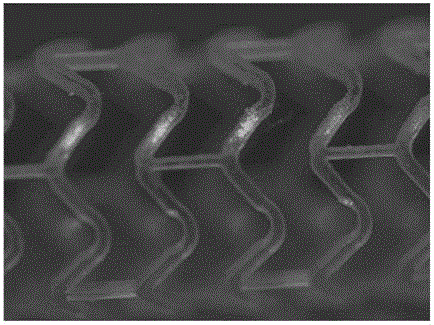
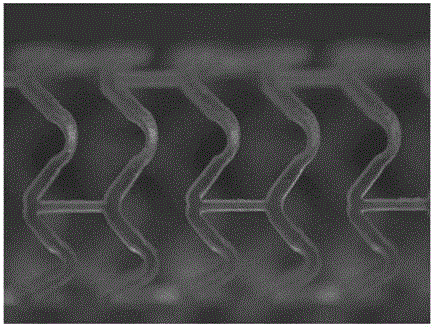
Machining method for degradable polymer intravascular stent
A technology for degrading polymers and processing methods, which is applied in the processing field of degradable polymer vascular stents, can solve the problems of small radial support force of stents, high rebound rate, high polymer viscosity, etc. The effect of radial support force and smooth surface of the stent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A degradable polymer vascular stent, using PLLA as a raw material, the molecular weight of PLLA is 800,000, the specific processing steps are as follows: (1) Tube forming: select L-polylactic acid PLLA with an average molar molecular weight of 800,000 as the stent matrix material, and The material is heated to 196°C in the plastic molding extruder (the melting point of PLLA is 180°C), the pressure is set to 9MPa, and other conditions are the same as the conventional extrusion process. After the material is completely melted to a uniform state, it is removed from the Extruded in a molding die to obtain a pipe with an outer diameter of 3.3 mm and a wall thickness of 0.21 mm.
[0025] (2) Laser engraving into a stent matrix: laser engraving is performed on the shaped pipe obtained in step (1) using laser light source equipment to obtain a stent matrix.
[0026] (3) Surface polishing of the stent matrix: suspend the stent matrix after laser engraving in step (2) in the ultr...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A kind of degradable polymer vascular stent, with embodiment 1, difference is: the molecular weight of PLLA is 200,000 in the step (1), and this polymer material is heated to 192 ℃ (the fusing point of PLLA) in plastic molding extruder The temperature is 180°C), the pressure is set to 14MPa, and other conditions are the same as the conventional extrusion process. After the material is completely melted to a uniform state, it is extruded from the molding die to obtain an outer diameter of 3.3mm and a wall thickness of 0.21mm tubing.
[0030] In step (3), the surface of the stent base is ultrasonically cleaned and polished for 20 minutes, and the cleaning agent solution is ethanol.
[0031] Finally, a clean polymer vascular stent was obtained, and its mechanical properties were tested, and it was concluded that under the pressure of 82kPa, the diameter change rate of the stent obtained by adopting the technical solution of Example 1 was 13.7%. The change rate of the diam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com