Bridge type input resistance negative feedback CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) pre-amplifying circuit
A technology of input resistance and pre-amplification circuit, which is applied in the field of CMOS circuits, can solve the problems of easy interference and mismatch of signals, and achieve the effect of benefiting equivalent input noise and reducing equivalent input noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
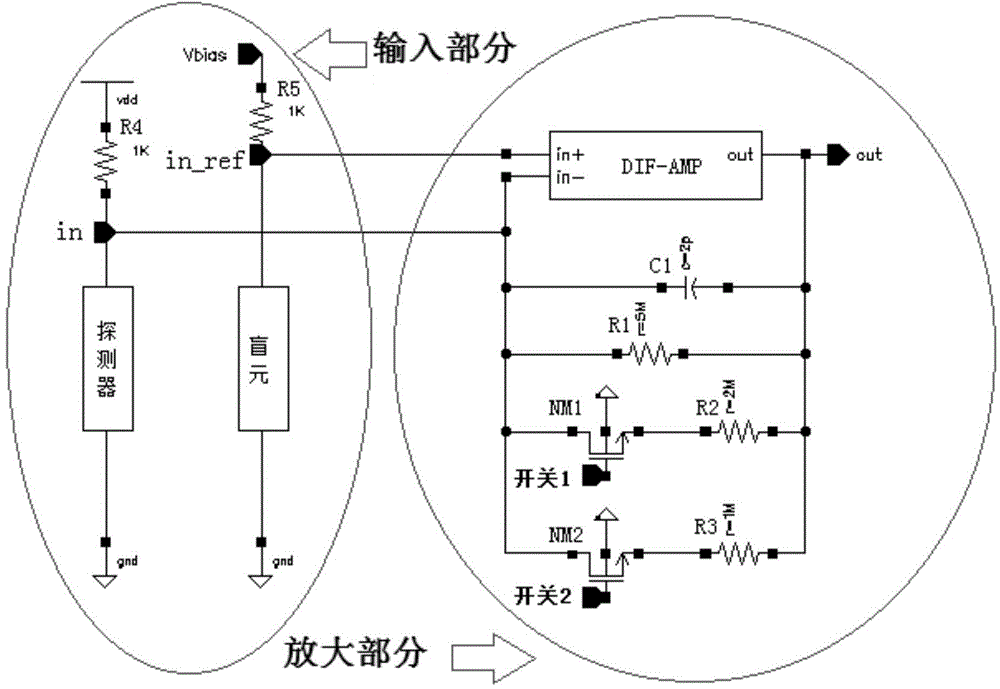
[0019] figure 1 The overall structure diagram of the CMOS preamplifier circuit for negative feedback of the bridge input resistance. R4 is connected with the infrared photoconductive detector to form a path, R5 is connected with the blind element of the detector to form another path, and the two paths form a balanced bridge structure. If you want to increase or decrease the current flowing through the photoconductive detector, you can increase or decrease the resistance of R4 and R5. R5 corresponds to R4, and its resistance should be designed to be equal, and the design of this circuit is 1K ohms. The resistance of the blind element and the detector are equal in size. If the resistance of the detector is inconsistent with the resistance of the blind element, the circuit can work normally by adjusting Vbias. The amplifier is suitable for amplifying signals of photoconductive detectors with low input impedance below 100 ohms. When the infrared photoconductive detector receive...
Embodiment 2
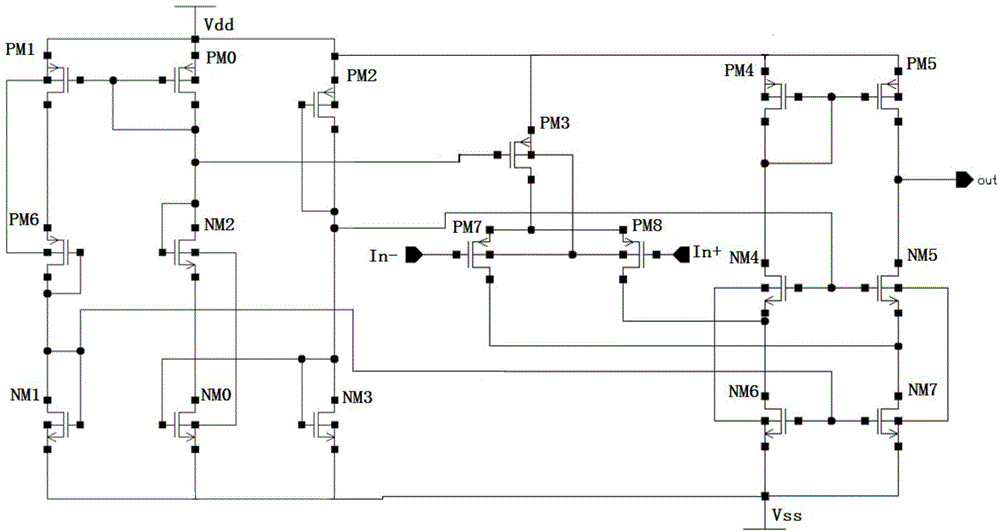
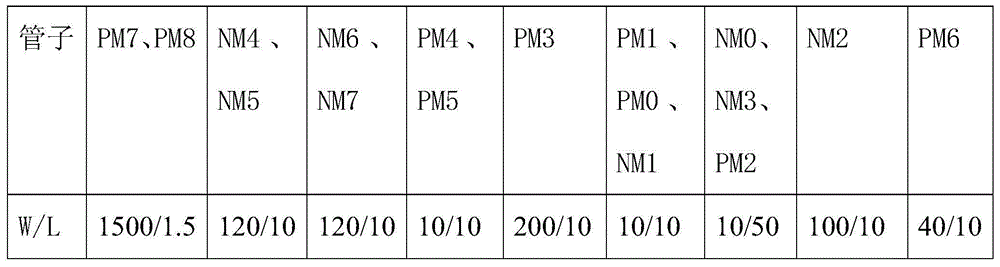
[0023] figure 2 It is the topological structure diagram of the differential amplifier circuit. One-stage folded cascode structure with differential input. Among them, PM7 and PM8 are input pair tubes, PM7, PM8, NM4, and NM5 form a cascode structure of differential input, PM4, PM5 are active loads of differential output, NM6, NM7 provide current source for cascode, In -, In+ are the positive and negative input terminals of the differential operational amplifier. NM3 and NM0 constitute the first-stage current mirror, PM0 and PM1 constitute the second-stage current mirror, NM1 and NM6 and NM7 of the amplifying part constitute a current mirror, and PM0 and PM3 of the amplifying part constitute a current mirror. The reference dimensions of the tubes are shown in the table below (in microns).
[0024]
[0025] The differential amplifier adopts a cascode structure and can be powered by positive and negative power sources, so that there is no minimum voltage requirement at the ...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Under the low temperature of liquid nitrogen, the CMOS preamplifier circuit was tested, and its minimum amplification factor was 400 times (0.6M ohm feedback resistance). Then the CMOS preamplifier circuit was interconnected with the low-impedance detector, and the component was tested. The working condition of the circuit and the detector is good. The 3dB bandwidth of the component is greater than 2KHZ, and the noise of the equivalent input point is less than 30nV / Hz -1 / 2 . The passband noise was tested with a lock-in amplifier EG Model 117, and the results are shown in the table below:
[0028]
[0029] From the test results, the bridge-type input resistance negative feedback CMOS preamplifier circuit can be read out smoothly after the low-impedance detector is connected to the low-temperature liquid nitrogen, and the noise test results are excellent, successfully realizing the high-impedance CMOS circuit and low-impedance detector matching.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com