Application of a marker for auxiliary diagnosis of macrosomia
A marker and a huge technology, applied in the fields of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine, can solve the problems of complex experimental steps and low sensitivity, and achieve the effects of simple sample processing, high sensitivity and specificity, and rapid and accurate instrument analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Embodiment 1: Research object selection and group basis
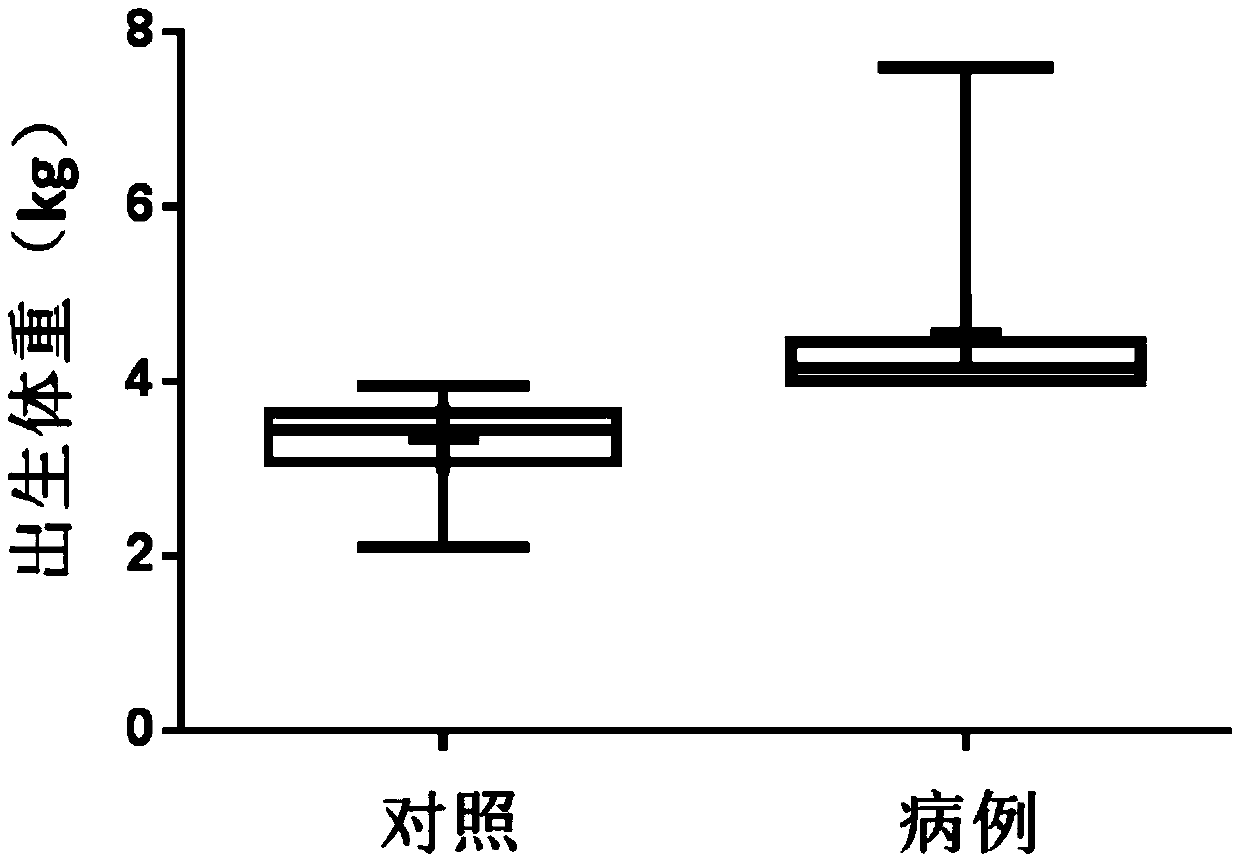
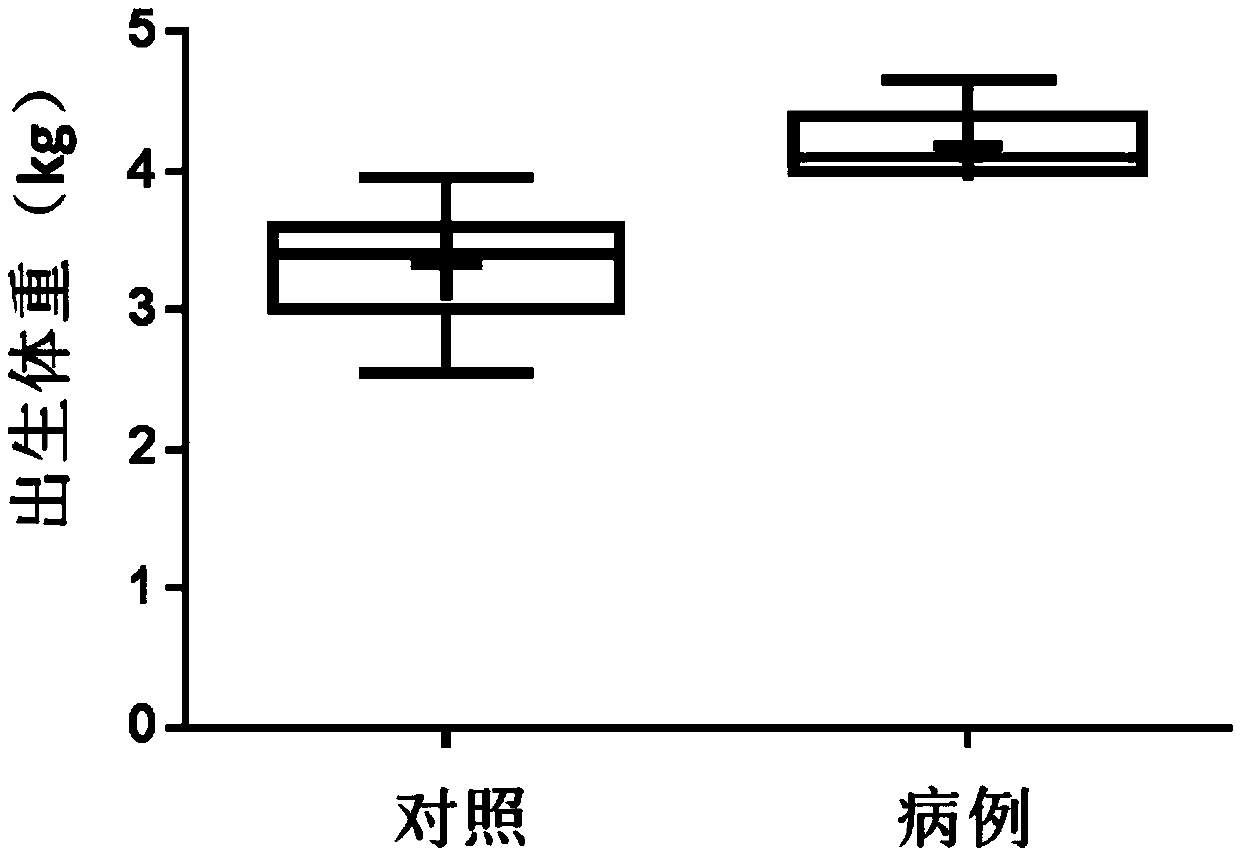
[0084] The present inventor collected blood samples from mothers of macrosomia patients and normal children who met the requirements from the Nanjing Maternal and Child Health Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University (see figure 1 , figure 2 ). Weigh the newborn after birth, and if the weight is equal to or greater than 4kg within 1 hour after birth, it is diagnosed as "macrosomia". In the first stage, 100 samples of pregnant women who met the requirements were randomly included, 15 of which were macrosomia; in the second stage, 30 samples of pregnant women were included, of which 15 were compared with 15 cases of macrosomia. Screening subjects for markers. Specific sample classification criteria are as follows:
[0085] first stage screening
[0086] A total of 100 pregnant women were randomly included.
[0087] 1. Between 23 and 36 years old;
[0088] 2. No gestational hypertension, gestational...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Example 2: UPLC-MS Metabolomics Biomarker Screening for Macrosomia
[0111] 1. Sample pretreatment
[0112] 1.1. Fresh pregnant blood (100 samples in the screening stage) was centrifuged in a centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes, and 100 μl of the supernatant was taken and dispensed into clean 1.5ml EP tubes.
[0113] 1.2.50 μl of plasma was precipitated with 150 μl of methanol (reagent C).
[0114] 1.3. Aspirate the supernatant, blow dry with nitrogen and then vacuum dry.
[0115] 1.4. Dissolve the dry matter with 100 μL of water (reagent D).
[0116] 2. Instrument testing
[0117] 2.1. Analytical instruments: UPLCUltimate3000system (Dionex) high-performance liquid chromatography; Q-Exactive high-resolution mass spectrometer.
[0118] 2.2. Liquid phase conditions:
[0119] 2.2.1 The liquid chromatographic column is a C18 chromatographic column (100mm×2.1mm, particle size 1.9μm), and the column temperature is 40°C. The preferred liquid chromatography column is a Hyp...
Embodiment 3
[0132] Example 3: Stability Analysis of Plasma Metabolic Small Molecules
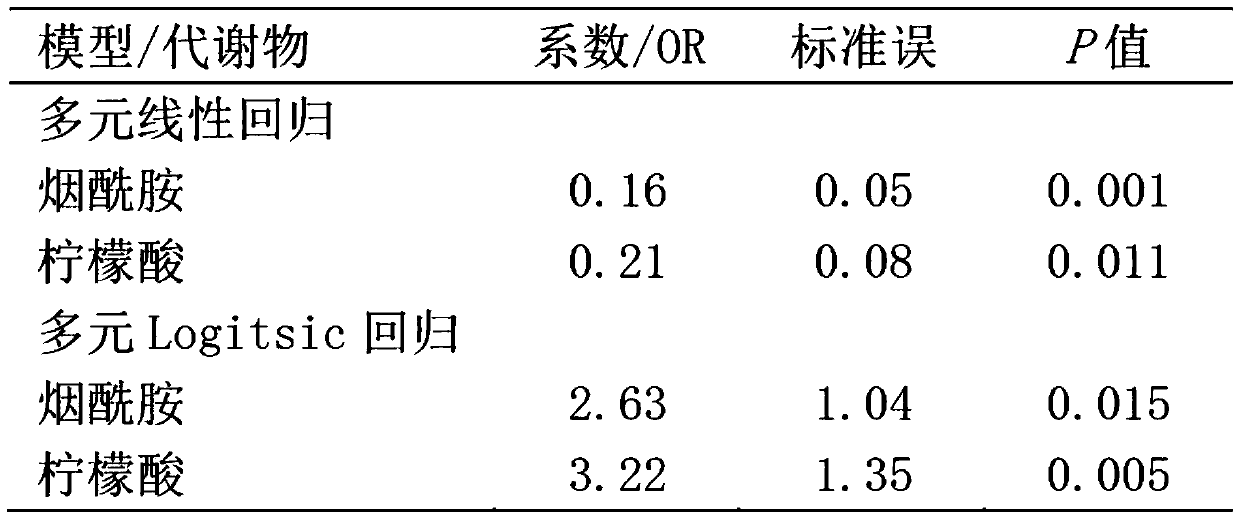
[0133] The same collection method as in Example 1 was used to collect plasma from nine mothers during pregnancy, and the method in Example 2 was used to evaluate the stability of plasma levels of nicotinamide and citric acid (the interval was 2 weeks). The results showed that the measured levels of nicotinamide and citrate in plasma were stable ( Figure 4 ), with properties as diagnostic / monitoring markers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com