Ameliorant for saline alkali soil and processing process and application thereof
A processing technology and improver technology, applied in saline-alkali land improver and its processing technology and application field, can solve the problems of high cost of improver, low soil pH adjustment ability, etc., to improve physical and chemical properties, increase adsorption capacity, and reduce pH value Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
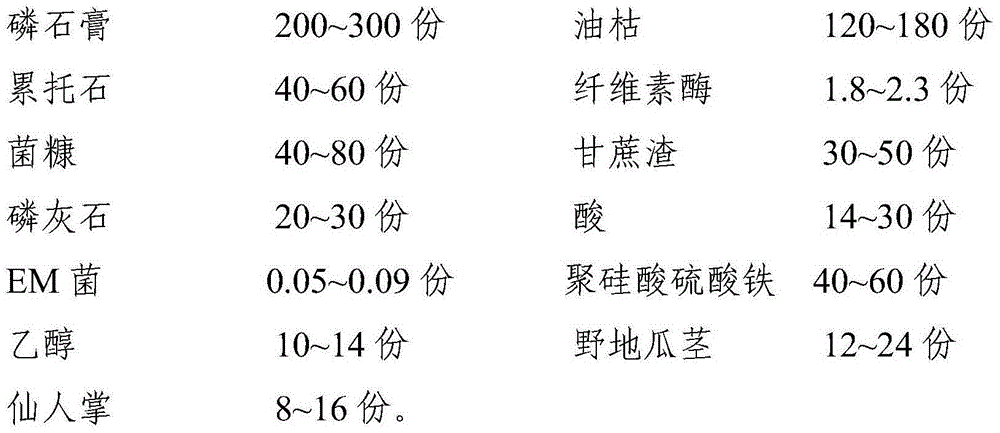
[0041] raw material:
[0042] Phosphogypsum 200kg, oil dry 120kg, rectorite 40kg, cellulase 1.8kg, fungus chaff 40kg, bagasse 30kg, apatite 20kg, acid 14kg, EM bacteria 0.05kg, polysilicate ferric sulfate 40kg, ethanol 10kg, 12kg of wild sweet potato stems and 8kg of cactus.
[0043] Preparation:
[0044] (1) Drying the phosphogypsum and apatite until the moisture content is 5%, and then pulverizing them into 60-mesh fine powder to obtain phosphogypsum powder and apatite powder;
[0045] (2) Cut the stems of wild sweet potatoes into 1cm-long segments, and then dry them at a temperature of 400°C until the moisture content is 3% to obtain the stems of wild sweet potatoes; cut the fleshy stems of cactus into 1cm in length and width and 0.5mm in thickness. cm, and then dried at a temperature of 400°C until the moisture content is 3%, to obtain cactus slices;
[0046] (3) Use a ball mill to grind the rectorite into a fine powder with a fineness of ≤0.05mm, then send it into an u...
Embodiment 2
[0053] raw material:
[0054] Phosphogypsum 300kg, oil dry 180kg, rectorite 60kg, cellulase 2.3kg, fungal chaff 80kg, bagasse 50kg, apatite 30kg, acid 30kg, EM bacteria 0.09kg, polysilicate ferric sulfate 60kg, ethanol 14kg, 24kg of wild sweet potato stems and 16kg of cactus.
[0055] Preparation:
[0056] (1) Drying the phosphogypsum and apatite until the moisture content is 10%, and then pulverizing them into 200-mesh fine powder to obtain phosphogypsum powder and apatite powder;
[0057] (2) Cut the stems of wild sweet potatoes into 3cm long sections, then dry them at a temperature of 600°C until the moisture content is 6% to obtain the stems of wild sweet potatoes; cut the fleshy stems of cactus into 3cm in length and width and 2cm in thickness The thin slices are then dried at a temperature of 600°C until the moisture content is 5% to obtain cactus slices;
[0058] (3) Use a ball mill to grind the rectorite into a fine powder with a fineness of ≤0.05mm, then send it in...
Embodiment 3
[0065] raw material:
[0066] Phosphogypsum 250kg, oil dry 150kg, rectorite 50kg, cellulase 2.1kg, fungus chaff 60kg, bagasse 40kg, apatite 25kg, acid 20kg, EM bacteria 0.07kg, polysilicate ferric sulfate 50kg, ethanol 12kg, 18kg of wild sweet potato stems and 12kg of cactus.
[0067] Preparation:
[0068] (1) drying the phosphogypsum and apatite until the moisture content is 7%, and then pulverizing them into 80-mesh fine powder to obtain phosphogypsum powder and apatite powder;
[0069] (2) Cut the stem of wild sweet potato into 2cm long segments, then dry it at a temperature of 500°C until the water content is 4%, to obtain the stem of wild sweet potato; cut the fleshy stem of cactus into 2cm in length and width and 1cm in thickness The thin slices are then dried at a temperature of 500°C until the moisture content is 4%, to obtain cactus slices;
[0070] (3) Use a ball mill to grind the rectorite into a fine powder with a fineness of ≤0.05mm, then send it into an ultras...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com