An in vitro glial scar formation model and its construction method and application
A technology of glial scars and construction methods, applied in the field of cell biology, can solve the problems that glial scars cannot be completely reproduced, the process of glial scars cannot be observed, and there is no intervention of central nervous system-related factors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1: Cultivation, purification and identification of brain (spinal) membrane fibroblasts and astrocytes
[0066] 1. Cultivation, purification and identification of brain (spinal) membrane fibroblasts
[0067] 1.1 Isolation of the brain
[0068] SD rats 24 hours after birth were soaked in 75% alcohol for disinfection; the ophthalmic curved scissors were used to decapitate the head, and the head was fixed with the thumb and forefinger, and the skull skin was cut with ophthalmic curved scissors; The skull was cut open and turned to both sides with the “people” seam. At this time, the cerebral hemispheres on both sides were exposed. The whole brain was separated from the base of the skull using curved micro-tweezers, and placed in pre-cooled HBSS buffer.
[0069] 1.2 Isolation of cerebral meninges and cerebrospinal fibroblasts for culture and purification
[0070] Under a stereomicroscope, the cerebral cortex is facing upwards, and the brain is fixed with one micros...
Embodiment 2
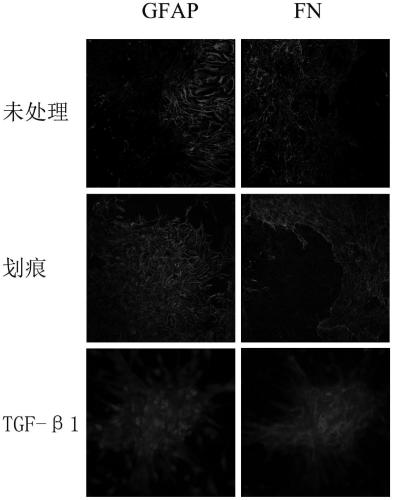
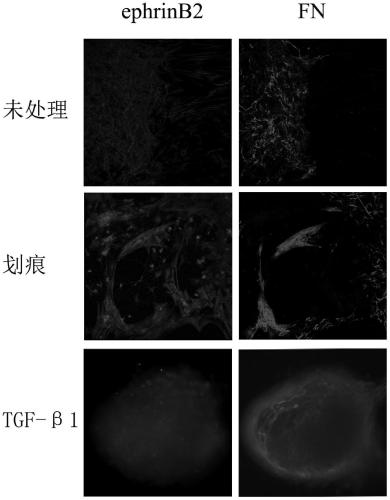
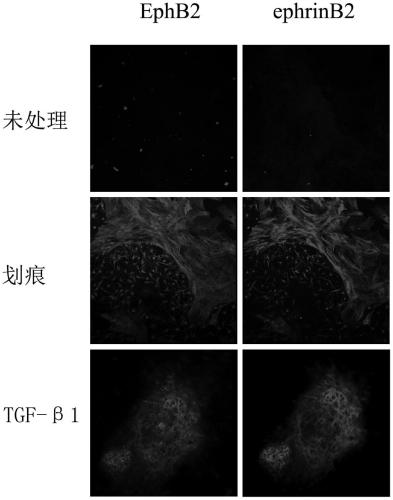
[0082] Example 2: Establishment and identification of the glial-like scar model of the present invention
[0083] 3.1 Establishment of glial-like scars
[0084] Purified 6×10 4 cerebrospinal fibroblasts and 8×10 4 Astrocytes were respectively planted in adjacent chamber slides (Nunc Company) chambers, the slides at the bottom of the chambers had been pre-coated with 50 μg / ml L-polylysine, about 200 μl per chamber Cell suspension (the density ratio of brain (spinal) membrane fibroblasts and astrocytes is 3:4), remove the small chamber after 0.5h, add 5ml DMEM / F12 medium containing 10% FBS, in 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in an incubator for about 3-5 days. The two types of cells have moved closer to each other. Take the needle tip of a disposable 1ml syringe. Under the microscope, there are scratches in the word "Feng" at the junction of the two cells, including 16 vertical scratches and 1 horizontal scratch. Change the medium. Afterwards, the culture was continued, and a glial-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com