A method for preparing lithium battery electrode materials by using waste slag extracted from vanadium
A technology for extracting vanadium slag and electrode materials, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low utilization rate of Ti resources, low added value, hidden dangers of disasters, etc., and achieve high utilization rate of added value, The effect of improving electrochemical performance and avoiding environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
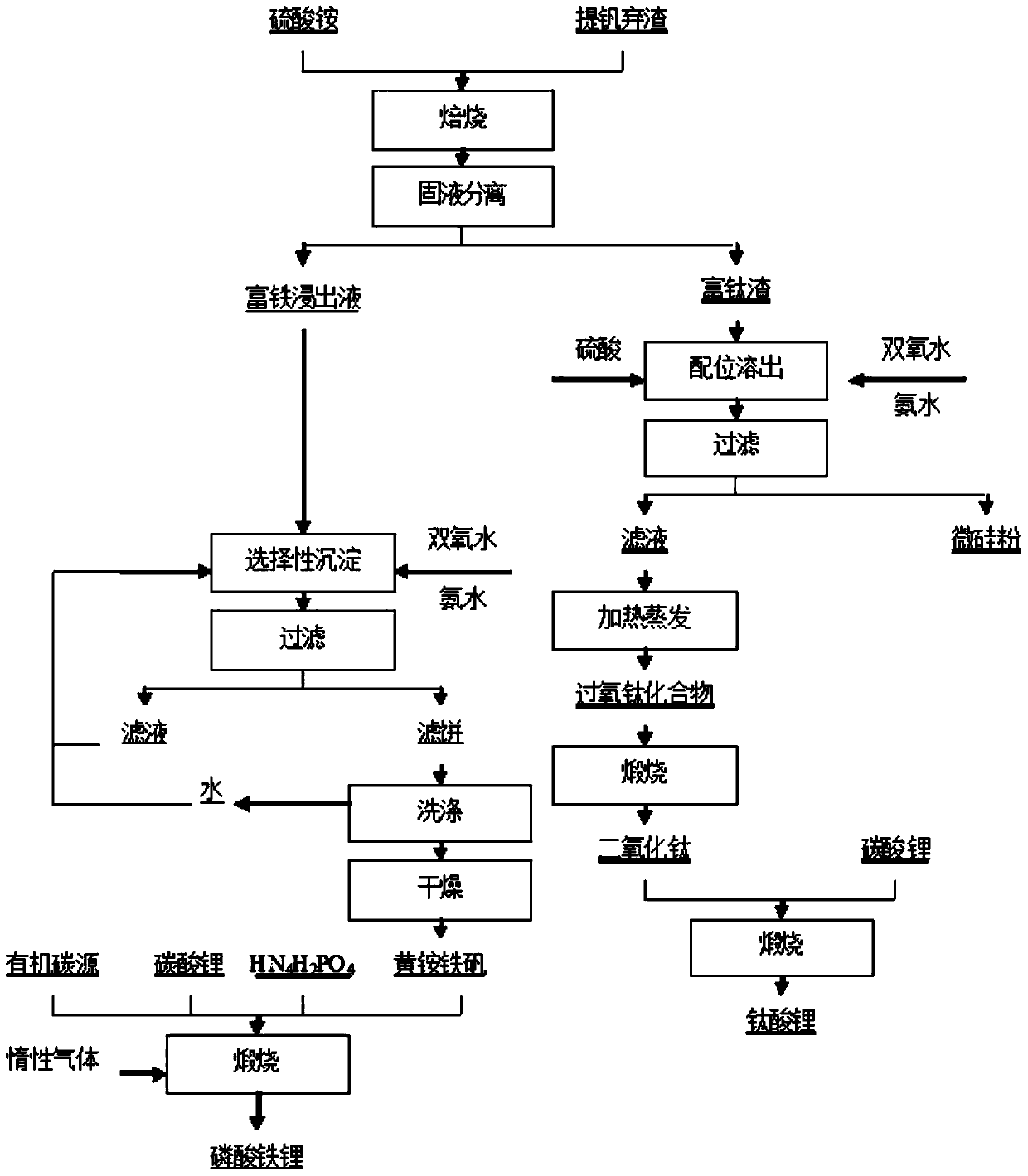
[0052] (1) Separation of iron and titanium:
[0053] After the vanadium extraction waste slag is mechanically crushed, the vanadium extraction waste slag is roasted with ammonium sulfate. The ammonium sulfate extraction vanadium waste slag ratio is 4:1. Ionized water was leached at 80°C for 60 minutes, and filtered to obtain iron-rich filtrate and titanium-rich filter residue;
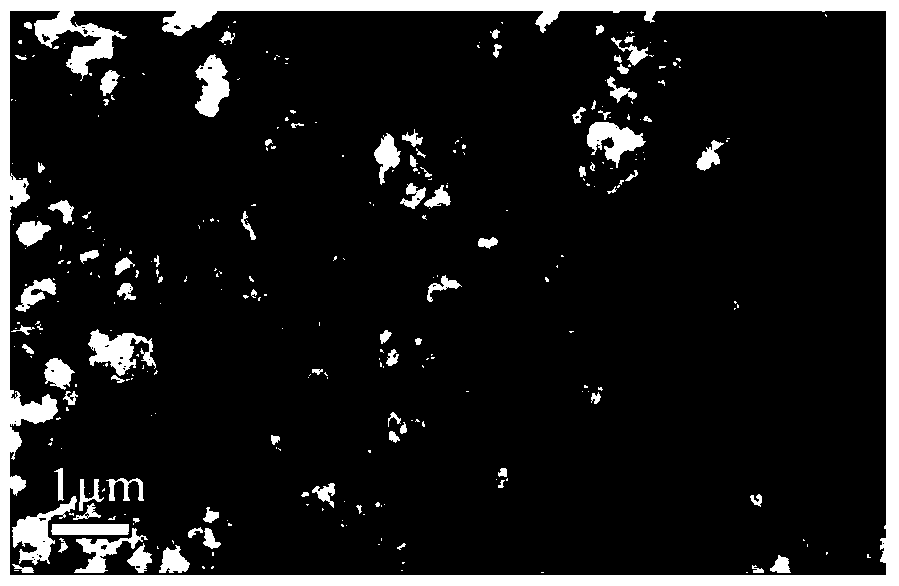
[0054] (2) Preparation of yellow ammonium jarosite:
[0055] Add hydrogen peroxide to the iron-rich filtrate gained in step (1), the Fe in the iron-rich filtrate 2+ Oxidized to Fe 3+ . Afterwards, heat the iron-rich filtrate under stirring conditions, the temperature is 80°C, add ammonia water at the same time to adjust the pH value of the filtrate to 2.0, and then start timing. The reaction time is 8 hours. During the reaction process, continuously add ammonia water to the filtrate to neutralize the of sulfuric acid. After the reaction is finished, the feed liquid is filtered, and the filter resi...
Embodiment 2
[0064] (1) Separation of iron and titanium:
[0065] After the vanadium extraction waste slag is mechanically crushed, the vanadium extraction waste slag is roasted with ammonium sulfate. The ammonium sulfate extraction vanadium waste slag ratio is 4:1. Ionized water was leached at 85°C for 120 minutes, and filtered to obtain iron-rich filtrate and titanium-rich filter residue
[0066] (2) Preparation of yellow ammonium jarosite:
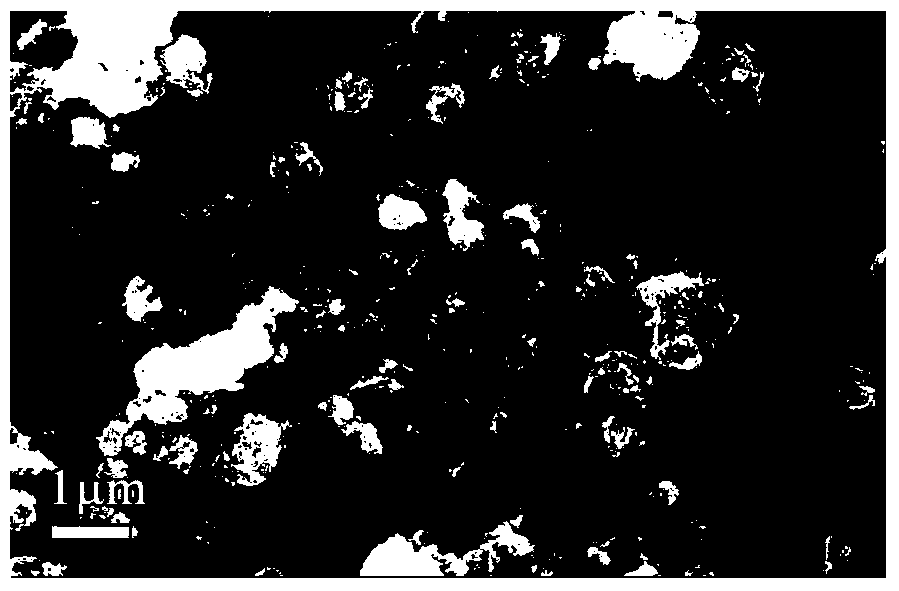
[0067] Add hydrogen peroxide to the iron-rich filtrate gained in step (1), the Fe in the iron-rich filtrate 2+ Oxidized to Fe 3+ . Afterwards, the iron-rich filtrate was heated with stirring at a temperature of 85° C., and ammonia water was added to adjust the pH value of the solution while the temperature was raised. The pH of the solution is 1.5. When the set condition is reached, the timing starts. The reaction time is 6 hours. During the reaction, ammonia water is continuously added to the solution to neutralize the sulfuric acid produced. ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] (1) Separation of iron and titanium:
[0077] After the vanadium extraction waste slag is mechanically crushed, the vanadium extraction waste slag is roasted with ammonium sulfate. The ammonium sulfate extraction vanadium waste slag ratio is 4:1. Ionized water was leached at 90°C for 180 minutes, and filtered to obtain iron-rich filtrate and titanium-rich filter residue
[0078] (2) Preparation of yellow ammonium jarosite:
[0079] Add hydrogen peroxide to the iron-rich filtrate gained in step (1), the Fe in the iron-rich filtrate 2+ oxidized to Fe 3+ . Afterwards, the iron-rich filtrate was heated under the condition of stirring, and the temperature was 90° C., and ammonia water was added to adjust the pH value of the solution while the temperature was raised. The pH of the solution is 2.5. When the set condition is reached, the timing starts. The reaction time is 8 hours. During the reaction, ammonia water is continuously added to the solution to neutralize the sulf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com