rpm for 12h, and centrifuge at 12000rpm at 4°C for 15min. Take 15 mL of the supernatant, add an equal volume of BHI medium and 0.6 mL of the host bacteria enrichment solution, let stand at room temperature for 30 min, and shake at 37°C for 4 h at 165 rpm. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm at 4°C for 20 minutes, collect the supernatant and filter it with a 0.22 μm filter membrane to obtain ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3, the screening of phage indicator bacteria
[0048] Using 20 clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, 20 MRSA strains, 20 food-borne strains and 17 clinical isolates, a total of 60 strains were used as indicator bacteria, and the double-layer agar plate method was used to screen the suspected plaques. flat. Specific process:
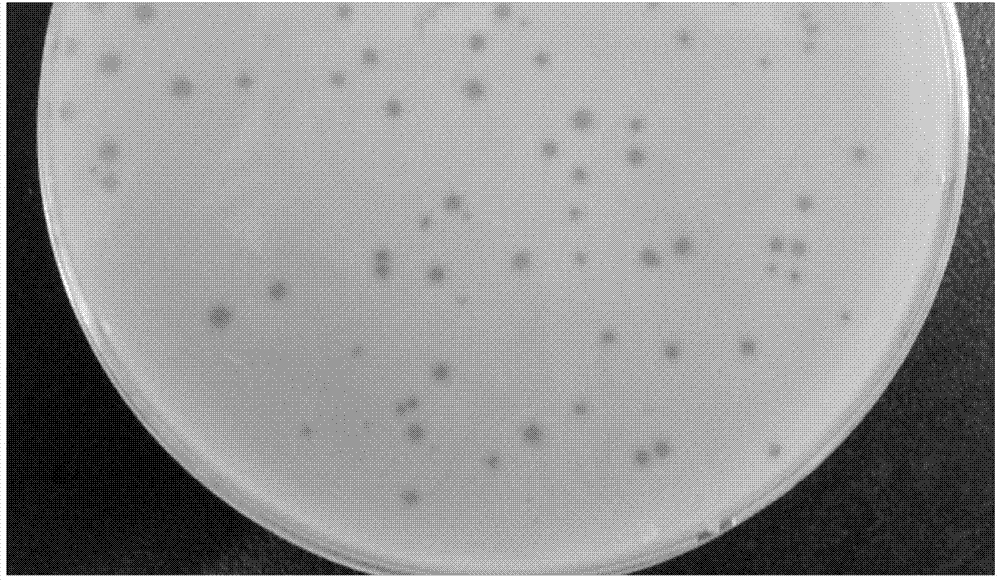
[0049] Take 300 μL of the phage stock solution of Example 2, mix them with 60 strains of the same amount of bacteria cultured overnight, incubate at 37°C for 20 minutes after gently vortexing, add to the upper layer of agar at about 40°C, mix well and quickly pour it on the bottom layer Plate—on a solid plate of BHI medium, place it at room temperature for 15 minutes. After it solidifies, place it upside down in a 37°C incubator and incubate for 11 to 13 hours to obtain a plate that can form phage plaques. Staphylococcus aureus 05L189 was screened as an indicator bacterium.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bronsted acidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com