Method for removing COD (chemical oxygen demand) from copper/molybdenum extraction raffinate mixed wastewater
A technology for mixing wastewater and raffinate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of inability to remove small molecular substances, inability to remove dissolved organic matter, COD Reduce and other problems, to achieve the effect of low overall operating cost, small dosage, and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
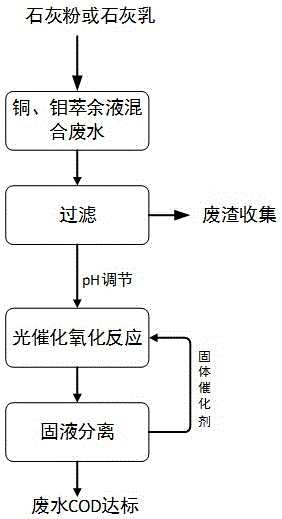
[0028] Mixed waste water from copper and molybdenum extraction and recovery system of an enterprise, pH=2.52, COD1240mg / L, SO 4 2- The content is 109.5g / L. (1) Take 5000mL of the above wastewater, add 15% milk of lime according to 1% of the theoretical dosage for removing all sulfate radicals, stir and react for 30 minutes, then let it stand for 20 minutes, and filter to remove the generated calcium sulfate slag;
[0029] (2) The filtrate obtained in step (1) was adjusted to pH=7 with 10% sodium hydroxide solution, the COD content was 450mg / L, and the SO 4 2- The content is 108.4g / L;
[0030] (3) The solution obtained in step (2) is first added with 2g / L of ZnO or ZnS as a catalyst, and then added with H 2 o 2 , where H 2 o 2 Dosing concentration is 1 times of influent COD mass concentration, namely 450mg / L. Catalytic oxidation is then carried out under the irradiation of light with a wavelength of 190 nm. The oxidation reaction temperature is 20°C, and the reaction t...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Wastewater from molybdenum extraction and recovery system of a copper mine enterprise, pH=1.25, COD2000mg / L, SO 4 2- The content is 202.3g / L.
[0034] (1) Take 5000mL of the above wastewater, add 15% milk of lime according to 10% of the theoretical dosage for removing all sulfate radicals, stir for 40 minutes, then let it stand for 30 minutes, and filter to remove the generated calcium sulfate slag;
[0035] (2) The filtrate obtained in step (1) was adjusted to pH=9 with 10% sodium hydroxide solution, the COD content was 750mg / L, and the SO 4 2- The content is 188.2g / L;
[0036] (3) Add 0.1g / L of ZnO and SnO to the solution obtained in step (2) 2 Two-component catalyst (ZnO and SnO 2 The mass ratio is 2:1), then add H 2 o 2 , where H 2 o 2 Dosing concentration is twice the mass concentration of influent COD, that is, 1.5g / L. Then catalyze oxidation under light with a wavelength of 350nm, the oxidation reaction temperature is 70°C, and the reaction time is 10mi...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Wastewater after neutralization of copper extraction and recovery system of an enterprise in Sichuan, pH=12, COD229mg / L, SO 4 2- The content is 1g / L.
[0040] (1) Take 5000mL of the above wastewater, add quicklime according to 200% of the theoretical dosage for removing all sulfate radicals, stir for 40 minutes, then let it stand for 30 minutes, and filter to remove the generated calcium sulfate slag;
[0041] (2) The filtrate obtained in step (1) was adjusted to pH=5 with 10% dilute hydrochloric acid solution, the COD content was 185mg / L, and the SO 4 2- The content is 0.05g / L;
[0042] (3) Add 0.5g / L of ZnS and ZrS to the solution obtained in step (2) 2 Two-component catalyst (ZnS and ZrS 2 The mass ratio is 1:1), then adding H 2 o 2 , where H 2 o 2 Dosing concentration is 3 times of influent COD mass concentration, namely 555mg / L. Then carry out catalytic oxidation under light with a wavelength of 780nm, the oxidation reaction temperature is 35°C, and the r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com