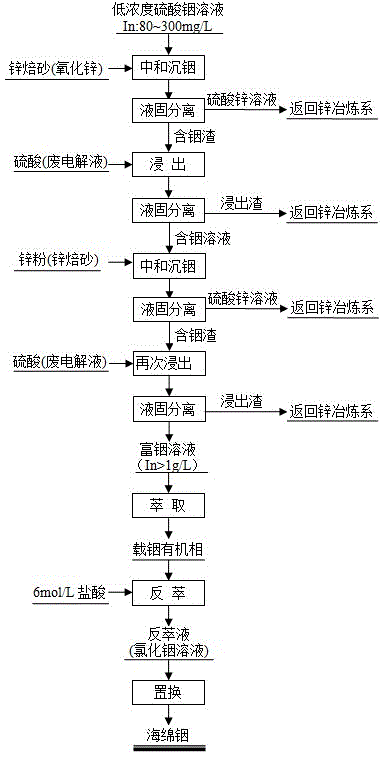
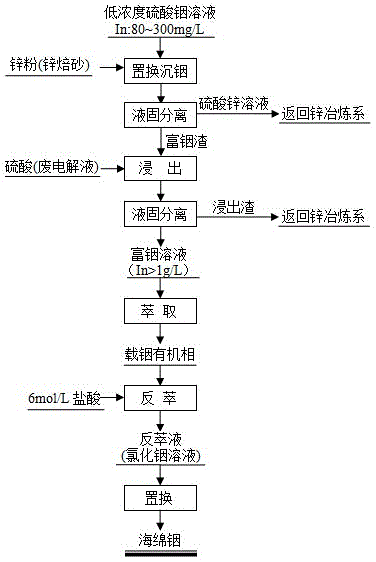
Method for separating, enriching and recycling indium from low-concentration indium sulphate solution
A technology of separation and enrichment and indium sulfate, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of unresolved chlorine-containing waste acid discharge, unsuitable for separation and recovery, etc., to reduce adverse effects, eliminate dispersion losses, and reduce production cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
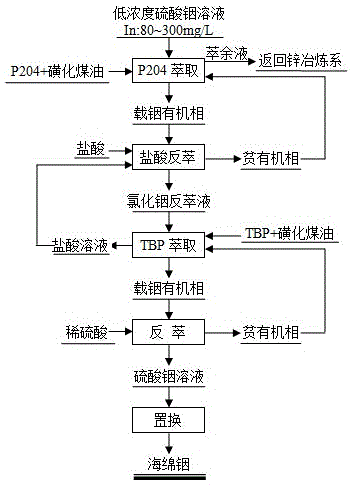
[0029] Such as figure 1As shown, the method for separating, enriching and recovering indium from a low-concentration indium sulfate solution comprises: first extracting the low-concentration indium sulfate solution with P204, and then back-extracting it with hydrochloric acid to obtain an indium chloride back-extraction solution; The obtained indium chloride back-extraction solution is then extracted with TBP, back-extracted with dilute sulfuric acid to obtain a high-concentration indium sulfate solution, and finally the high-concentration indium sulfate solution is replaced by metal to obtain sponge indium.
[0030] The specific steps are:
[0031] (1) P204 extraction: first mix P204 and sulfonated kerosene at a volume ratio of 20:80 to obtain an organic phase, then mix the low-concentration indium sulfate solution and the organic phase at a volume ratio of 2:1 and add them to a box-type mixing and settling tank Three-stage counter-current extraction was carried out in 50°C...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for separating, enriching and recovering indium from a low-concentration indium sulfate solution comprises: first extracting the low-concentration indium sulfate solution with P204, and then back-extracting it with hydrochloric acid to obtain an indium chloride back-extraction solution; The obtained indium chloride back-extraction solution is then extracted with TBP, back-extracted with dilute sulfuric acid to obtain a high-concentration indium sulfate solution, and finally the high-concentration indium sulfate solution is replaced by metal to obtain sponge indium.
[0038] The specific steps are:
[0039] (1) P204 extraction: First, mix P204 and sulfonated kerosene at a volume ratio of 30:70 to obtain an organic phase, then mix the low-concentration indium sulfate solution and the organic phase at a volume ratio of 2:1 and add them to a box-type mixing and settling tank Four-stage counter-current extraction was carried out in 45°...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for separating, enriching and recovering indium from a low-concentration indium sulfate solution comprises: first extracting the low-concentration indium sulfate solution with P204, and then back-extracting it with hydrochloric acid to obtain an indium chloride back-extraction solution; The obtained indium chloride back-extraction solution is then extracted with TBP, back-extracted with dilute sulfuric acid to obtain a high-concentration indium sulfate solution, and finally the high-concentration indium sulfate solution is replaced by metal to obtain sponge indium.
[0046] The specific steps are:
[0047] (1) P204 extraction: first mix P204 and sulfonated kerosene at a volume ratio of 25:75 to obtain an organic phase, then mix the low-concentration indium sulfate solution and the organic phase at a volume ratio of 2:1 and add them to a box-type mixing and settling tank Three-stage counter-current extraction was carried out in 40°...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com