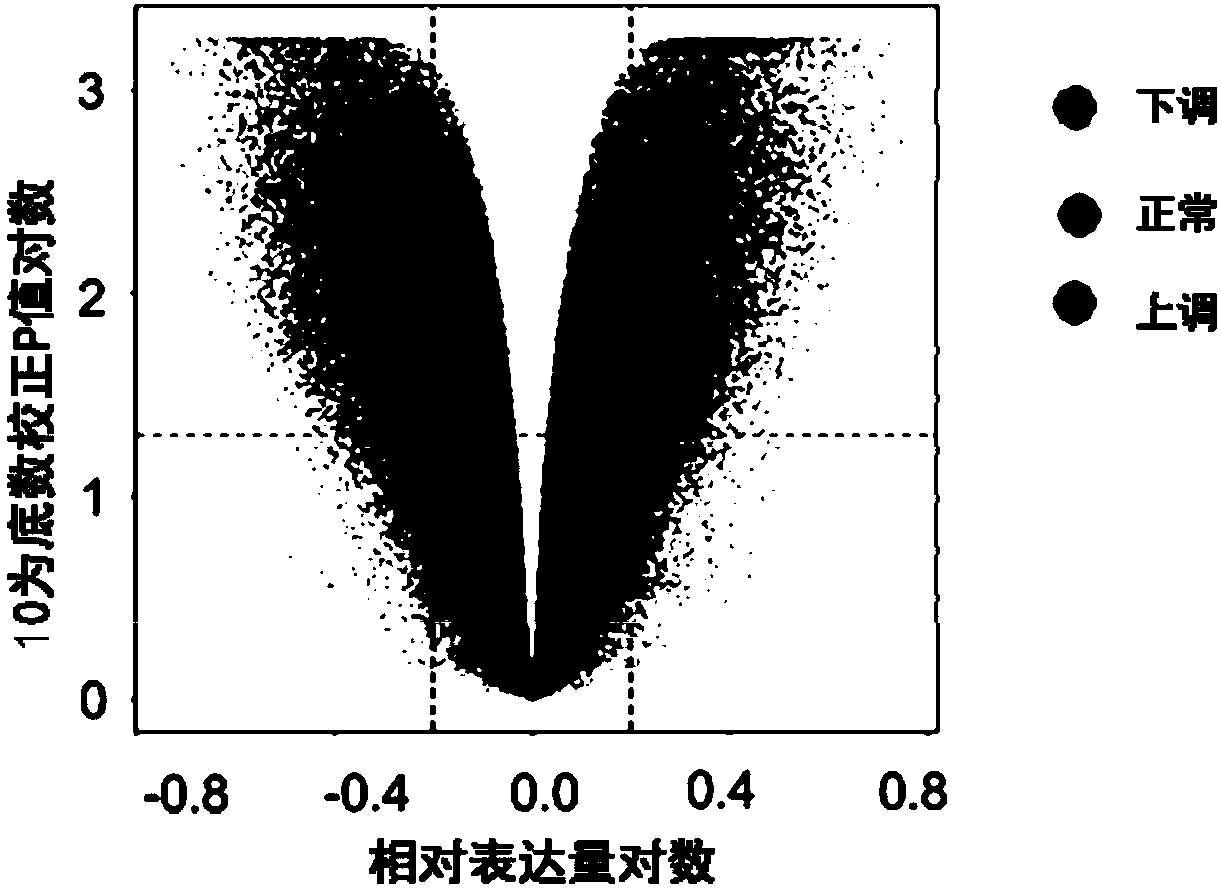
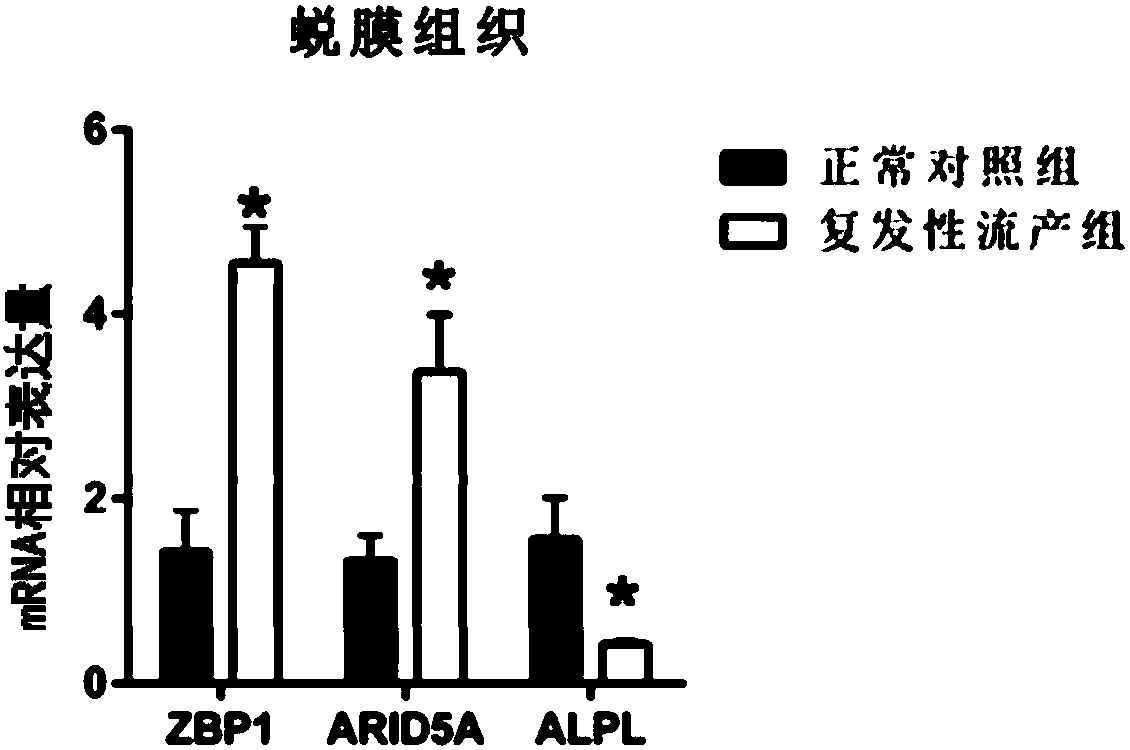
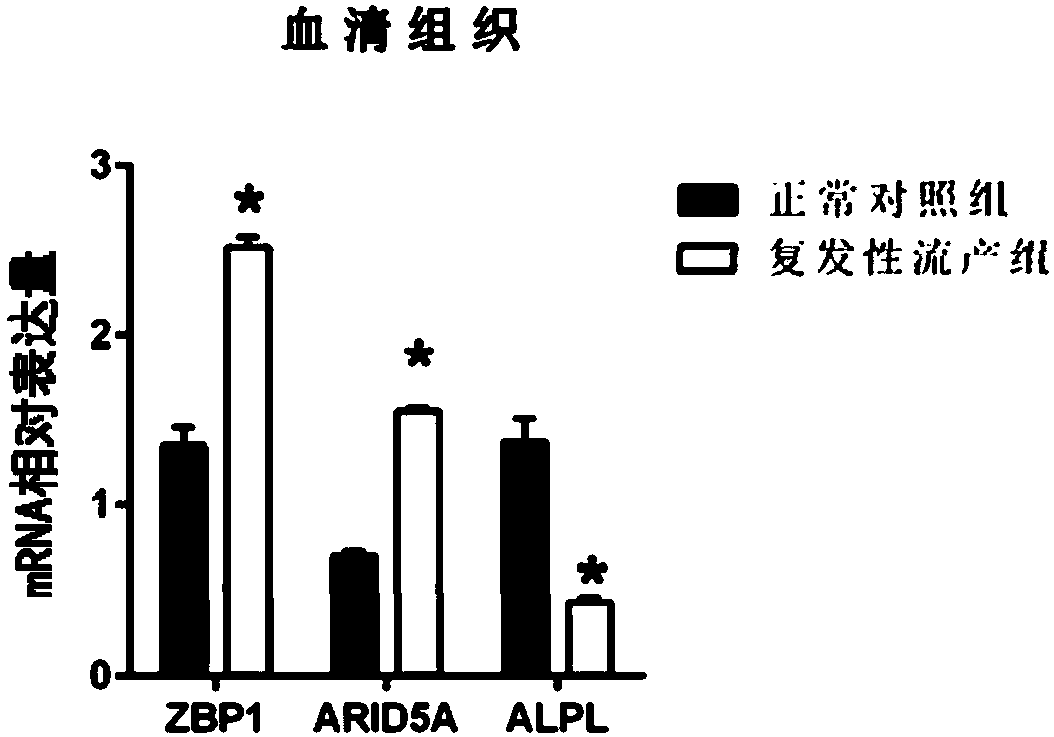
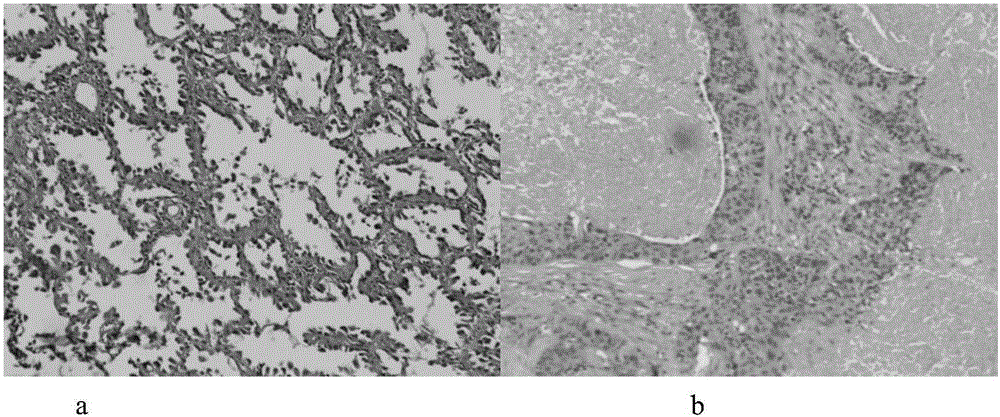
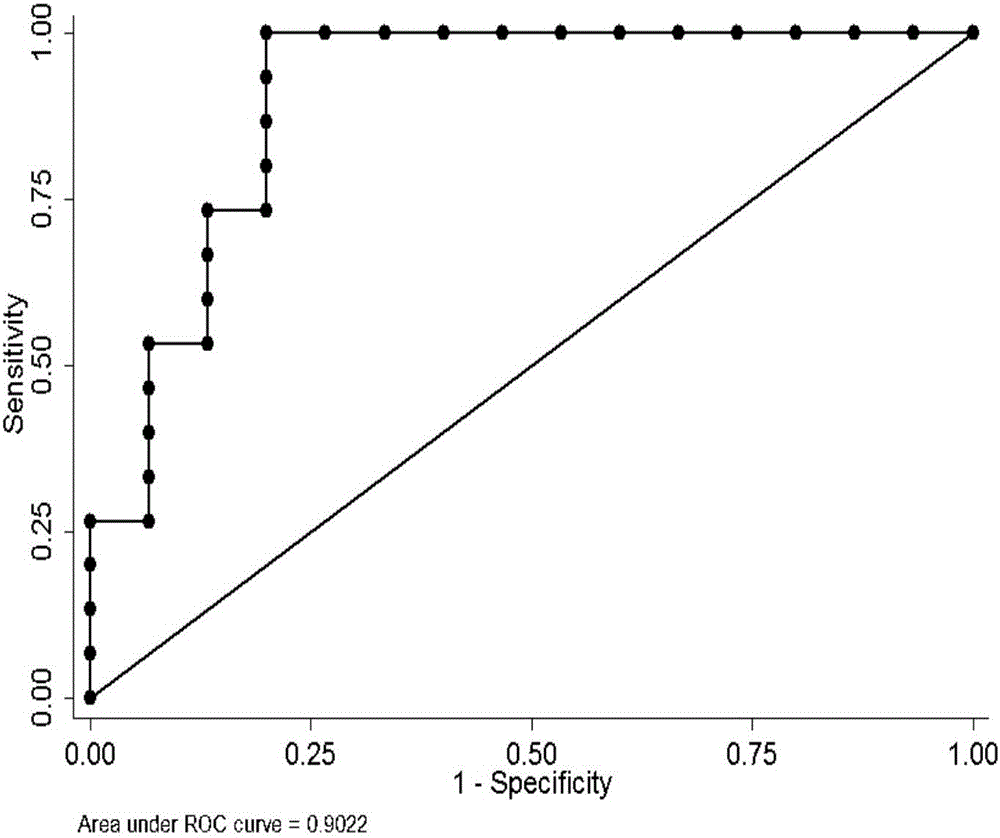
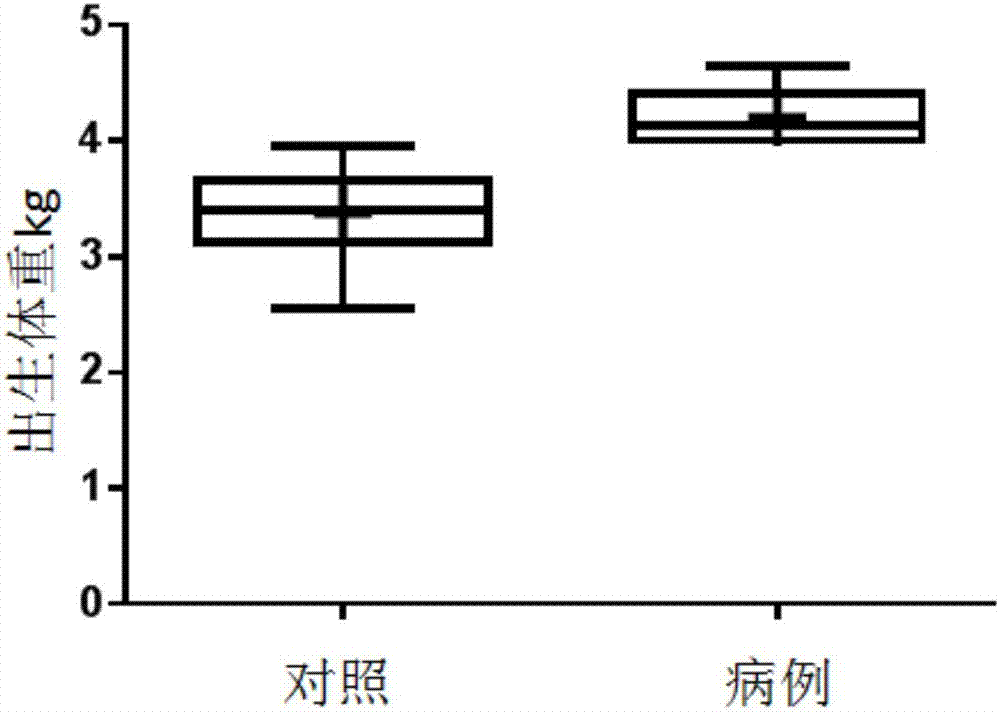
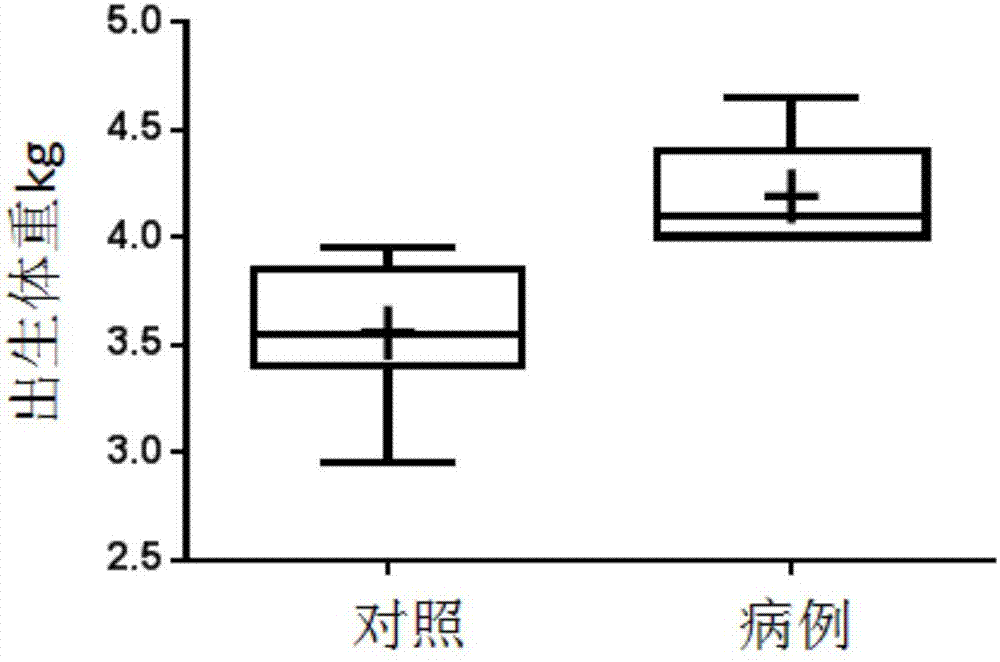
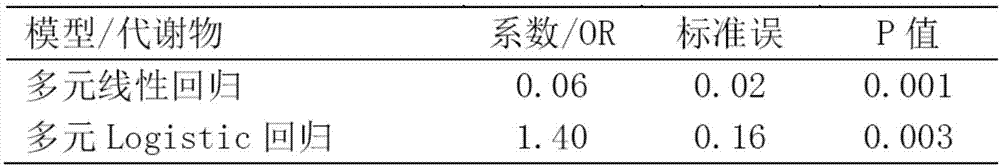
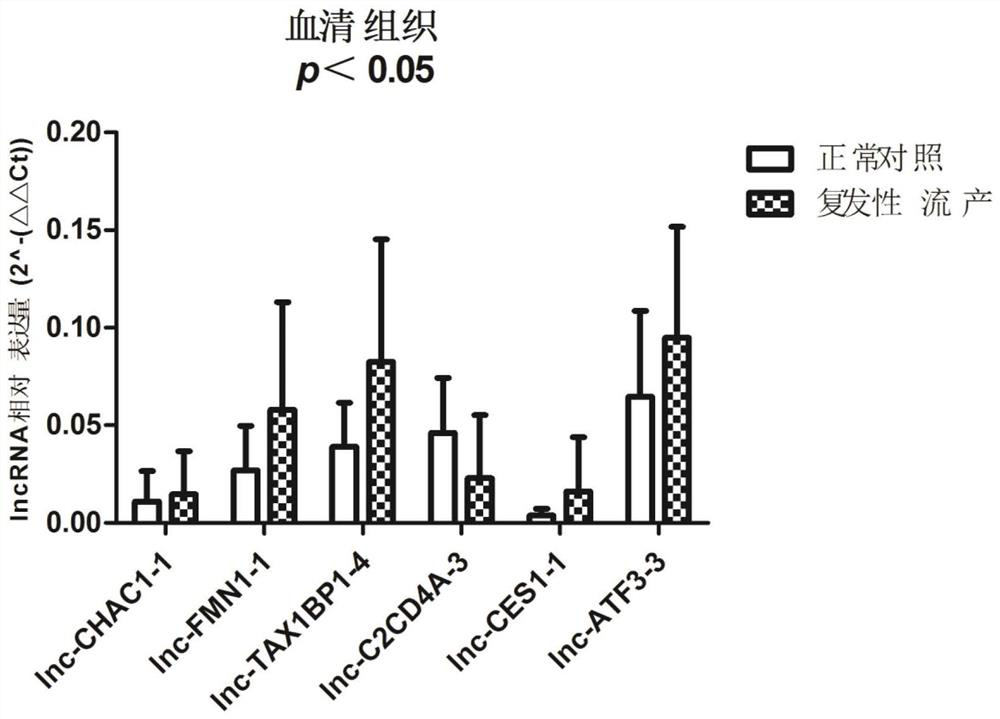
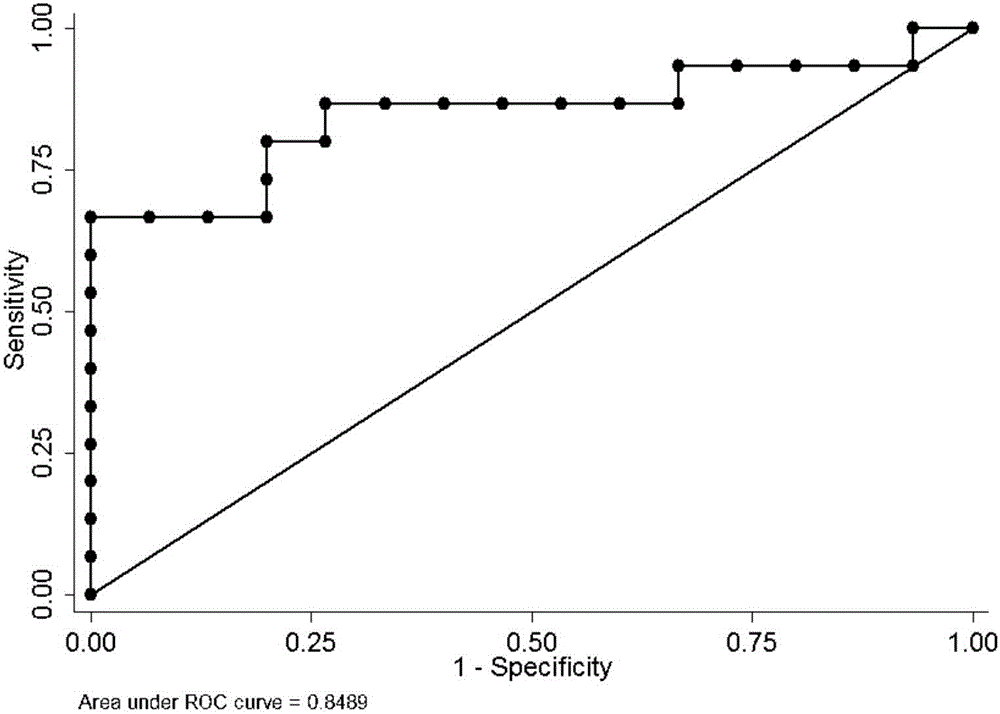Patents
Literature
61results about How to "Delay and stop disease progression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plasma micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) marker related with human Hirschsprung's disease and application of miRNA marker
ActiveCN102358900AEasy diagnosisHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseDynamic monitoring
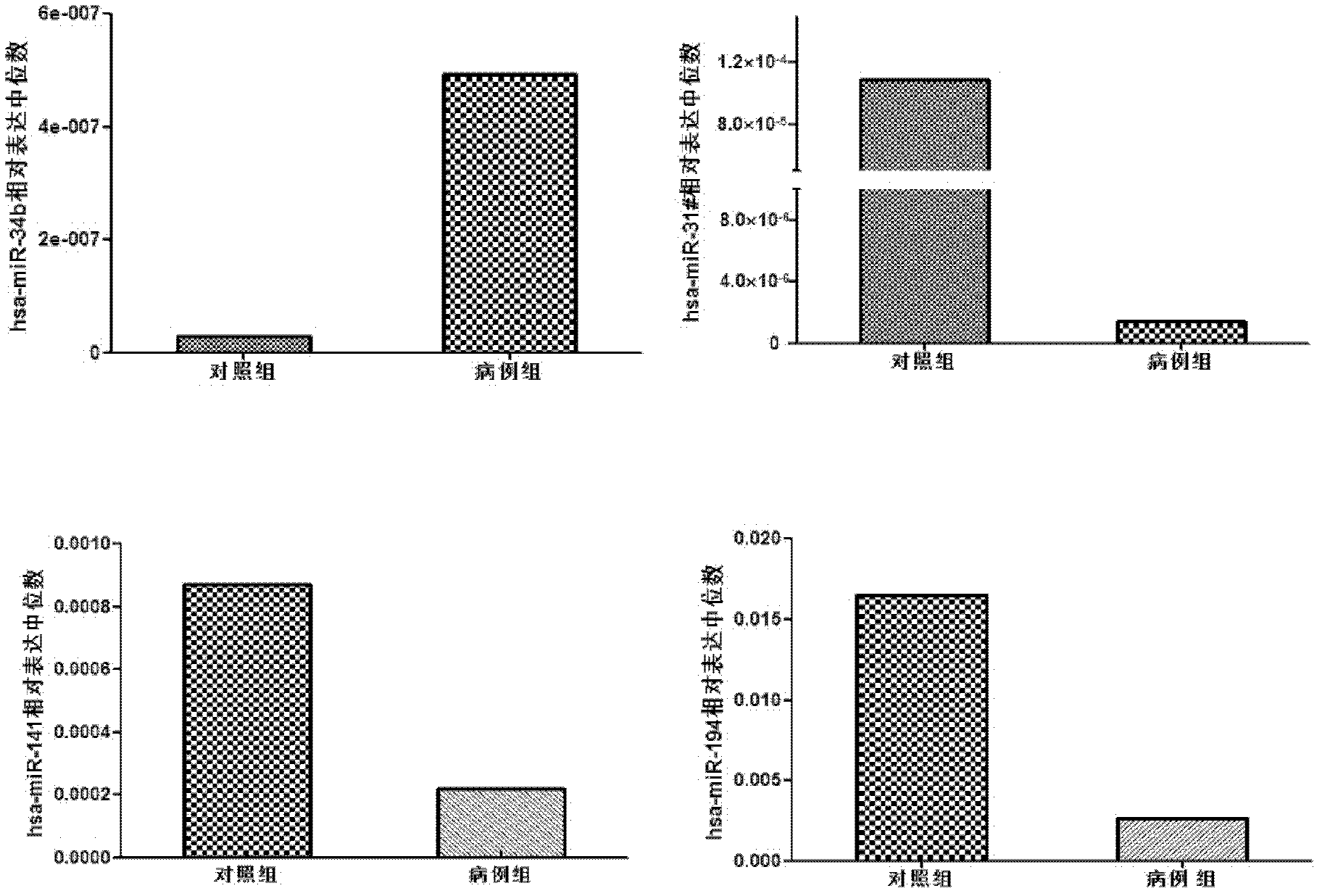
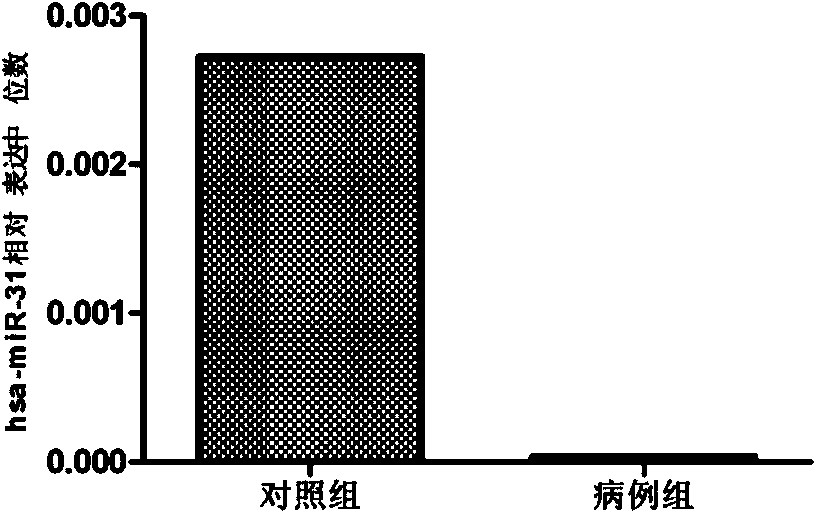
The invention belongs to the fields of gene engineering and clinical medicine, and discloses a plasma micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) marker related with a human Hirschsprung's disease and application of the miRNA marker. The marker is selected from multiple kinds of hsa-miR-34b, hsa-miR-31*, hsa-miR-141 and hsa-miR-194. The marker has specificity and sensitivity on the Hirschsprung's disease, canbe used for preparing a reagent for diagnosing or monitoring the Hirschsprung's disease, can avoid invasive diagnosis, can be used for screening and diagnosis at the early stage, can be repeatedly detected, and is easy in dynamic monitoring.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Related serum microribonucleic acid marker for human severe preeclampsia and application of marker
ActiveCN103205430AEasy to monitorHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic engineeringBlood serum
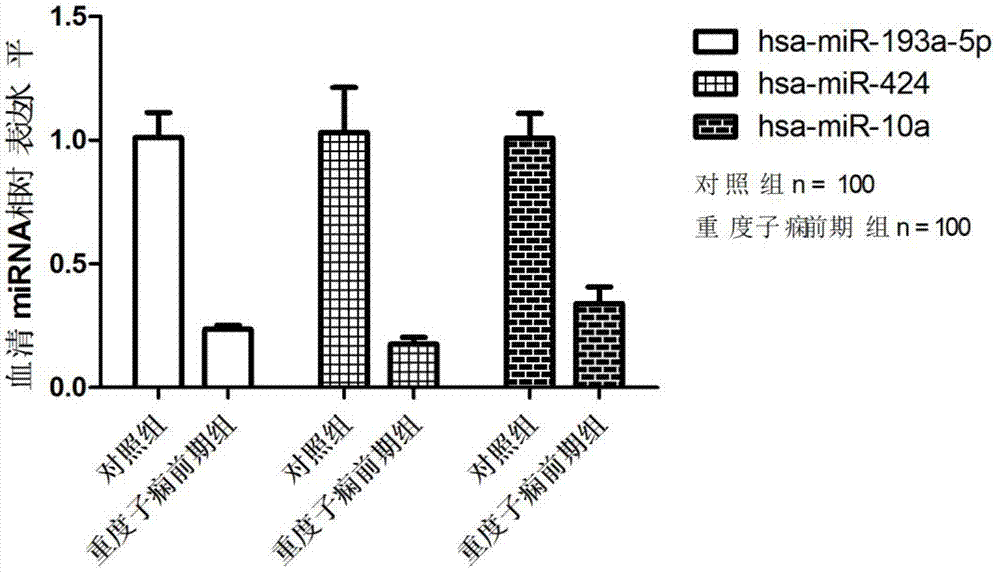
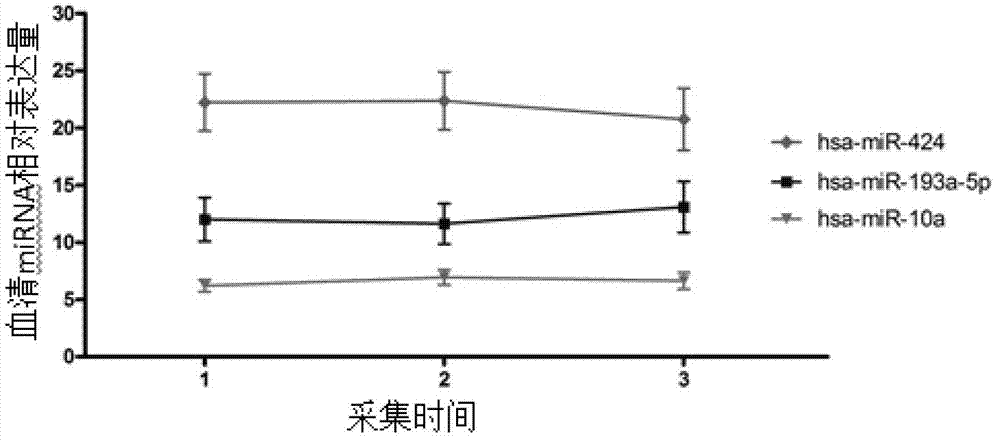
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and clinical medicine, and discloses a related serum microribonucleic acid marker for human severe preeclampsia and application of the marker. The marker is selected from more of hsa-miR-193a-5p, hsa-miR-424 and hsa-miR-10a. The marker has the specificity and sensitivity on a sufferer with severe preeclampsia, and can be used for preparing a diagnosis or monitoring kit for severe preeclampsia.
Owner:夏彦恺
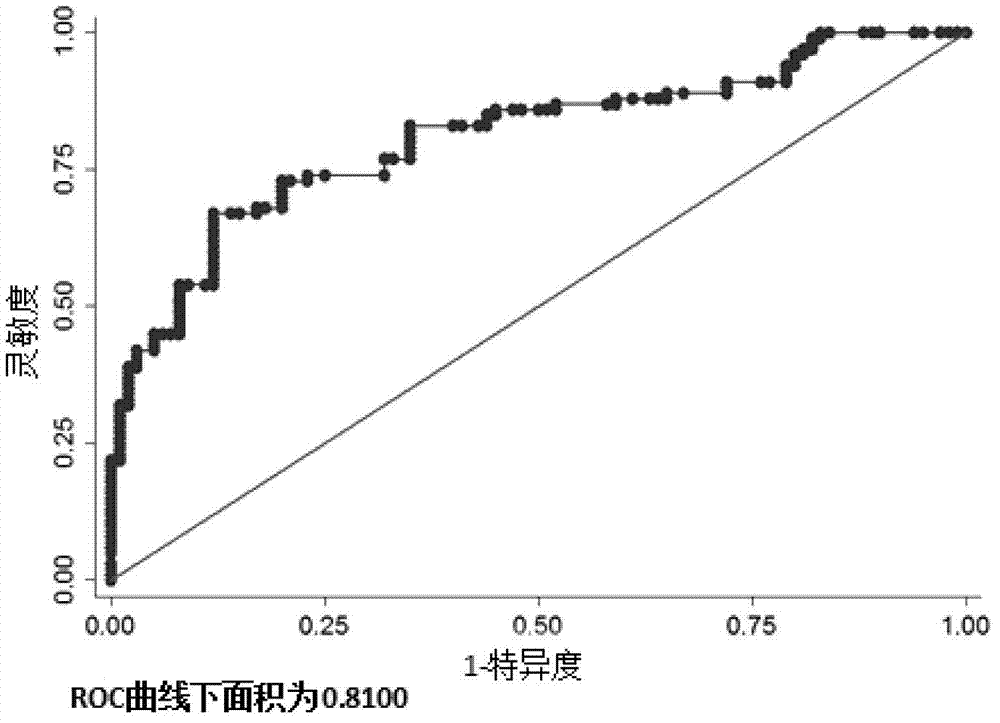
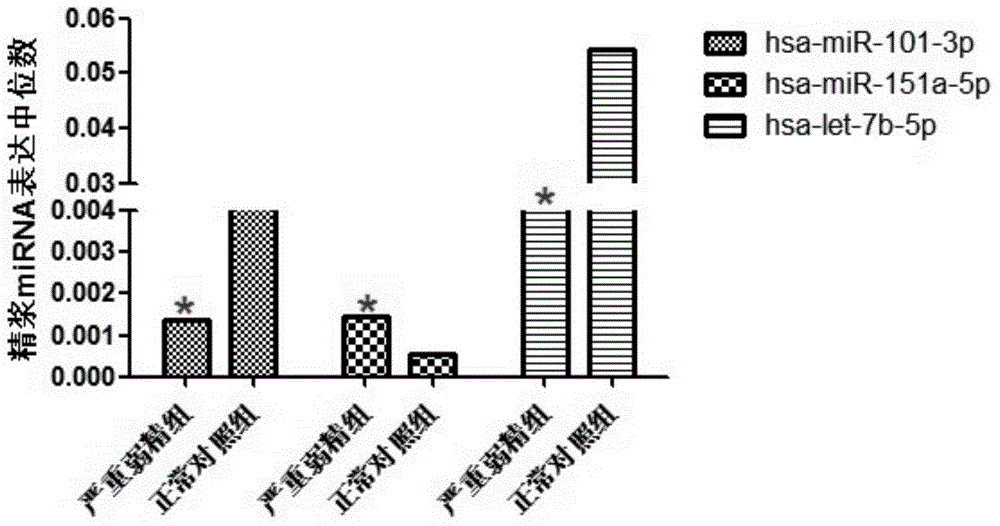
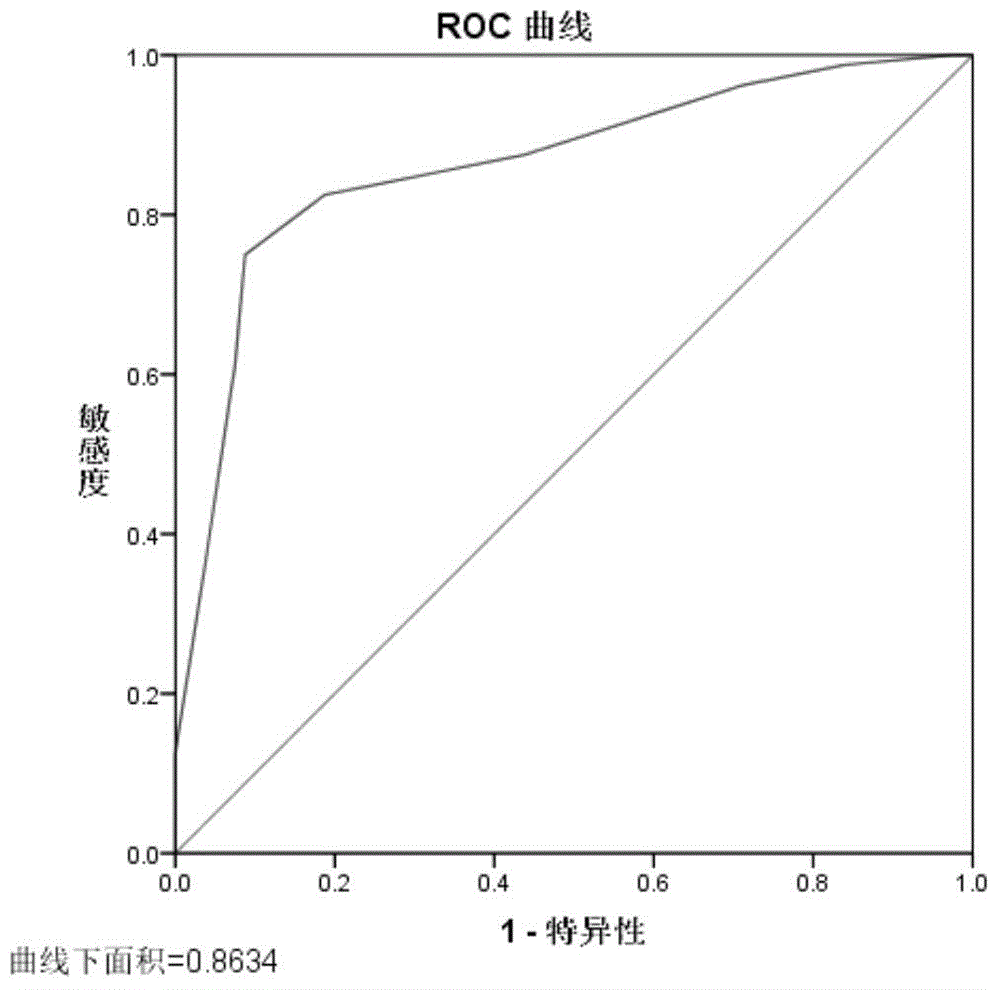
Mitochondria-related seminal plasma miRNAs taken as mankind severe asthenospermia markers, and applications thereof
ActiveCN105039530AConvenient for clinical operationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMir 101 3pNormal fertility
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and reproductive medicine, and discloses mitochondria-related seminal plasma miRNAs taken as mankind severe asthenospermia markers, and applications thereof. The markers are mitochondria-related miRNAs selected from hsa-miR-101-3p, hsa-miR-151a-5p, and hsa-let-7b-5p. The markers can be used for separating patients with severe asthenospermia from a control group with normal fertility, and can be used for preparing human severe asthenospermia diagnosis or monitor kits.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
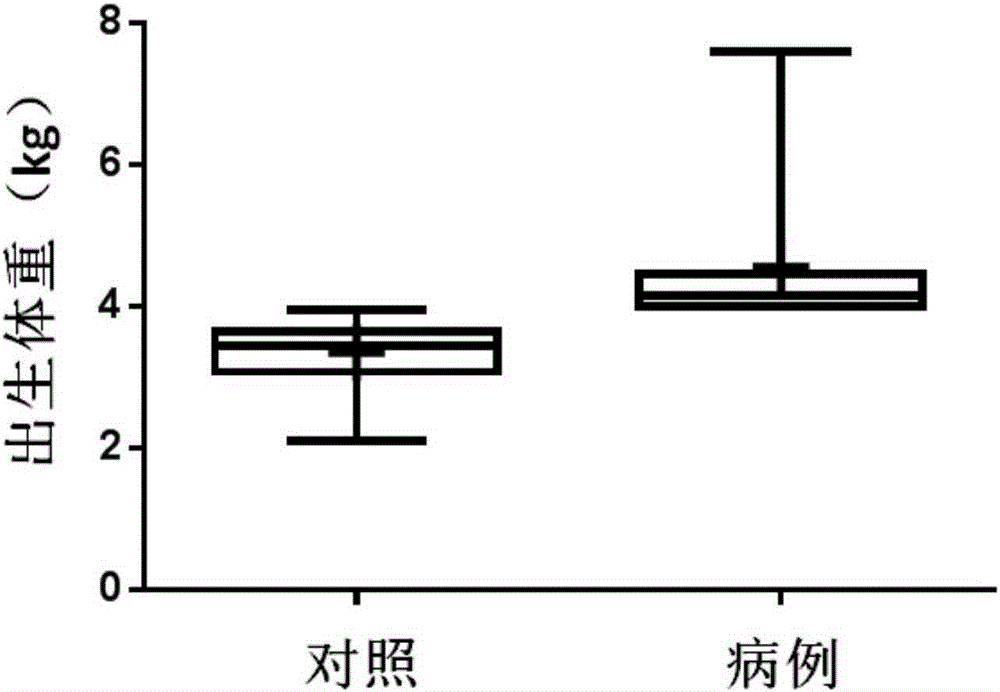
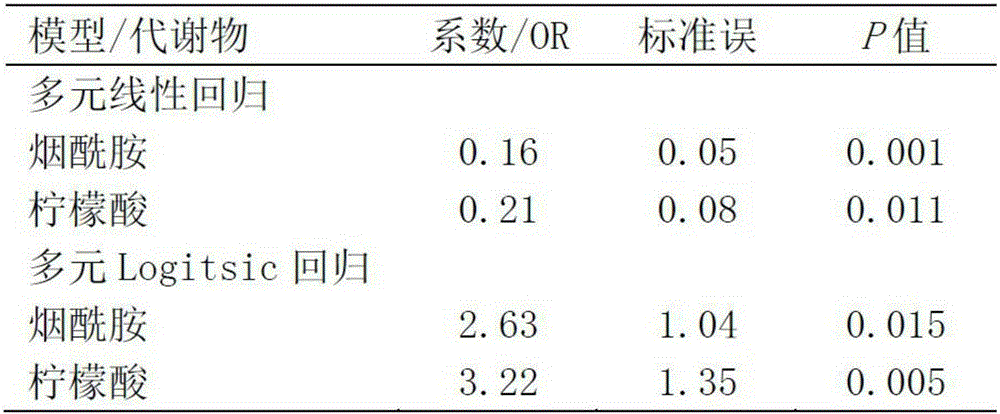
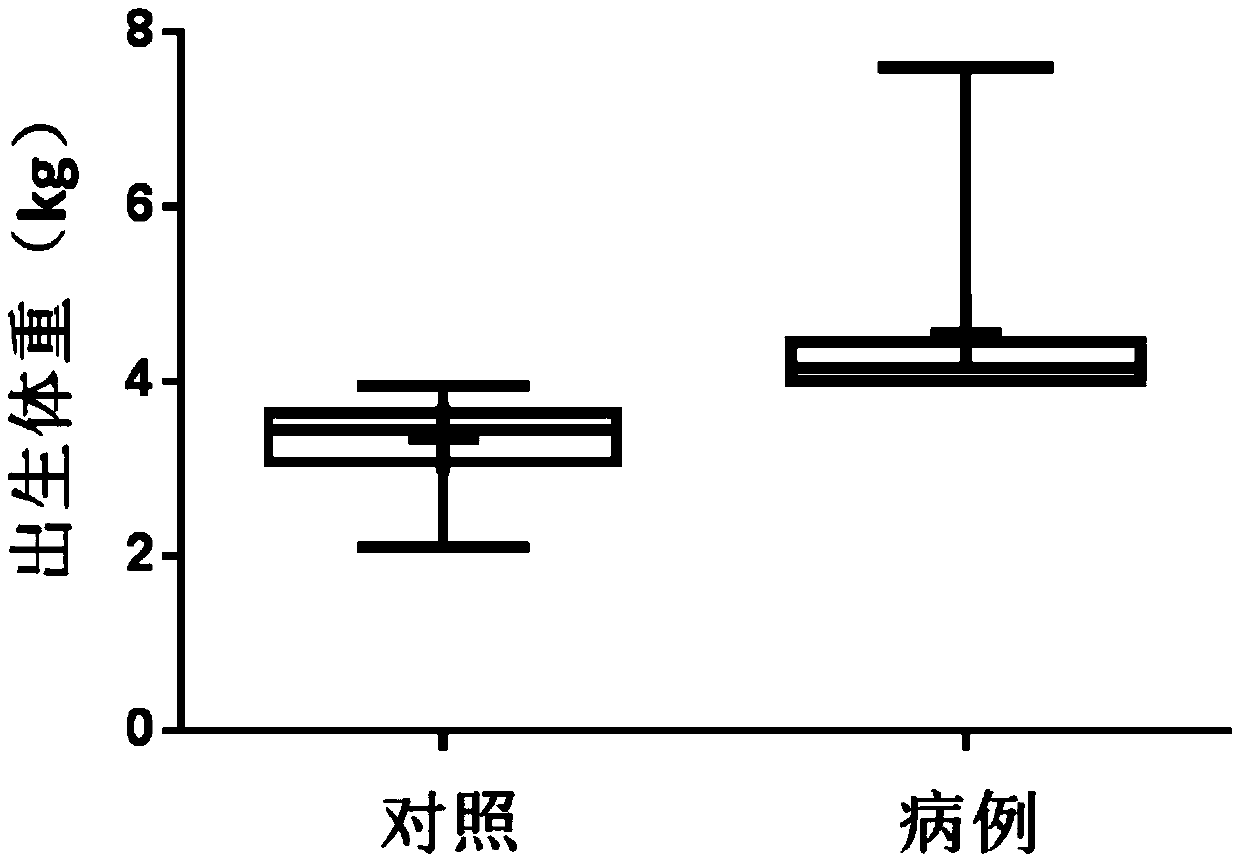
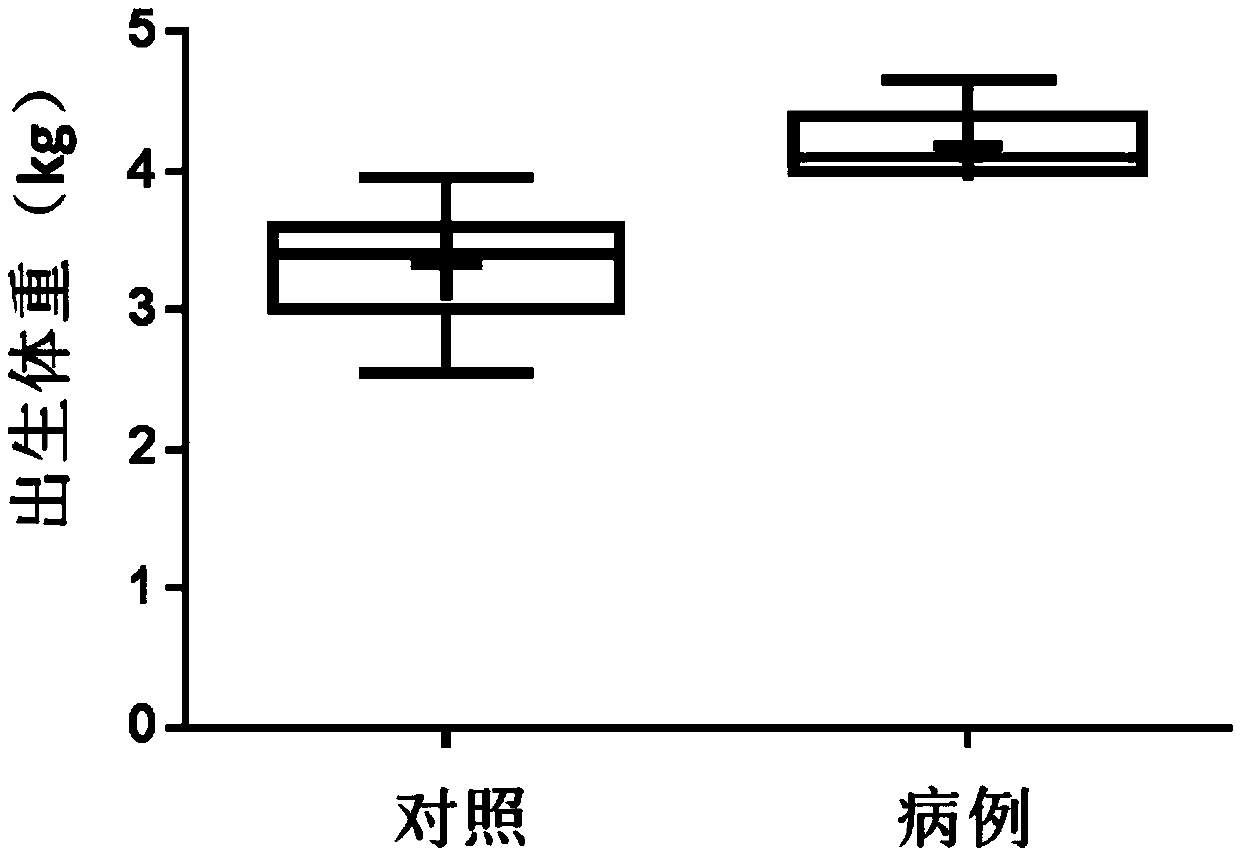
Fetal macrosomia auxiliary diagnostic marker and application thereof
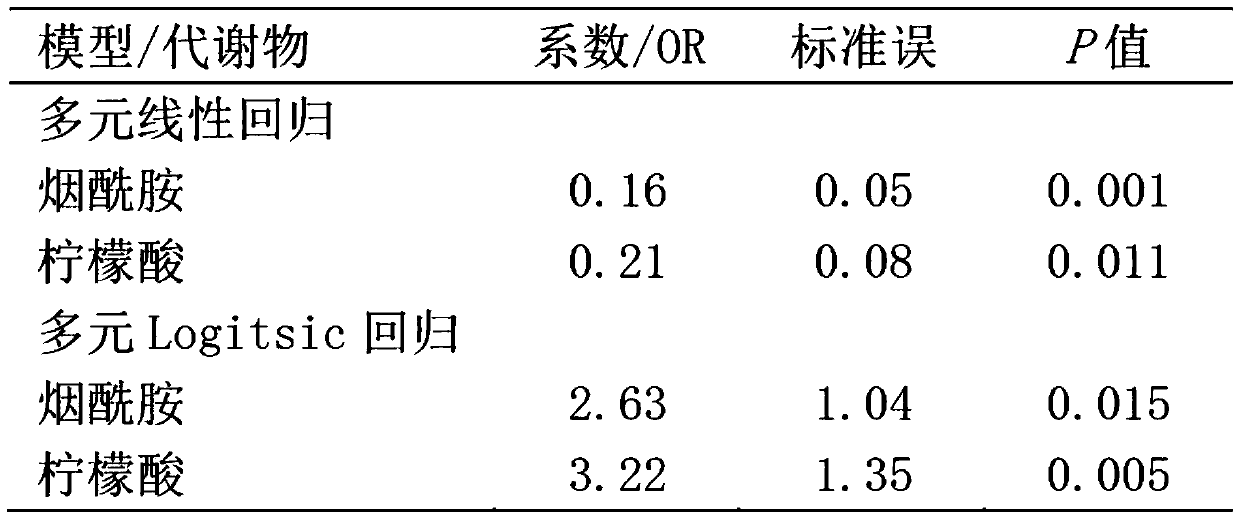
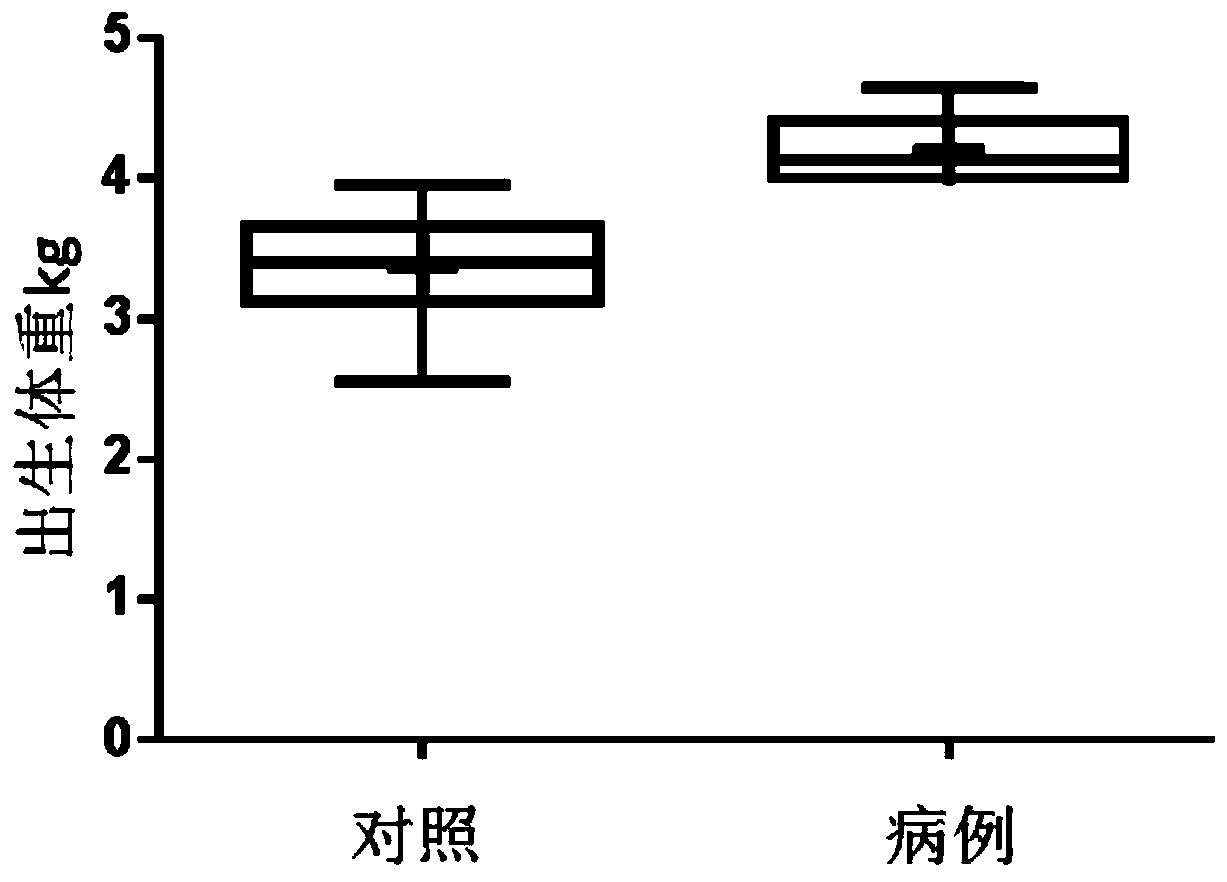
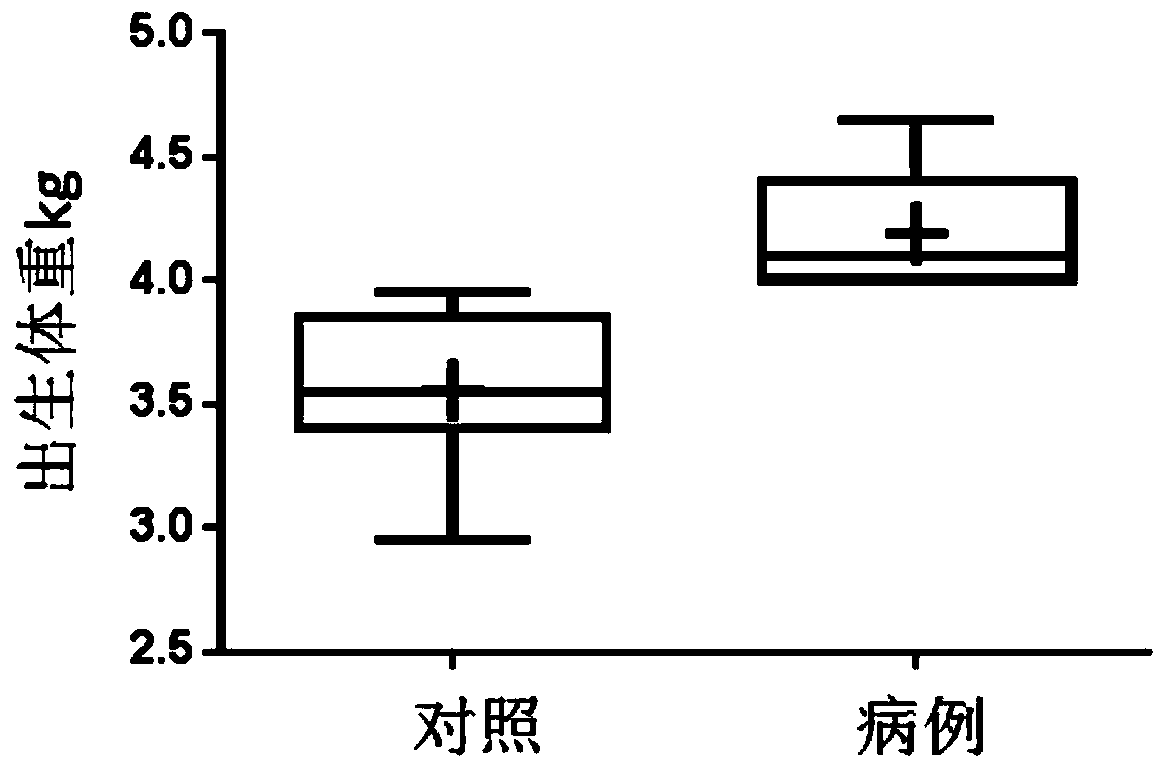
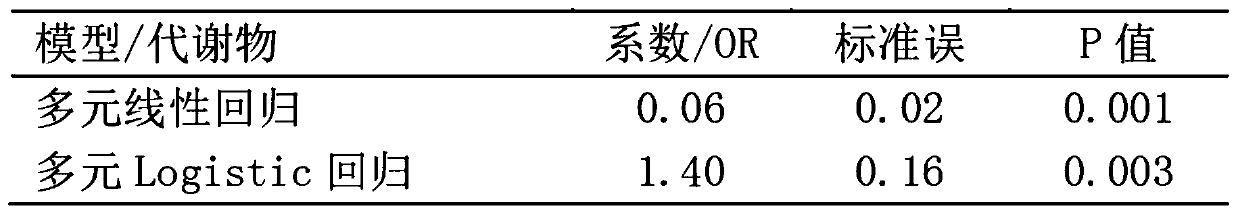
The invention belongs to the field of analytic chemistry and clinical medicine and discloses a fetal macrosomia auxiliary diagnostic marker and application thereof. The marker is the combination of nicotinamide and citric acid and can be used for manufacturing a fetal macrosomia diagnosing or monitoring kit. The marker has the better auxiliary diagnostic effect on fetal macrosomia, can lower the detection cost and reduce economical burdens of a patient and is beneficial to clinical usage and popularization.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
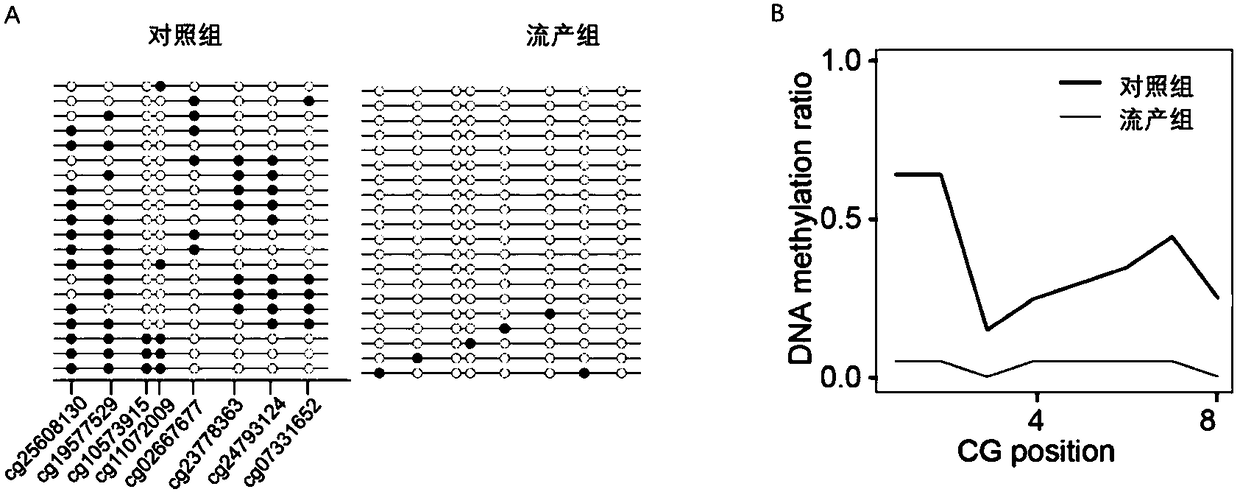
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) methylation marker for evaluating early abortion risk, primer and application thereof
ActiveCN108315410AEasy to detectQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTranscription initiationPRDM1
The invention belongs to the field of the genetic engineering, and particularly provides a blood DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) methylation marker for evaluating an early abortion risk, a primer and theapplication thereof. The DNA methylation marker comprises eight DNA methylation sites positioned near a PRDM1 gene transcription starting area: cg25608130, cg19577529, cg10573915, cg11072009, cg02667677, cg23778363, cg24793124 and cg07331652. The successful development of the category of the differentiated DNA methylation biological marker is the overturn of a traditional biomarker which gives a priority to protein, a brand new situation is started for diagnosing, preventing and curing the early abortion, and a reference is provided for researching the biomarkers of other diseases. The DNA methylation marker has the advantages of abundant raw materials and convenience in operation and is the biomarker with prospect.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Urine fatty acid metabolite marker related to idiopathic male infertility, as well as detection method and application thereof
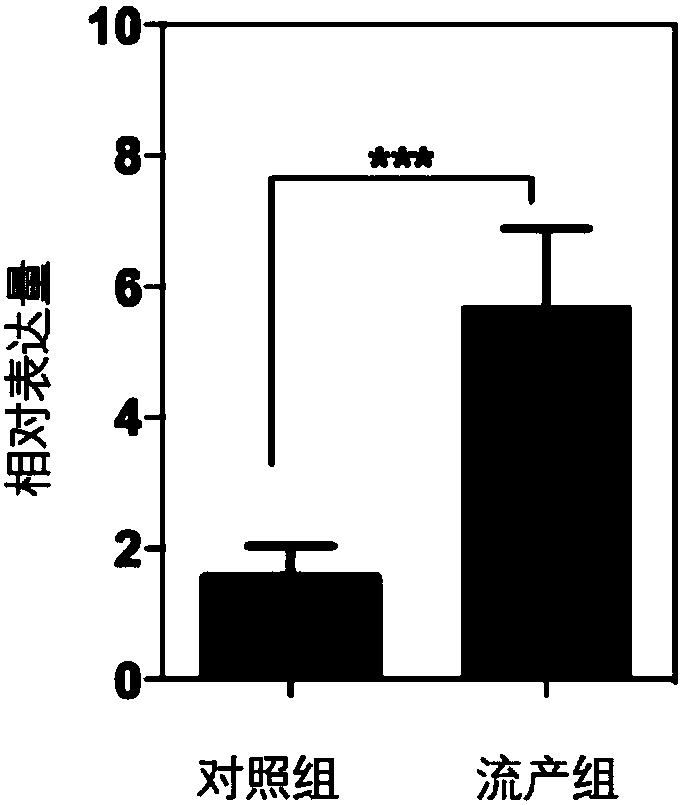
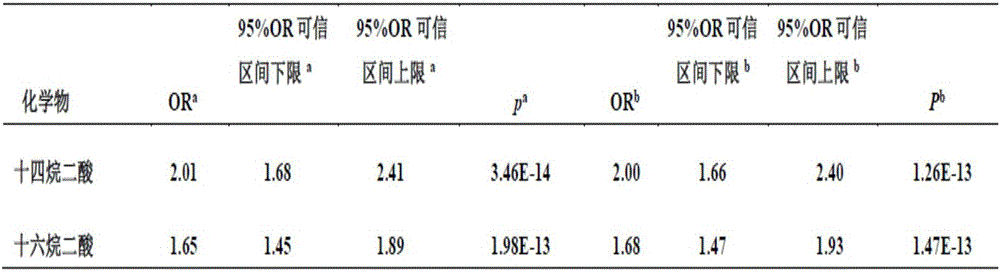
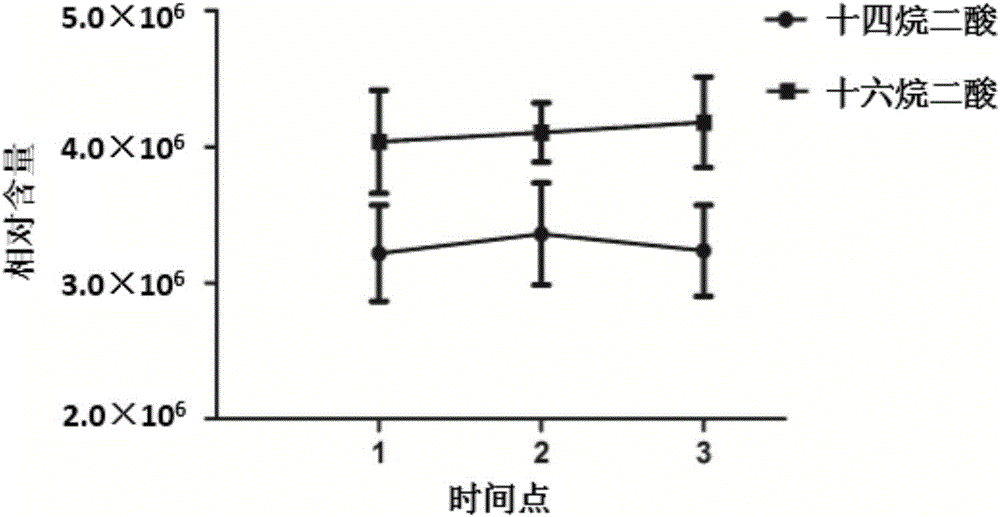
The invention belongs to the fields of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine, and discloses a urine fatty acid metabolite marker related to idiopathic male infertility, as well as a detection method and application thereof. The marker is urine fatty acid metabolites, namely, tetradecanedioic acid and / or hexadecanedioic acid, and is detected by adopting a UPLC-Q exactive MS method; the marker can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and monitoring of the idiopathic male infertility, has high sensitivity and specificity, and has a clinical popularization value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Idiopathic male infertility-related medium-chain fatty acid marker in serum and detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN106556655AEasy to monitorStrong associationComponent separationDisease diagnosisMale infertilityPhysiology
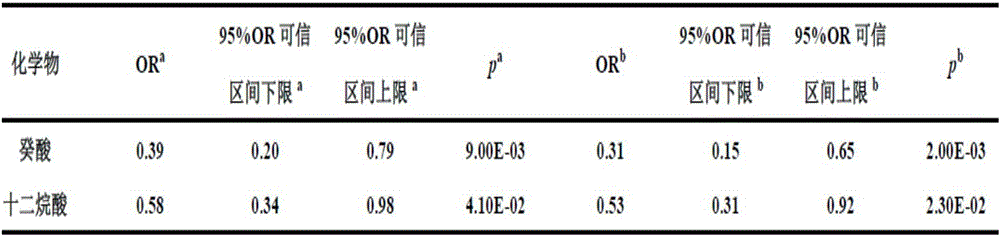
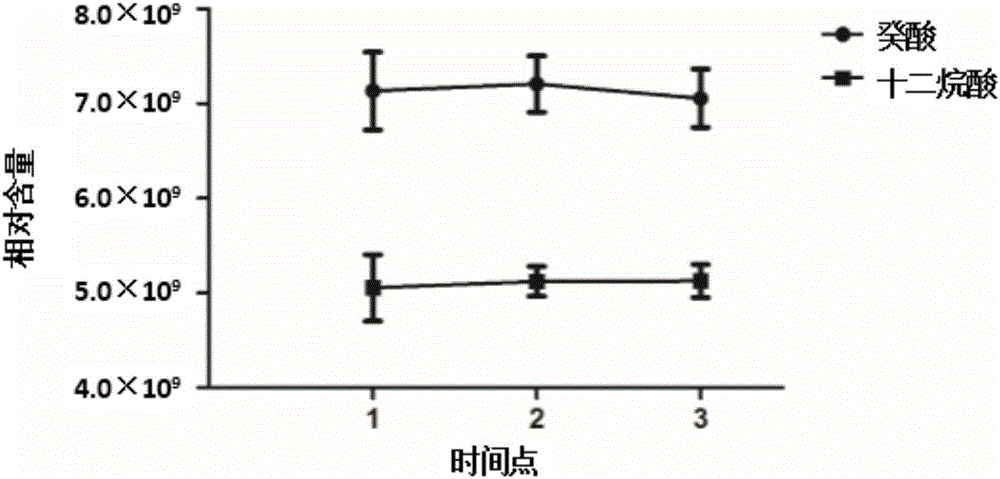
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine and discloses an idiopathic male infertility-related medium-chain fatty acid marker in serum and a detection method and application thereof. The marker is capric acid and / or lauric acid, and an UPLC-Q exactive MS method is adopted for detection. The marker can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and monitoring of idiopathic male infertility, has high sensitivity and specificity, and has clinic promotion value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Idiopathic male infertility-related seminal plasma metabolic small molecular marker as well as detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN106442770AEasy to monitorStrong associationComponent separationDisease diagnosisMale infertilityINFERTILITY MALE
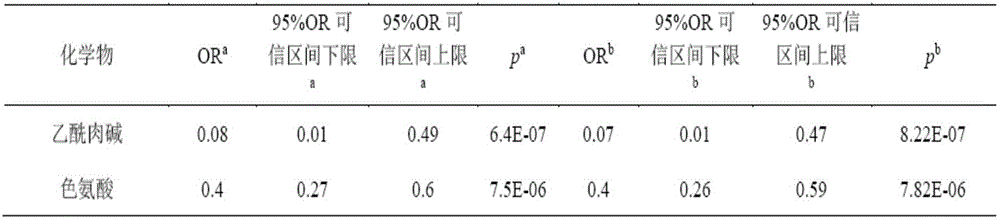
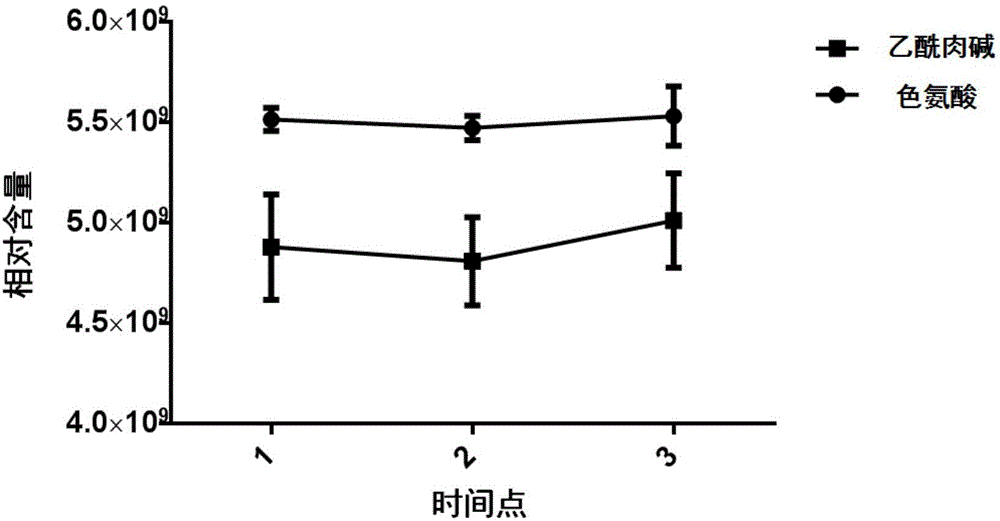
The invention belongs to the fields of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine, and discloses an idiopathic male infertility-related seminal plasma metabolic small molecular marker as well as a detection method and application thereof. The marker is prepared from seminal plasma metabolic small molecular acetylcarnitine and / or tryptophan, and is detected by adopting a UPLC-Q exactive MS method; the marker can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and monitoring of the idiopathic male infertility, and has higher sensitivity and specificity, thus having a clinical popularization value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Idiopathic male infertility related steroid hormone marker in serum, detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN106568852AEasy to aid in diagnosisEasy to monitorComponent separationMale infertilityPhysiology
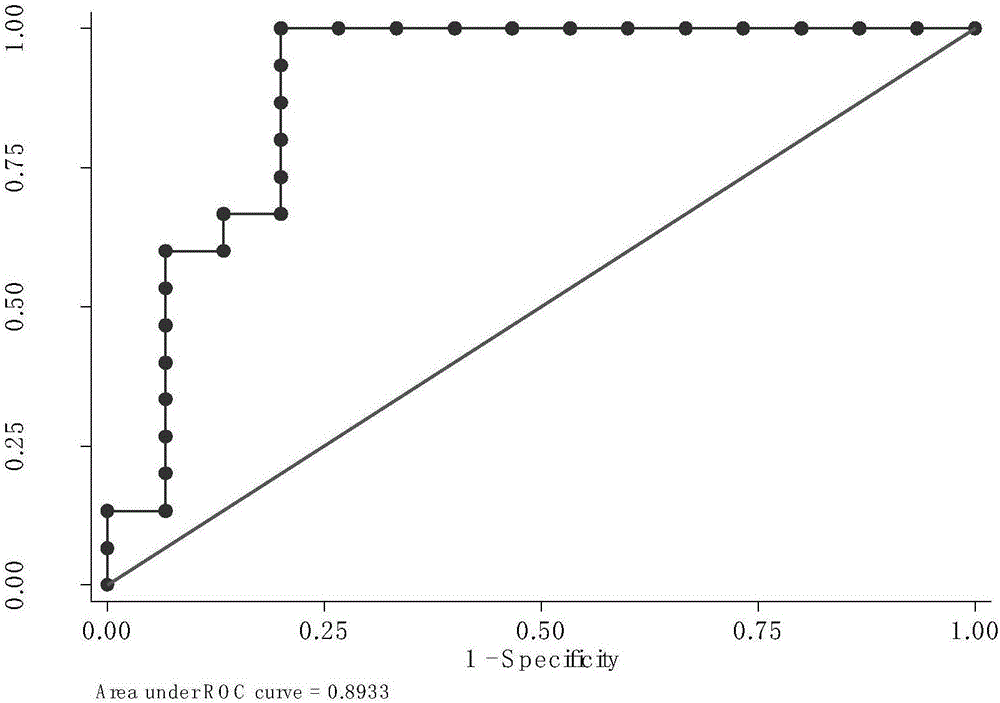
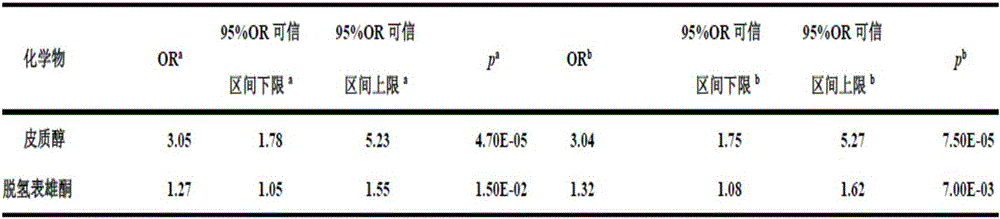
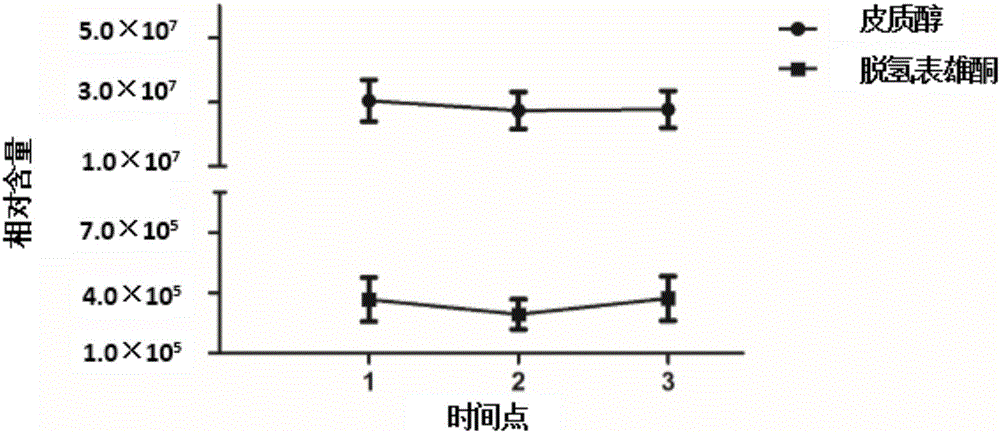
Belonging to the field of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine, the invention discloses an idiopathic male infertility related steroid hormone marker in serum, a detection method and application thereof. The marker is cortisol and / or dehydroepiandrosterone, a UPLC-Q exactive MS method is employed for detection, the marker can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and monitoring of idiopathic male infertility, has high sensitivity and specificity, and has clinical promotion value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
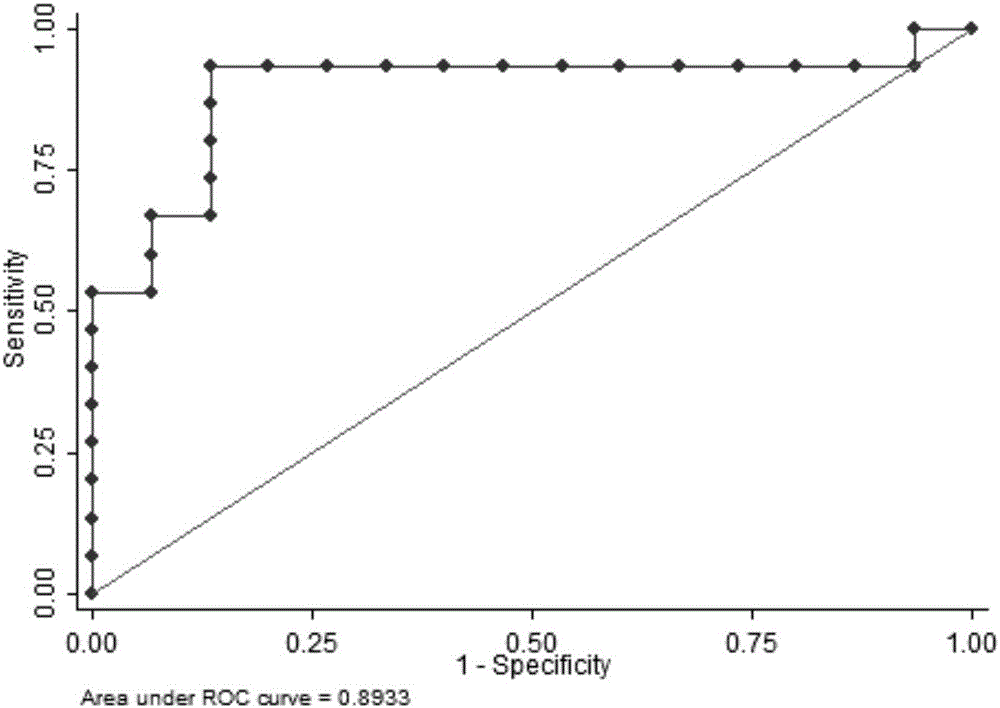
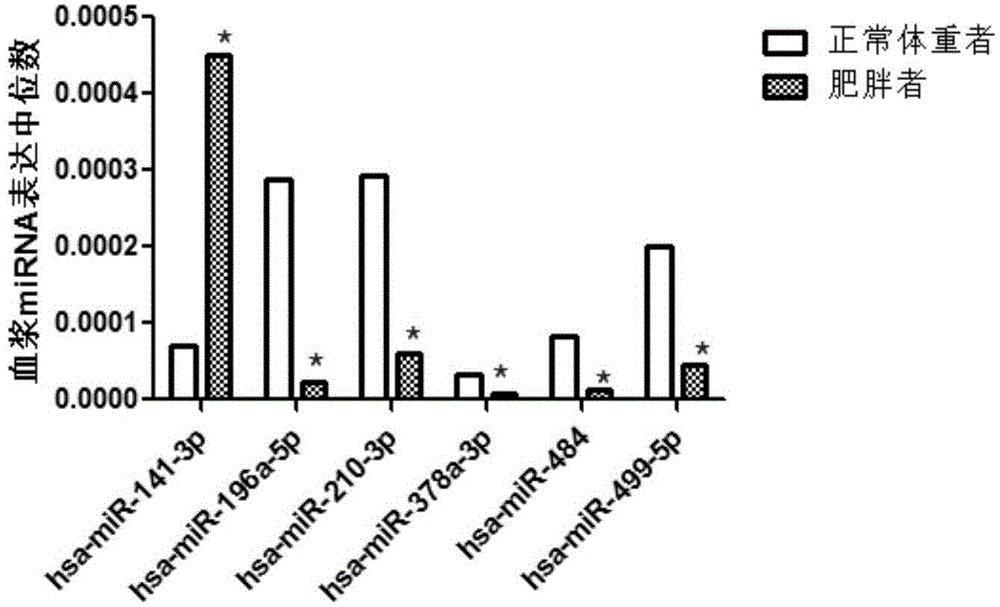
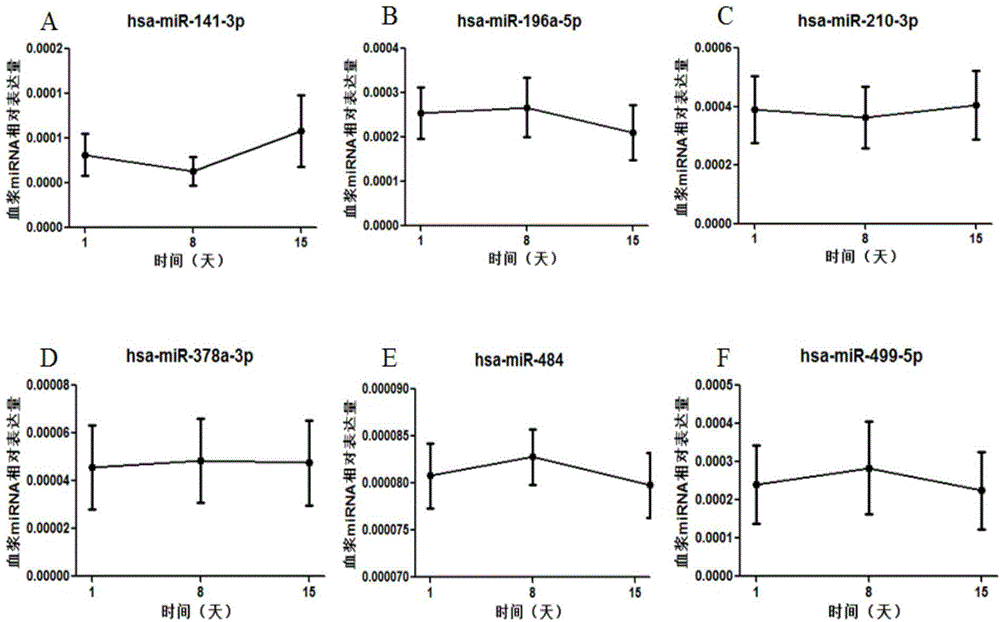
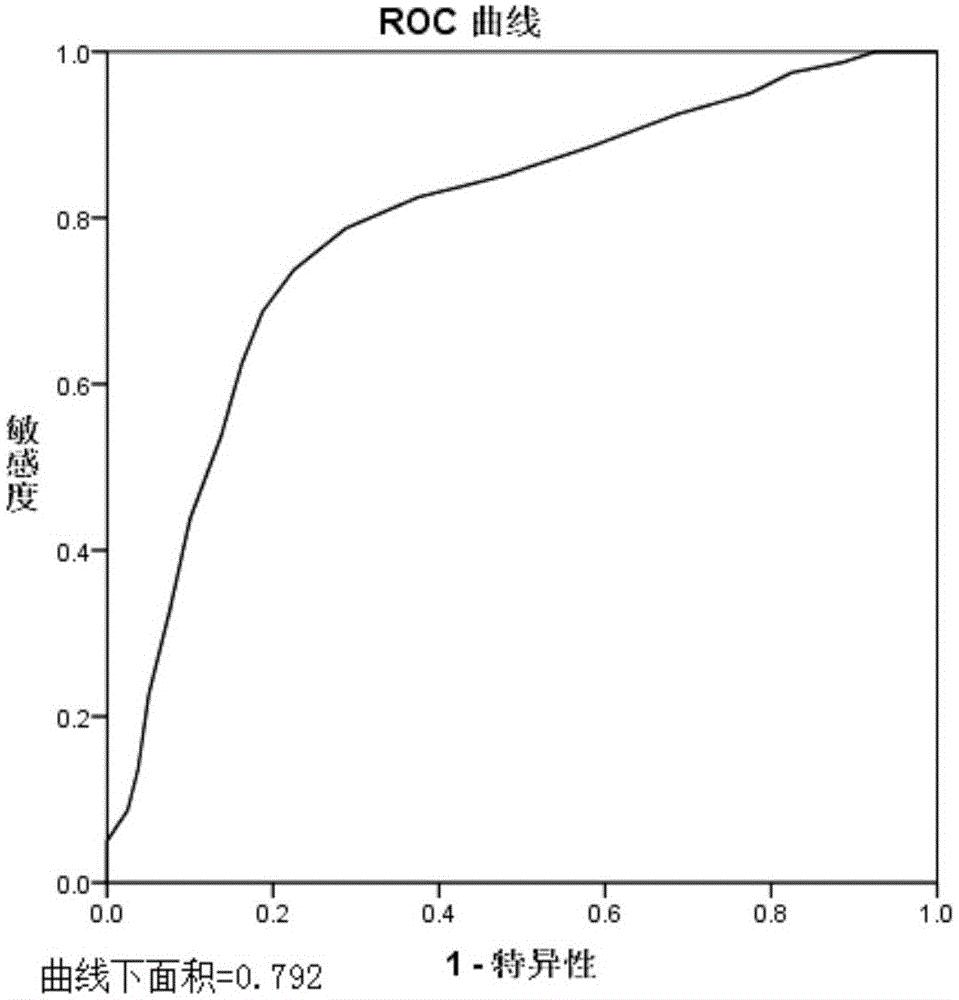
Mitochondrion correlation serum micro ribonucleic acid serving as markers of human obesity occurrence and application thereof
ActiveCN104946772AConvenient for clinical operationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSerum igeMir 196a
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and discloses mitochondrion correlation serum micro ribonucleic acid serving as markers of human obesity occurrence and application thereof. The markers are some miRNA which is mitochondrion correlation miRNA and is selected from hsa-miR-141-3p, hsa-miR-196a-5p, hsa-miR-210-3p, hsa-miR-378a-3p, hsa-miR-484 and hsa-miR-499a-5p. Obesity cases and normal body weight can be well contrasted and separated, and the markers can be used for preparing obesity diagnosing or monitoring kits.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
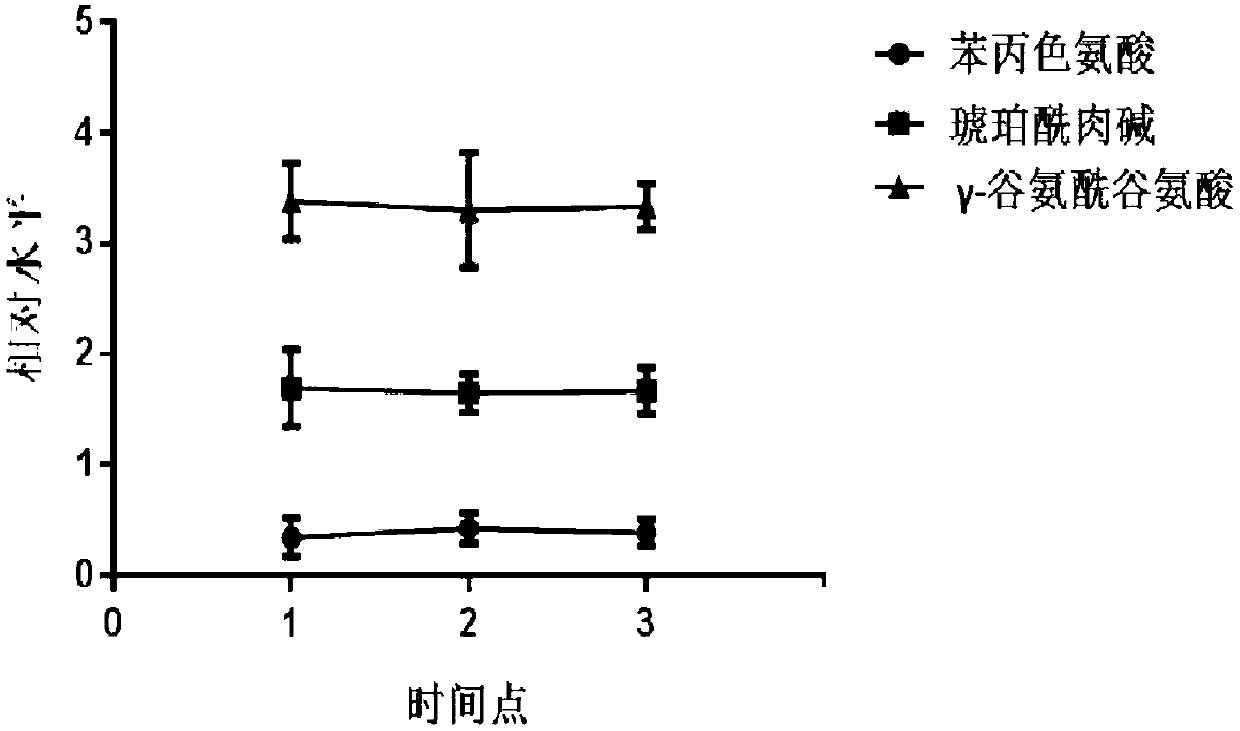
Plasma metabolism micromolecular marker related to human intestinal canal aganglionosis and application of plasma metabolism micromolecular marker
ActiveCN103278579AEasy to detectImprove sensitivity and specificityComponent separationTryptophanCHEMISTRY METHODS
The invention belongs to the fields of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine and discloses a plasma metabolism micromolecular marker related to human intestinal canal aganglionosis and an application of the plasma metabolism micromolecular marker. The plasma metabolism micromolecular marker is one or more than one of phenylpropyl tryptophan, succinyl carnitine and gamma-glutamoyl glutamic acid. The plasma metabolism micromolecular marker has specificity and sensibility on intestinal canal aganglionosis. A kit provided by the invention adopts UPLC-MS (ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry) and can accurately detect phenylpropyl tryptophan, succinyl carnitine and gamma-glutamoyl glutamic acid in plasma, better auxiliary information can be provided for diagnosing intestinal canal aganglionosis, invasive diagnosis can be avoided, screening and diagnosis can be carried out in early stage, repeated detection can be realized, and dynamic monitoring is easy to realize.
Owner:夏彦恺
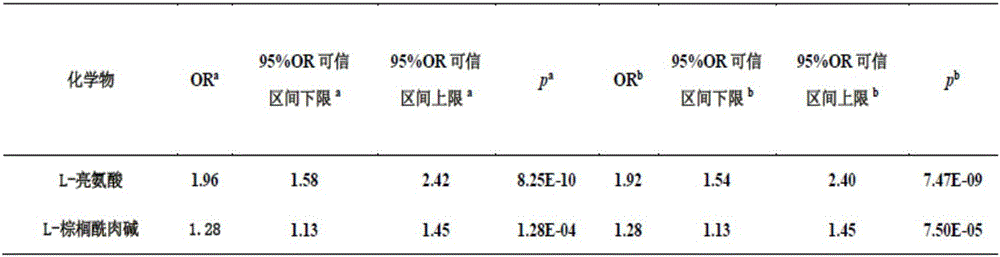
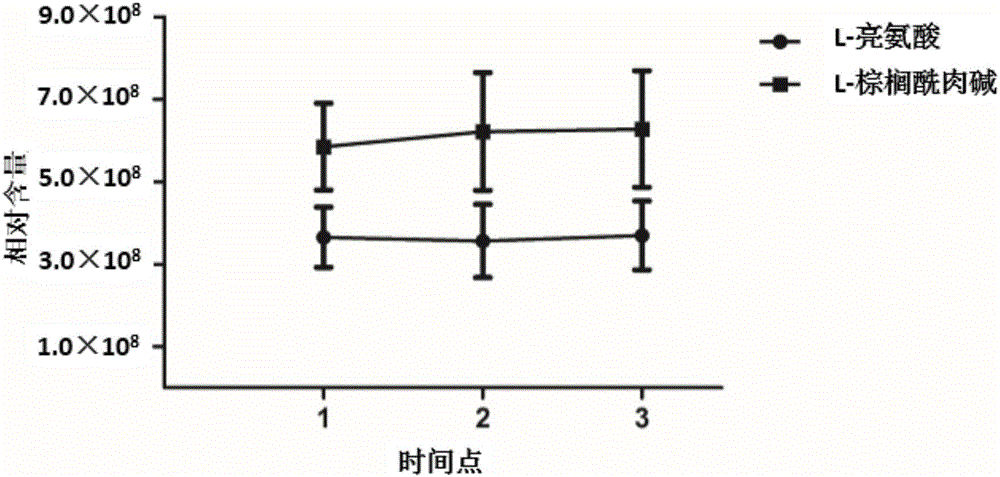
Metabolism marker related to idiopathic male infertility in urine, and detection method and application thereof
ActiveCN106198815AConvenient for clinical operationStrong associationComponent separationMale infertilityTert-leucine
The invention belongs to the field of analytic chemistry and clinical medicine, and discloses a metabolism marker related to idiopathic male infertility in urine, and a detection method and application thereof. The metabolism marker is L-leucine and / or L-palmitoyl carnitine, is detected by adopting UPLC-Qexactive MS method, can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and monitoring of idiopathic male infertility, has higher sensitivity and specificity, and has a clinical spread value.
Owner:NANJING HANWEI PUBLIC HEALTH RES INST CO LTD
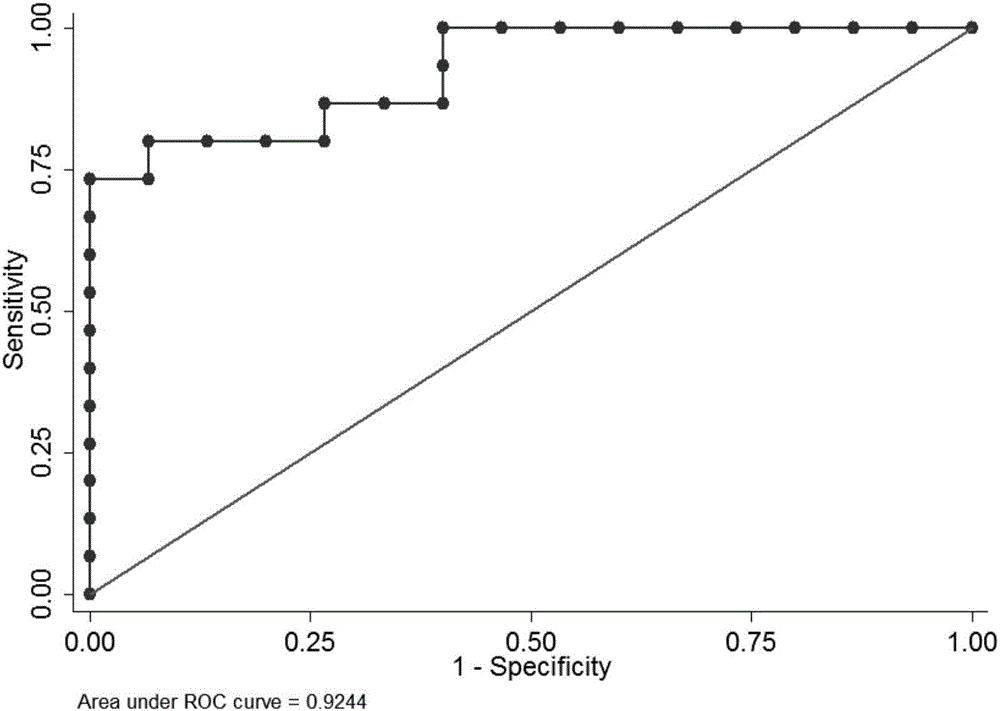
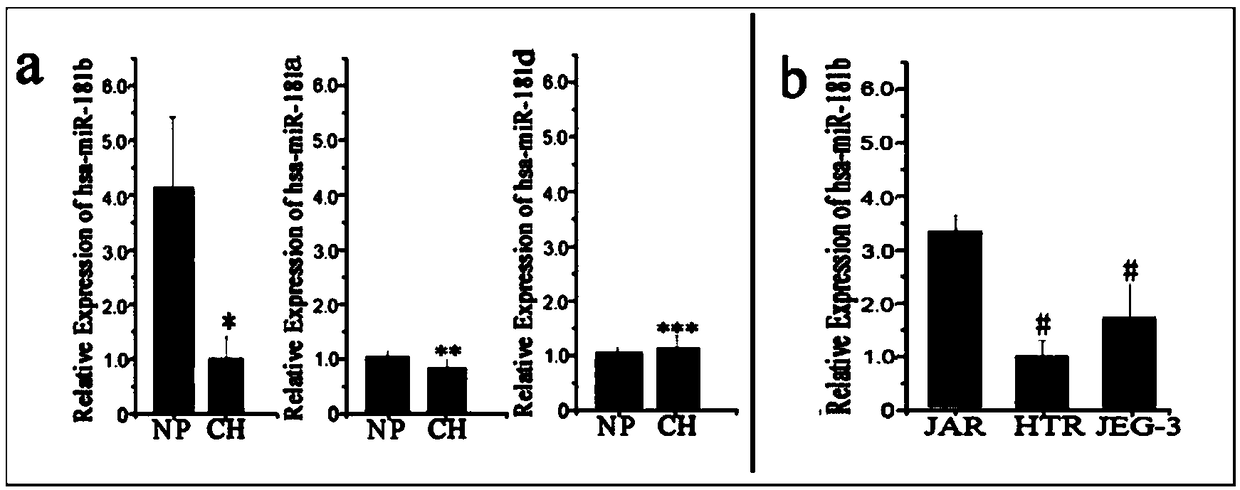
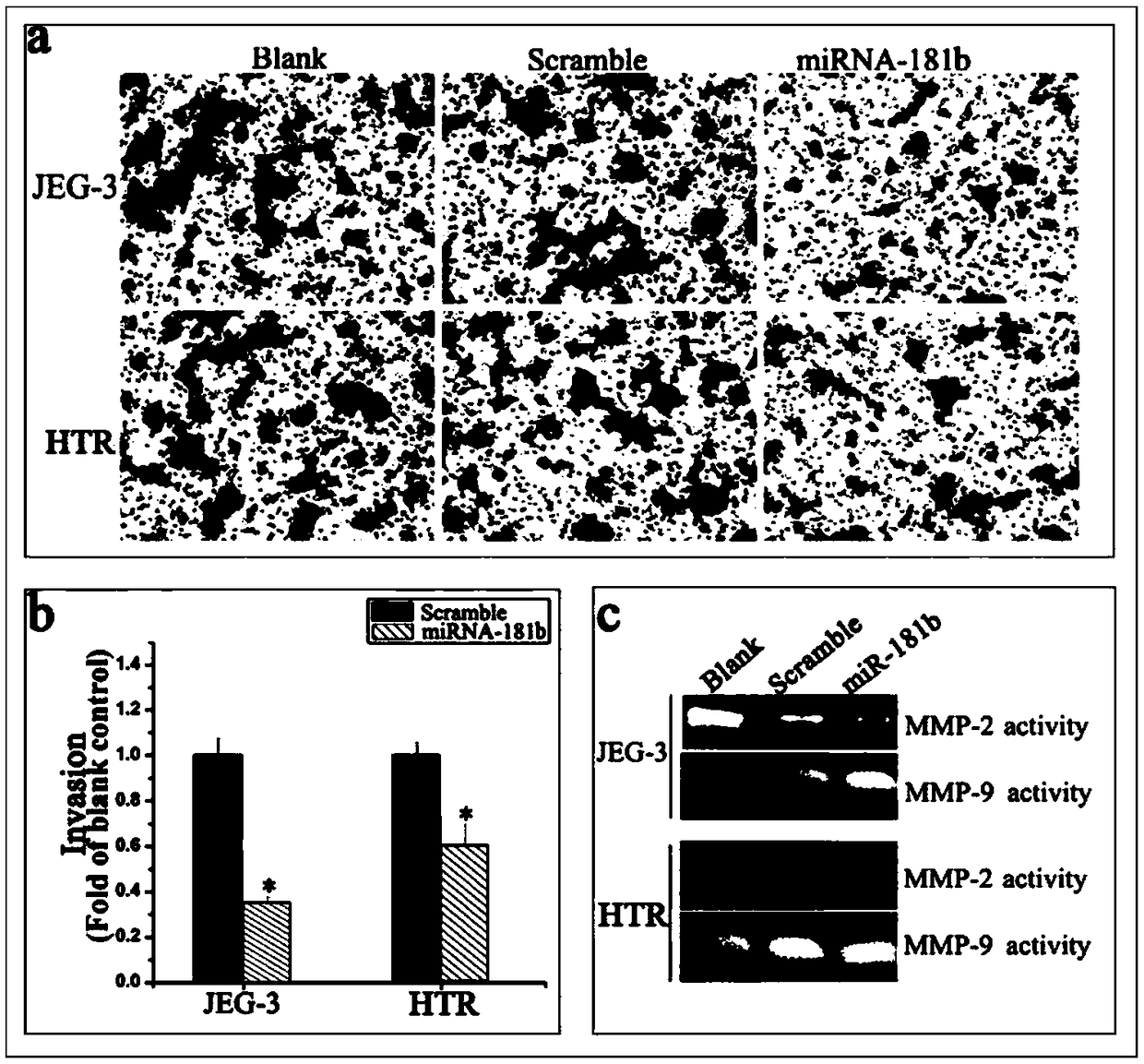
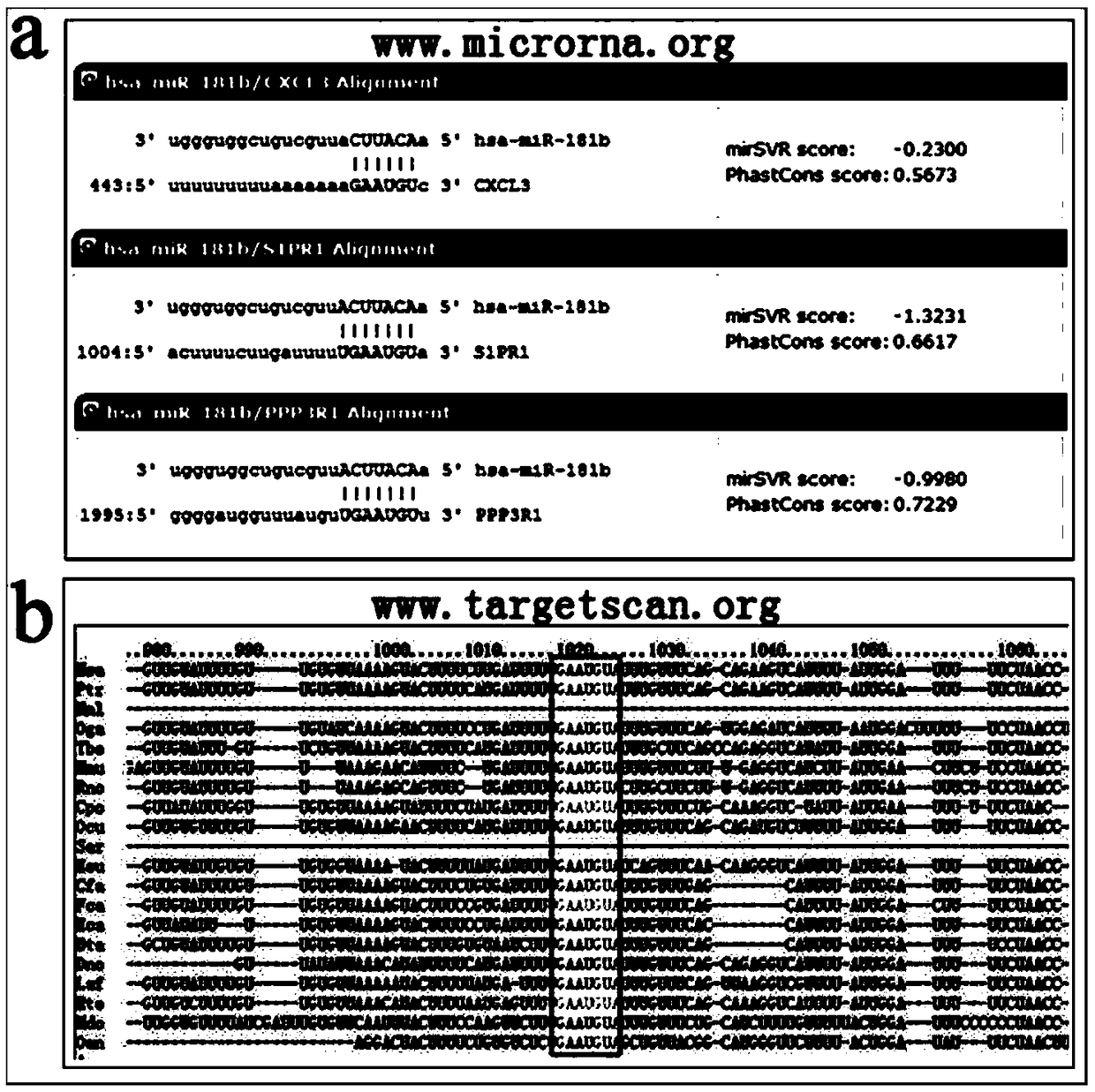
Biomarker for abnormal invasion of trophoblast cells and application thereof
ActiveCN108949973AEasy to detectQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePregnancy
The invention relates to a biomarker for abnormal invasion of trophoblast cells and application thereof. It is proved that miR-181b is generally and differentially expressed in pregnancy-related disease tissue with abnormal trophoblast invasion, and S1PR1 is a direct effect target gene of miR-181b; and the discovery of the influence of a miR-181b-S1PR1 pathway on the molecular mechanism of the invasion ability of trophoblast cells provides new clues and potential intervention targets for the prevention and treatment of pregnancy-related diseases caused by abnormal trophoblast invasion.
Owner:NANJING MATERNITY & CHILD HEALTH CARE HOSPITAL
Serum messenger ribonucleic acid biomarker for diagnosing recurrent spontaneous abortion, primer set and application and kit
ActiveCN108486241AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSerum igeNucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a serum messenger ribonucleic acid biomarker for diagnosing recurrent spontaneous abortion, a primer set and application and akit. The serum messenger ribonucleic acid biomarker comprises at least one of first mRNA with 90% or more of homology with a nucleotide sequence shown by a SEQ ID NO: 1, second mRNA with 90% or moreof homology with a nucleotide sequence shown by a SEQ ID NO: 2 and third mRNA with 90% or more of homology with a nucleotide sequence shown by a SEQ ID NO: 3. Serum mRNA is a novel biomarker which isstable, minimally invasive, easy to detect and quantitatively accurate, and can greatly improve the sensitivity and specificity of recurrent spontaneous abortion diagnosis.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
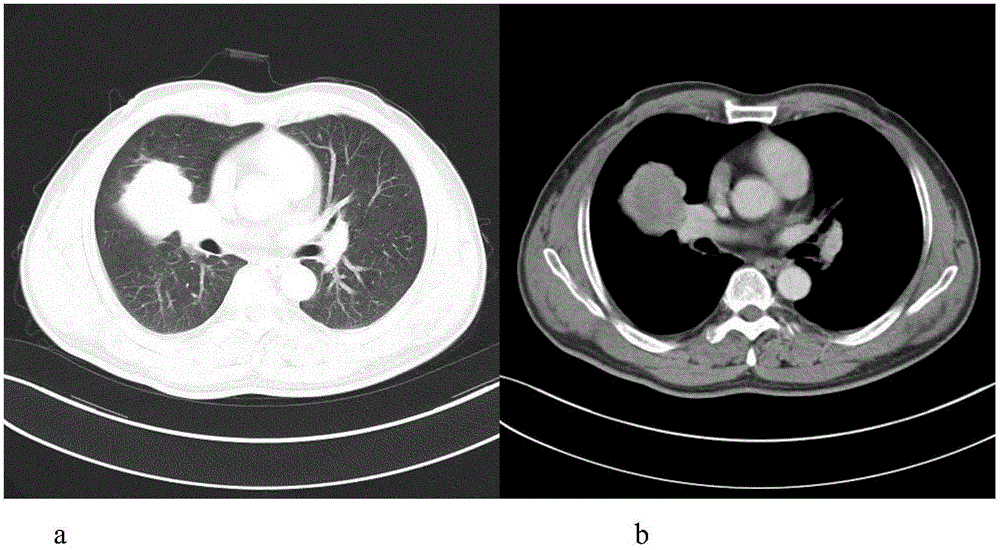
Plasma metabolization micromolecule marker related to human non-small-cell lung cancer and application of plasma metabolization micromolecule marker
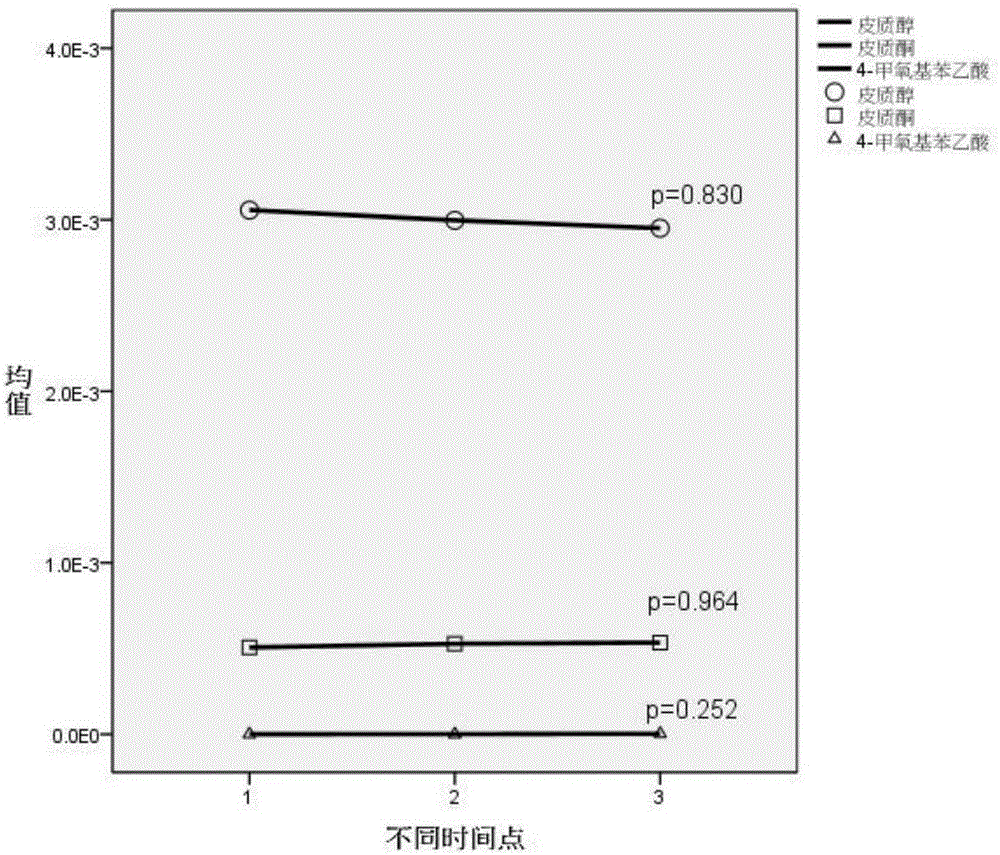
InactiveCN105203683ARepair inhibitionIncrease contractilityComponent separationMetaboliteConfidence interval
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine and relates to a plasma metabolization micromolecule marker related to the human non-small-cell lung cancer and an application of the plasma metabolization micromolecule marker. The plasma metabolization micromolecule marker related to the human non-small-cell lung cancer is one or more of cortisol, corticosterone and 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid. The plasma metabolization micromolecule marker is prepared from cortisol, corticosterone and 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid. The content range (95% confidence interval) of cortisol is 0.00018-0.00067, the content range (95% confidence interval) of corticosterone is 0.000029-0.00010, the content range (95% confidence interval) of 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid is 0.000015-0.000022, and metabolite can prompt occurrence of tumors within the ranges. The horizontal range, corresponding to a normal group, of cortisol is 0.0030-0.0037, the horizontal range, corresponding to the normal group, of corticosterone is 0.00044-0.00056, and the horizontal range, corresponding to the normal group, of 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid is 7.39 E-07-2.09 E-06. The plasma metabolization micromolecule marker is a novel biomarker, compared with a traditional protein biomarker, the relevance between the marker and the disease outcome is higher, and the plasma metabolization micromolecule marker is stable, minimally invasive, easy to detect and accurate in quantitation.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL
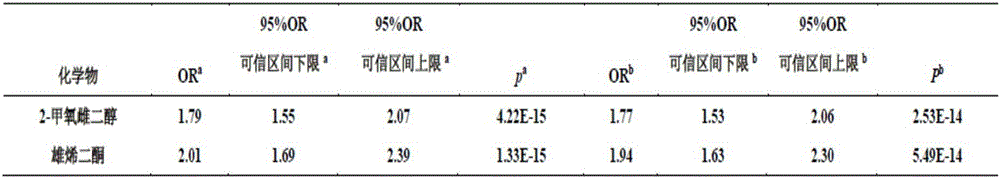
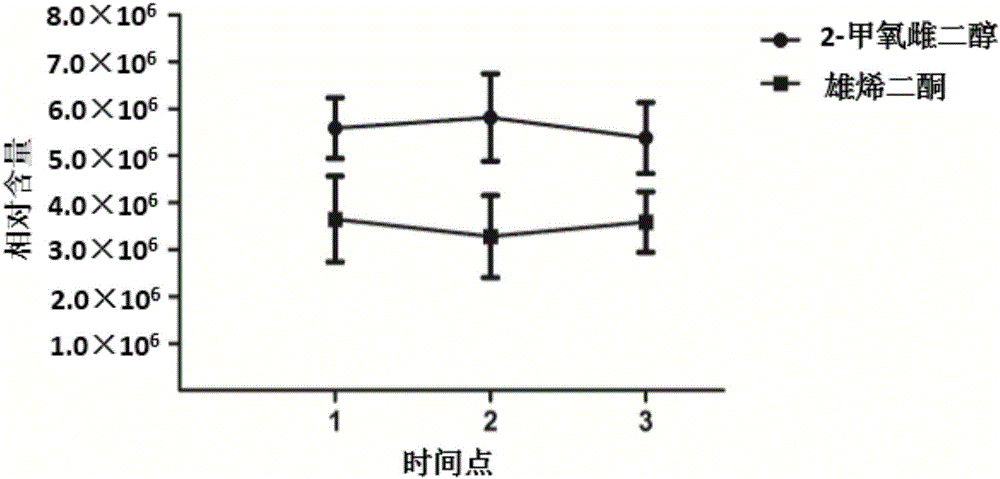
Urine estrogen metabolite markers related to idiopathic male infertility and the detection methods and application
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine and discloses the urine estrogen metabolite markers related to idiopathic male infertility and the detection methods and application. The marker is the urine estrogen metabolite 2-methoxyestradiol and / or androstenedione and detected by UPLC Q exactive MS method. The urine estrogen metabolite markers related to idiopathic male infertility can be used for auxiliary diagnosis and monitoring of idiopathic male infertility, and has high sensitivity, specificity, and clinical spread value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
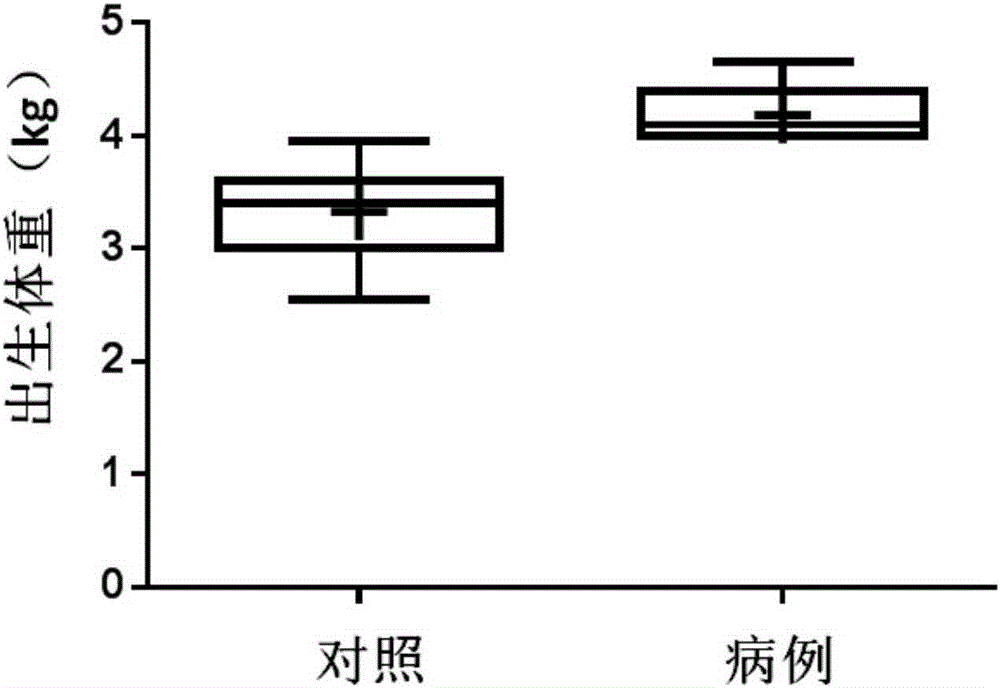
Capric acid and prostaglandin E2 combination as giant baby auxiliary diagnosis marker and application thereof
ActiveCN107576747AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresComponent separationCapric AcidAIDS diagnosis
The invention belongs to the fields of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine, and discloses a capric acid and prostaglandin E2 combination as a giant baby auxiliary diagnosis marker and the application thereof. The auxiliary diagnosis marker is a combination of micromolecular capric acid and prostaglandin E2, can be used for preparing a giant baby auxiliary diagnosis or monitoring kit, is relatively high in sensitivity and specificity and rapid in detection, and has a relatively high clinical application value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Plasma miRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) marker associated with common type congenital intestinal canal total colonic aganglionosis and application thereof
ActiveCN103805603AEasy to monitorHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDynamic monitoringBlood plasma
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and clinical medicines, and discloses a plasma miRNA (micro ribonucleic acid) marker associated with common type congenital intestinal canal total colonic aganglionosis and an application thereof. The marker is selected from more of hsa-miR-31, hsa-miR-147 and hsa-miR-206. The marker has specificity and sensitivity to the common type congenital intestinal canal total colonic aganglionosis, can be used for the preparation of reagents for diagnosing or monitoring the common type congenital intestinal canal total colonic aganglionosis, can avoid invasive diagnosis, can be used for screening and diagnosis in an early stage, and can be used for detecting repeatedly and is easy for dynamic monitoring.
Owner:NANJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
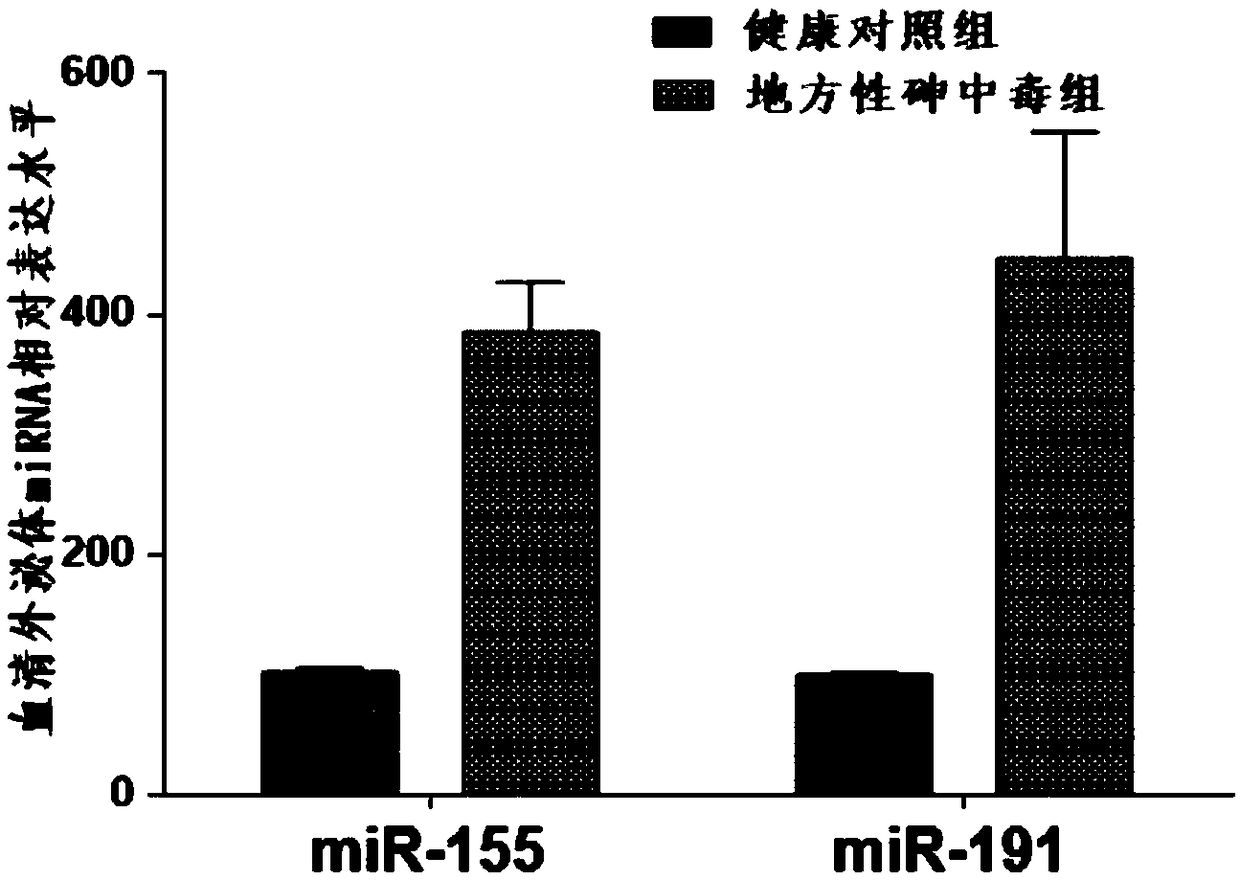
Application of serum exosome miRNAs marker to early diagnosis of endemic arsenism
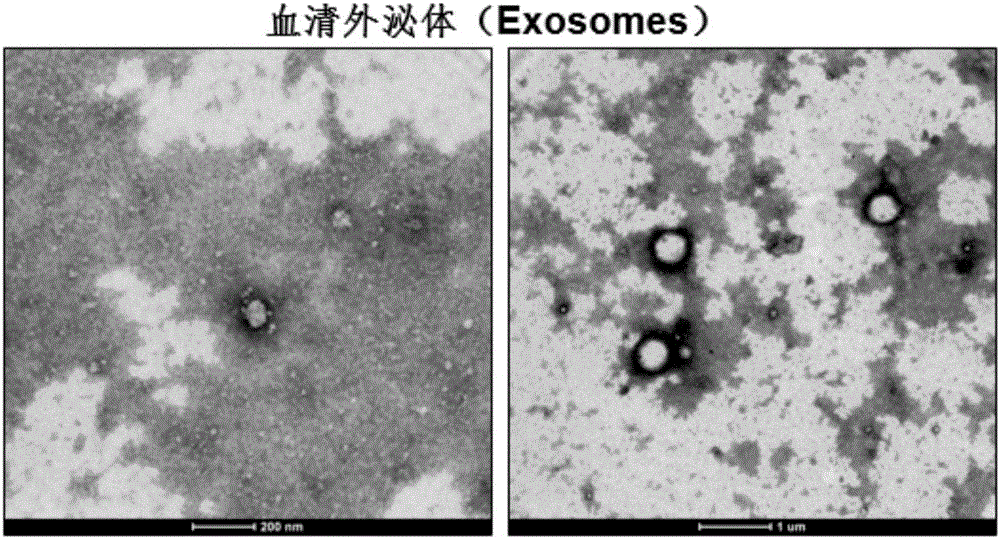
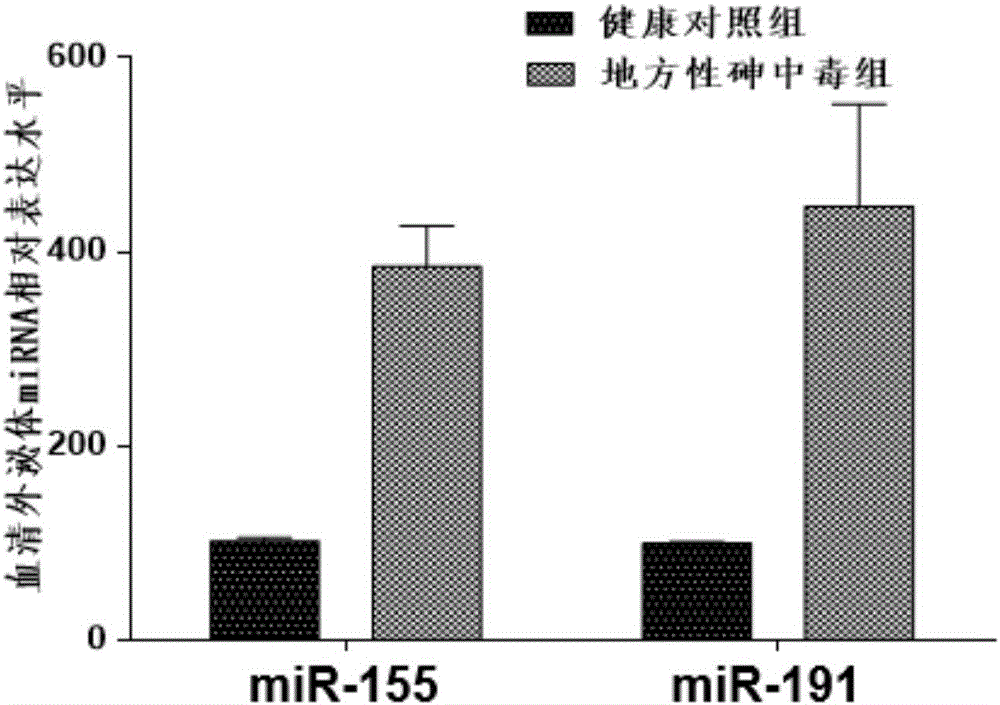
InactiveCN106435004AEasy extractionReduce the amount of serum drawnMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSerum igeExosome
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and clinical medicine and particularly relates to an endemic arsenism early diagnosis associated serum exosome miRNAs marker and application thereof. The marker is a combination of has-miR-155 and has-miR-191. The marker and a primer thereof can be used for preparation of a kit for early diagnosis of endemic arsenism.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
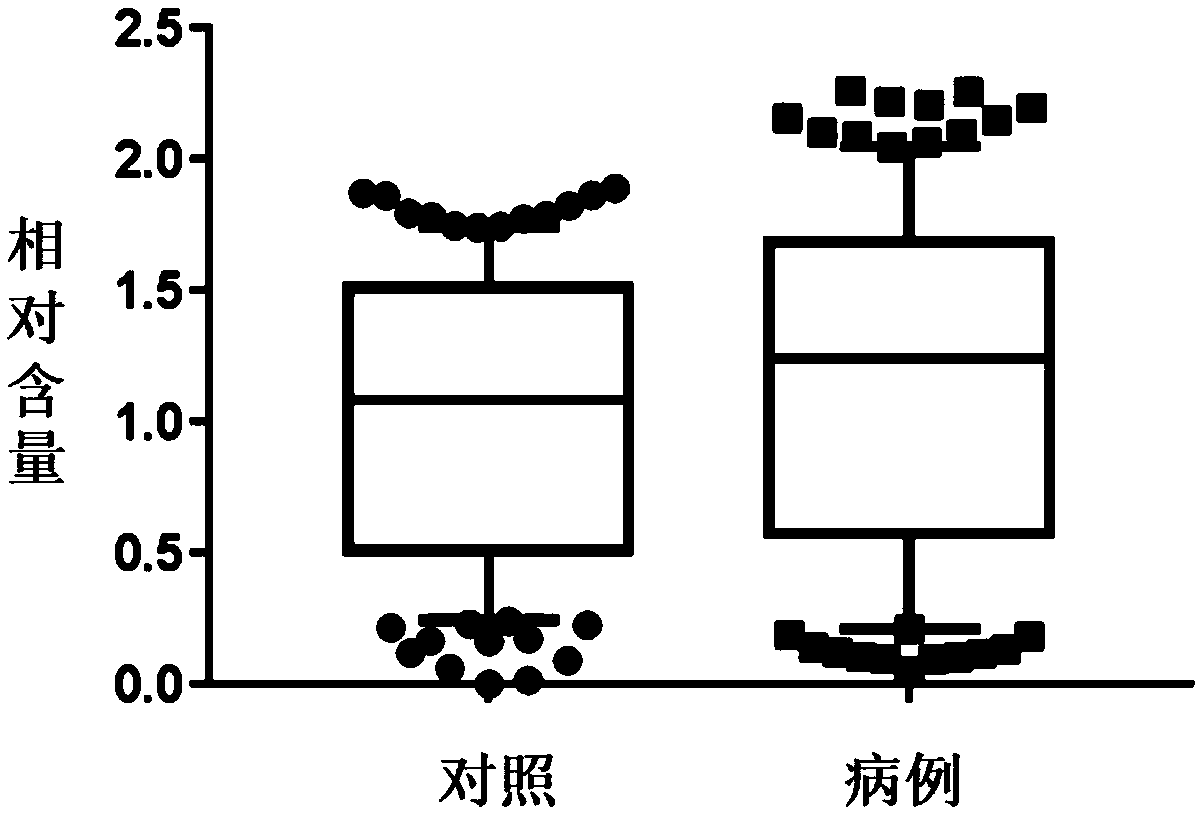
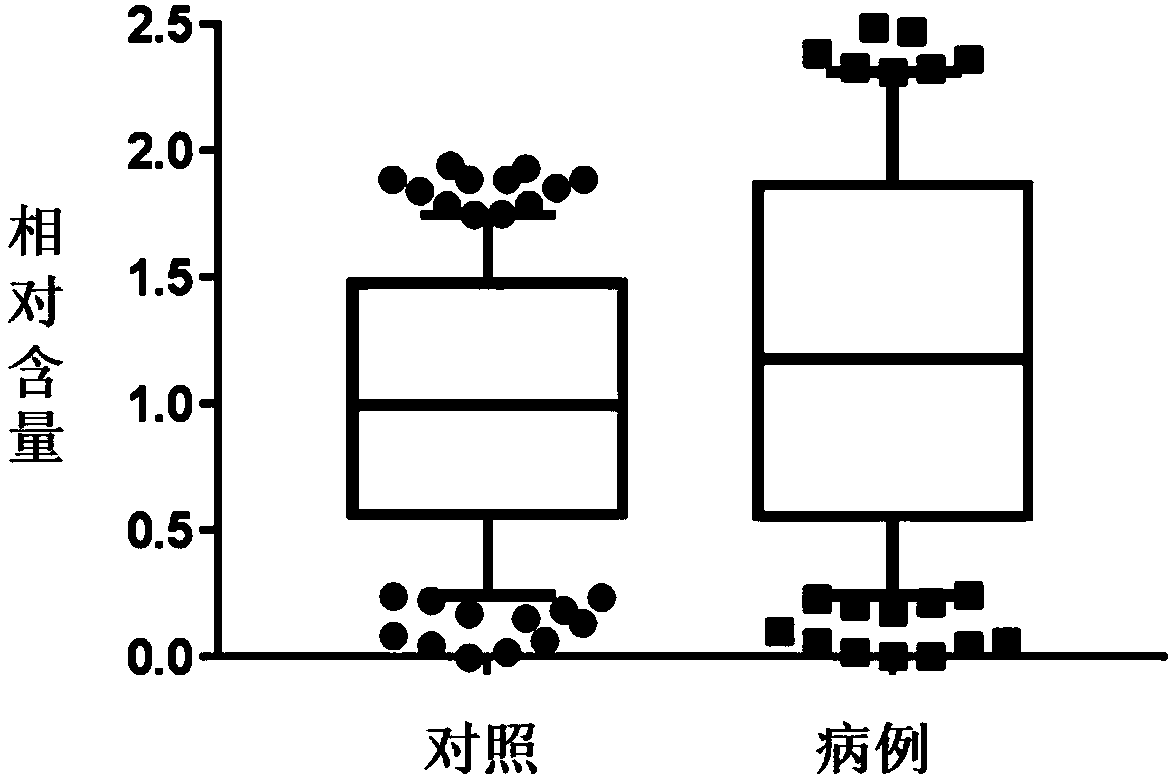
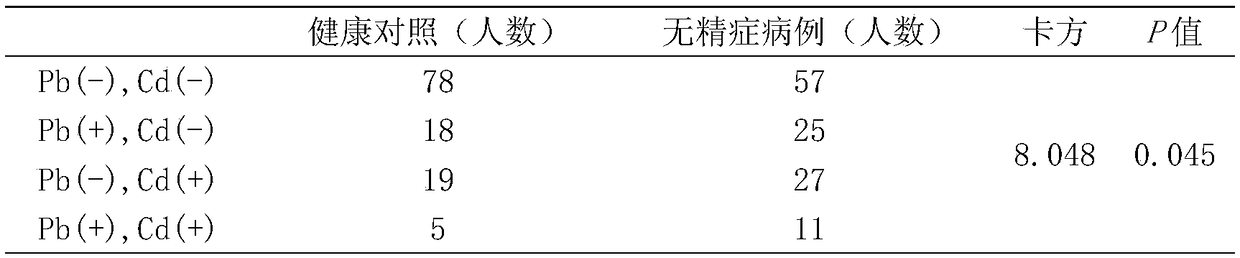
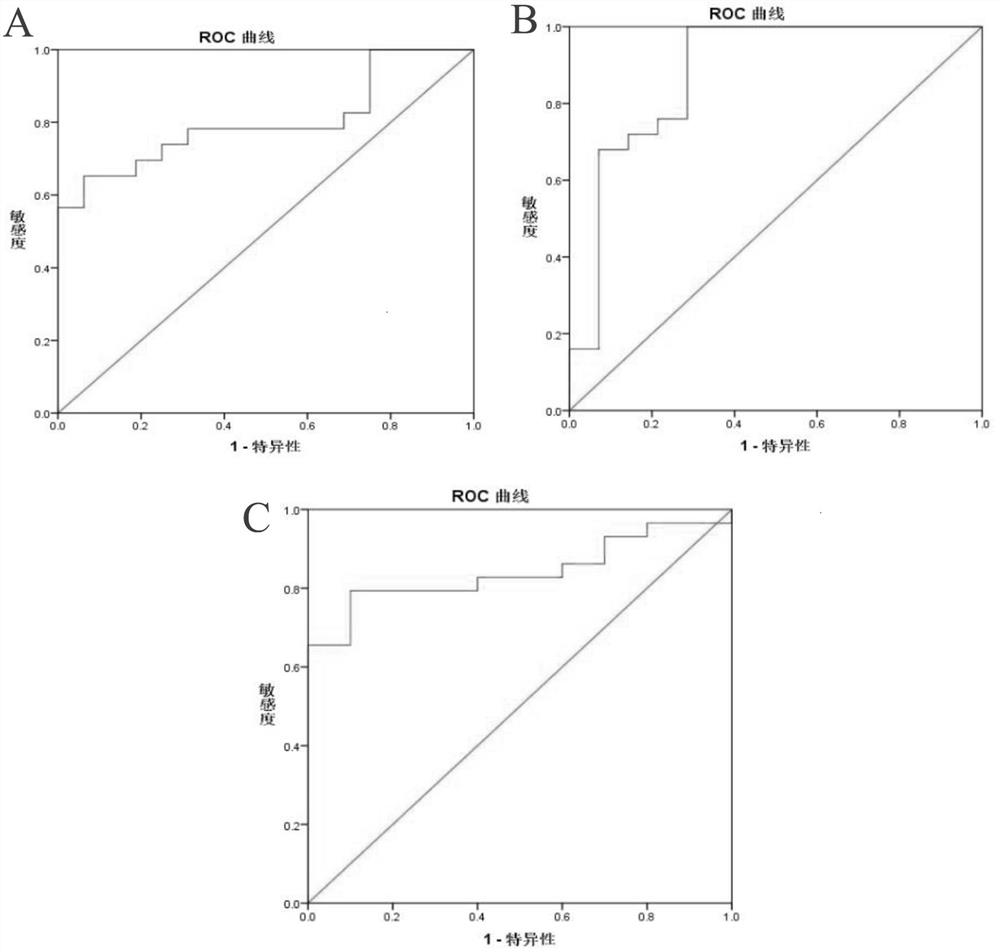
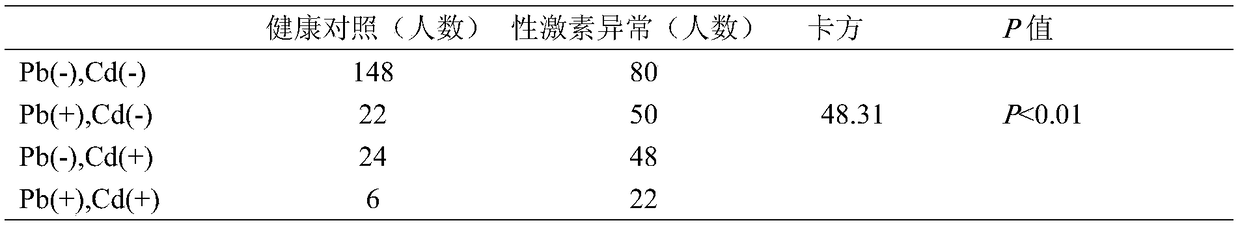
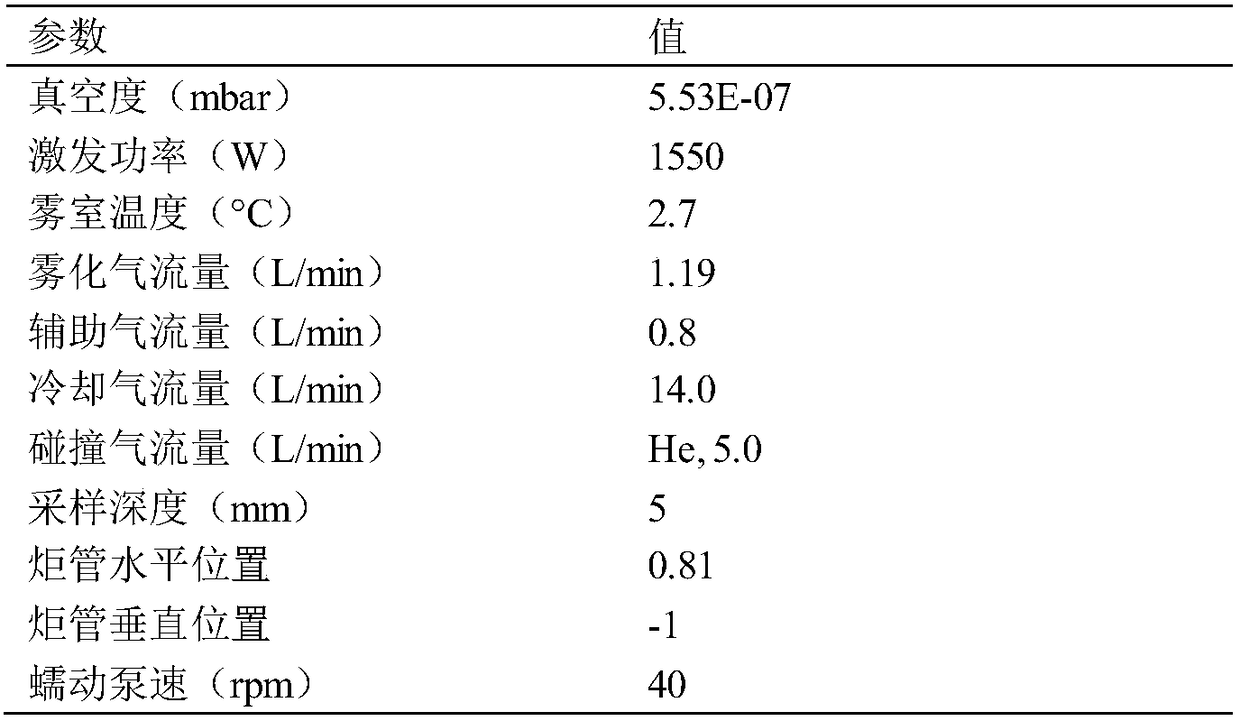
Application of lead and cadmium mixing exposure detection in assistant diagnosis of azoospermia
InactiveCN109212011AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingMedicineNormal blood volume
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine, and discloses an application of lead and cadmium mixing exposure detection in an assistant diagnosis of azoospermia. An exposed biomarker associated with the azoospermia is the mixing exposure of the lead and the cadmium. The concentration of the lead and the cadmium in whole blood can be detected by ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry), which can be used for the assistant diagnosis of the azoospermia. The application of the lead and the cadmium mixing exposure detection in the assistant diagnosis of the azoospermia has the advantages of less blood volume, simple operation, fast, accurate, and good clinical promotion value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
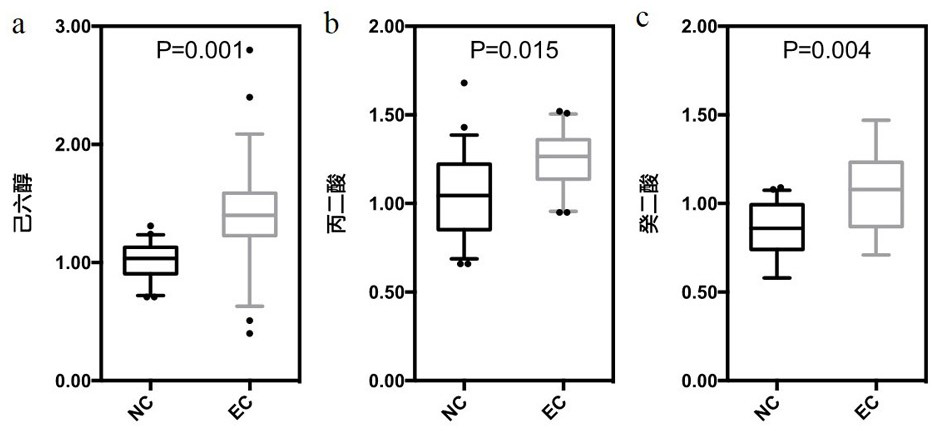
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma early screening marker based on metabonomics and kit thereof
PendingCN113466370AGood distinguishing effectGood diagnosisComponent separationEsophageal squamous cell carcinomaMass screening
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical biology, and discloses an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma early screening marker based on metabonomics and a kit thereof. The marker for screening the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, provided by the invention, is at least one of N-o-tolueneglycine, D-sorbitol and N-acetyl-D-mannosamine, and a detection reagent of the marker can be used for preparing a product for screening the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The invention also provides a kit for screening esophageal squamous carcinoma. The kit contains a detection reagent for detecting the marker. According to the kit, the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, especially the early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, can be effectively detected by detecting the expression levels of N-o-tolueneglycine, D-sorbitol and N-o-tolueneglycine in human serum; and when the three markers are combined, the detection sensitivity reaches up to 92.2%, the specificity reaches 98.0%, and the kit can be used for large-scale screening of asymptomatic crowds in high-incidence areas of esophageal squamous carcinoma and is beneficial to screening and early discovery of asymptomatic high-risk crowds.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
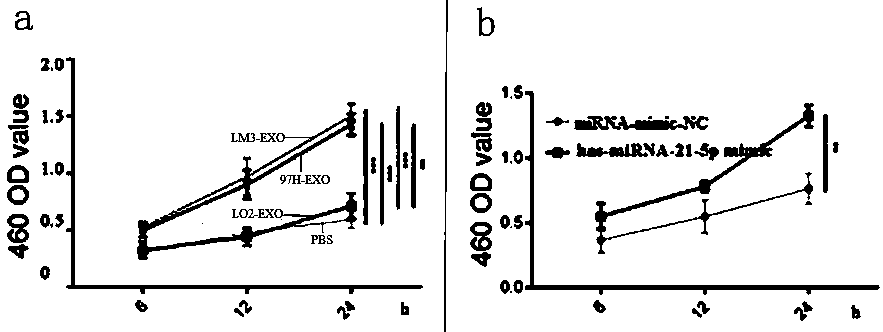
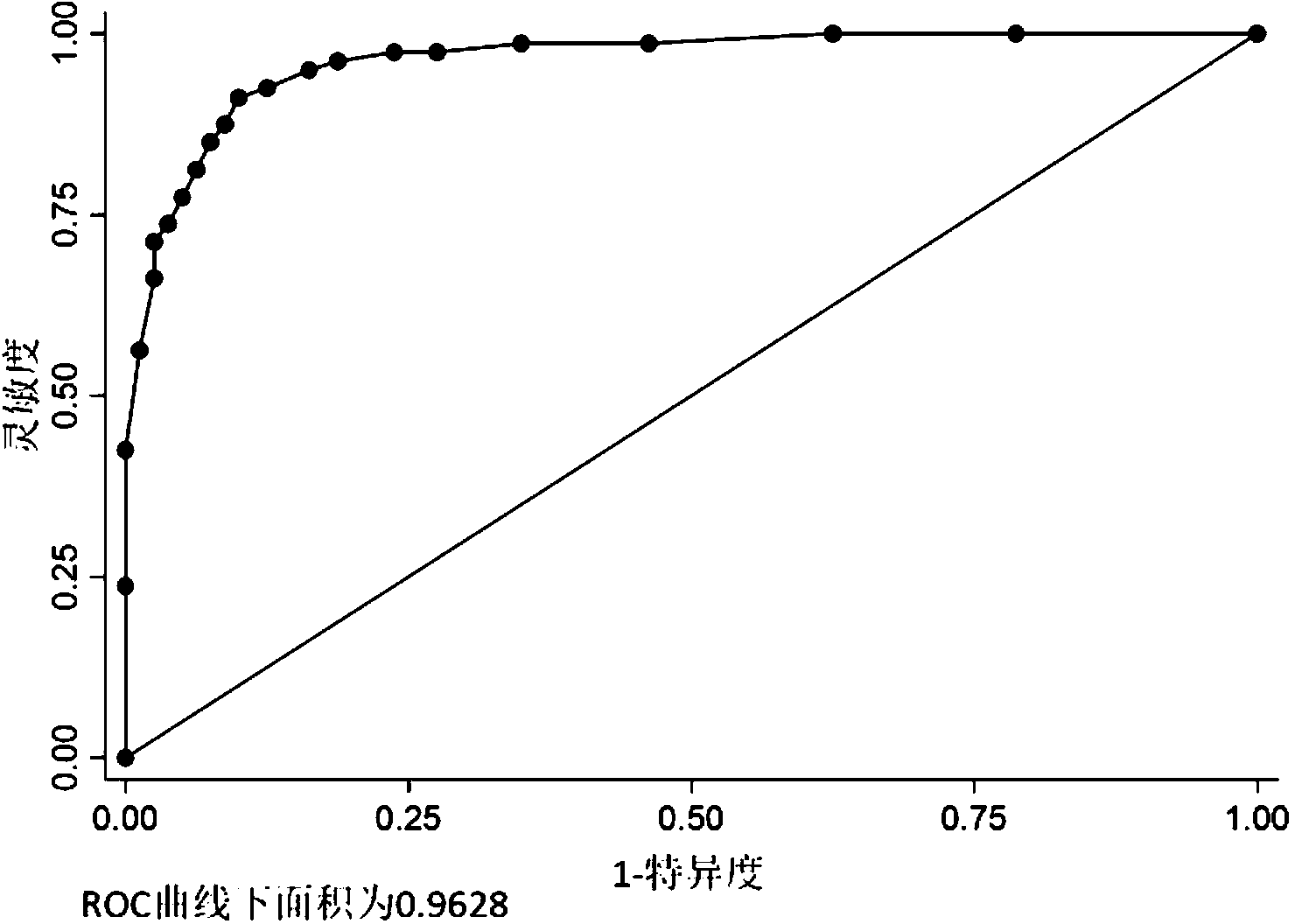
Serum exosome miRNA marker related to liver cancer diagnosis, and application thereof
InactiveCN111206102AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAIDS diagnosisBiomarker (medicine)
The invention belongs to the field of biological diagnosis and medicine, and particularly relates to a serum exosome miRNA marker related to liver cancer diagnosis and application thereof. The markeris has-miRNA-21-5p which is used as a biomarker of liver cancer, whether a detected person has liver cancer or liver cancer risk or not is diagnosed by detecting the expression level of the marker, the marker has the characteristics of convenience in detection, small damage and the like, and meanwhile, the quantification is accurate, the sensitivity and the specificity of detection can be improved, and the has-miRNA-21-5p and a specific amplification primer thereof can be used for preparing a liver cancer diagnosis kit, so that the rapid and auxiliary diagnosis can be conveniently carried outat the early stage, and a basis is provided for further deeply examining or rapidly and accurately mastering the disease state of a patient by a clinician.
Owner:NANJING DRUM TOWER HOSPITAL
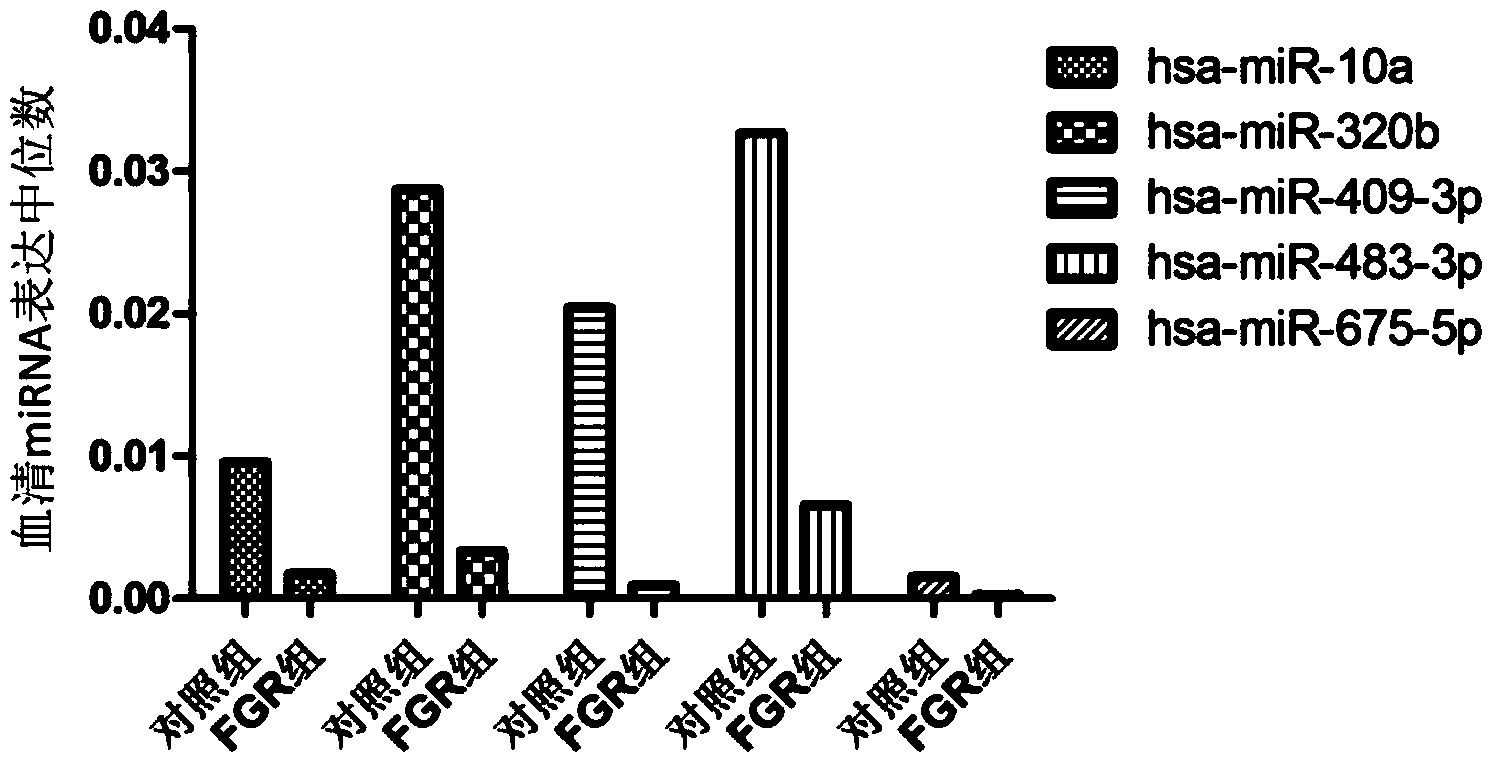
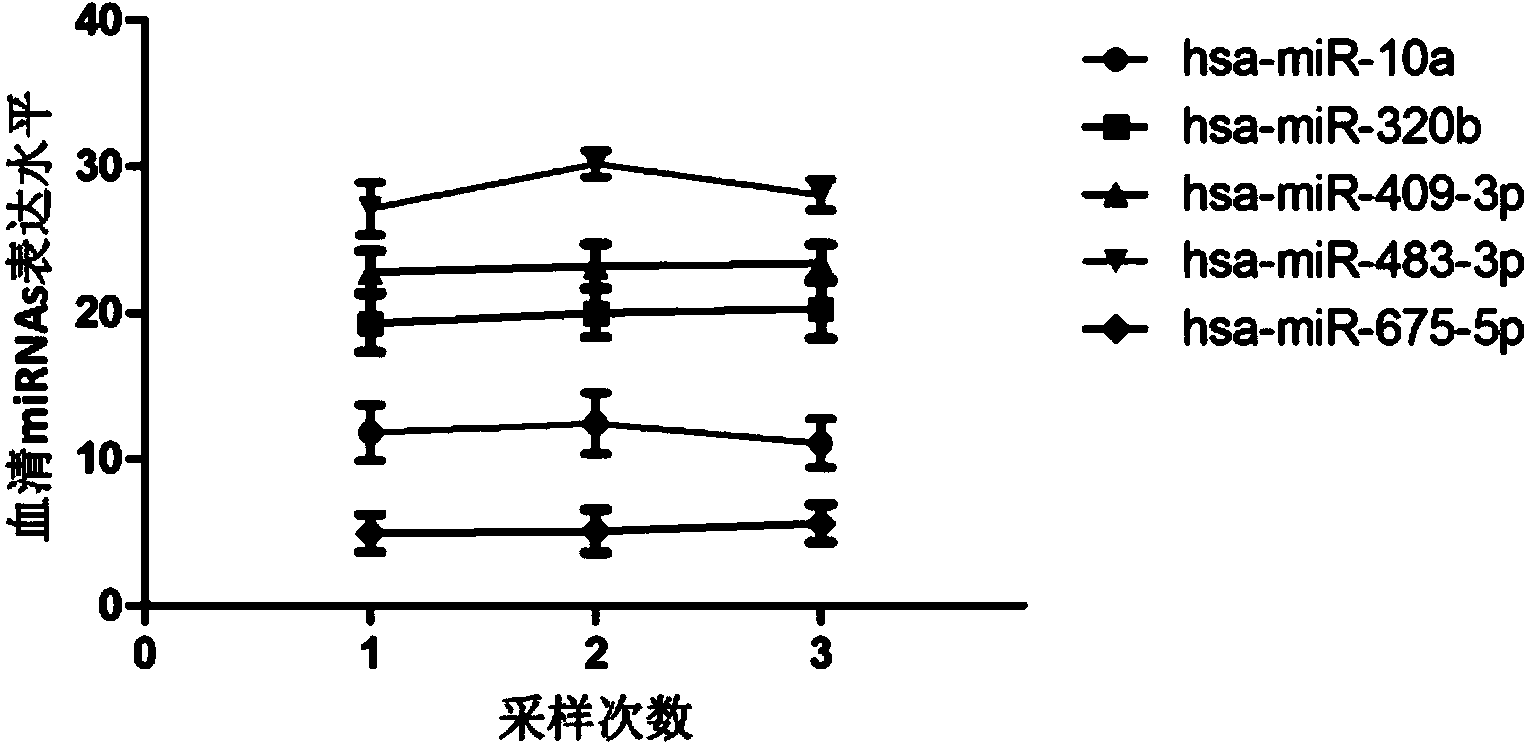
Tiny serum ribonucleic acid marker related to human fetal growth restriction and application thereof
ActiveCN103757017AHigh sensitivityEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFetal growthHuman fetal
The invention belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and reproductive medicine, and discloses a tiny serum ribonucleic acid marker related to human fetal growth restriction and application thereof. The marker is a plurality of hsa-miR-10a, hsa-miR-320b, hsa-miR-409-3p, hsa-miR-483-3p and hsa-miR-675-5p. The marker has specificity and sensibility on the fetal growth restriction, can be applied to preparation of the kit for diagnosing and monitoring the fetal growth restriction, can repeatedly detect, and is easy to dynamically monitor the fetal growth restriction degree.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
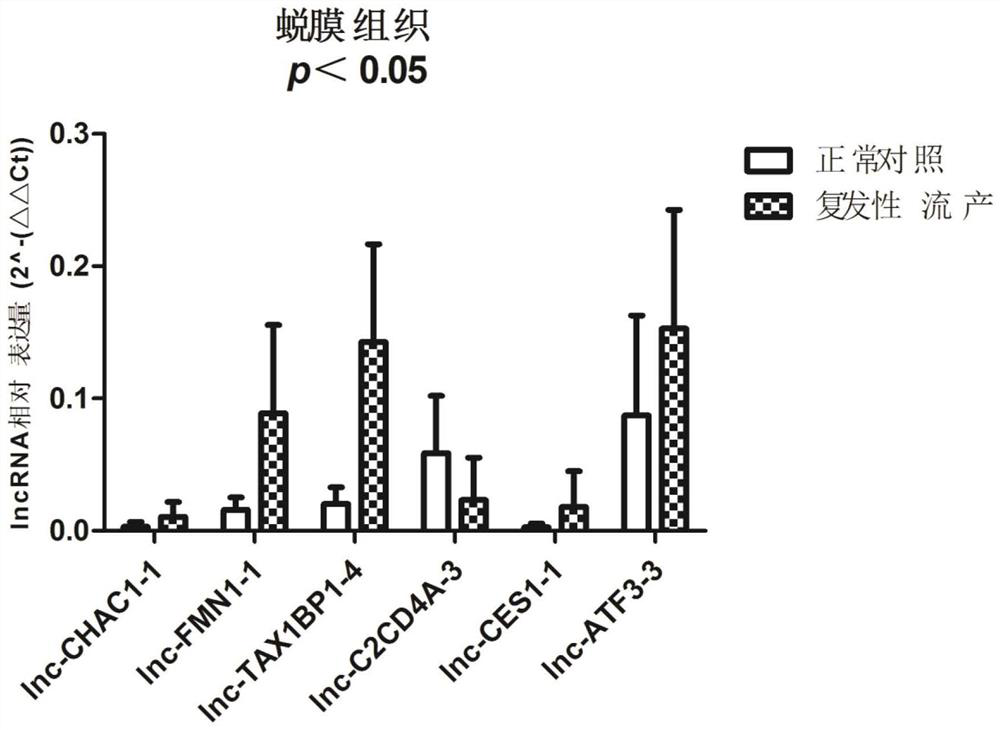
Serum lncRNA markers, primer sets, applications and kits for diagnosing unexplained recurrent miscarriage
ActiveCN107338324BIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRecurrent miscarriageSerum markers
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a serum lncRNA marker, a primer set, an application and a kit for diagnosing unexplained recurrent miscarriage. The serum lncRNA markers include: the first lncRNA having more than 90% homology with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and having more than 90% homology with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 The second lncRNA of sex, the third lncRNA having more than 90% homology with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, and the third lncRNA having more than 90% homology with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 The fourth lncRNA, the fifth lncRNA having more than 90% homology with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5, and the sixth lncRNA having more than 90% homology with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 6 lncRNA. Serum lncRNA is a novel biomarker that can greatly improve the sensitivity and specificity of recurrent miscarriage diagnosis.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Detecting method of lead-cadmium mixed-exposure marker related to sex-hormone abnormality and application thereof
InactiveCN109374722AStrong associationQuantitatively accurateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMixed exposureMedicine
The invention belongs to the fields of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine and discloses a detecting method of a lead-cadmium mixed-exposure marker related to sex-hormone abnormality and an application thereof. The lead-cadmium mixed-exposure marker related to sex-hormone abnormality is the lead-cadmium mixed-exposure marker. The detecting method adopts ICP-MS to detect the concentration oflead and cadmium in whole blood, can be used for auxiliary diagnosis on the sex-hormone abnormality, is less in blood use amount, is simple, fast and accurate in operation and has better clinical promotion value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
ICP-MS-based (inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry-based) mercury and arsenic mixed exposure test low-birth-weight auxiliary diagnosis marker and application thereof
InactiveCN109459482ADelay and stop disease progressionHigh Mercury, Arsenic Exposure LevelsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMixed exposureInductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
The invention discloses an ICP-MS-based mercury and arsenic mixed exposure test low-birth-weight auxiliary diagnosis marker and application thereof and belongs to the fields of analytic chemistry andclinical medicine. The ICP-MS-based mercury and arsenic mixed exposure test low-birth-weight auxiliary diagnosis marker, namely, a low-birth-weight related exposure biomarker, is a mixture of mercuryand arsenic and applies an ICP-MS-based detecting method. Comparison of the mercury and arsenic mixed exposure levels in normal contrast whole blood and the whole blood of a low-birth-weight case through ICP-MS helps discover that man's whole blood contains a marker combination applicable to assessing risk low-birth-weight and achieving auxiliary diagnosis values. The invention also relates to application of ICP-MS of detection of the ICP-MS-based mercury and arsenic mixed exposure test low-birth-weight auxiliary diagnosis marker to help develop a low-birth-weight auxiliary diagnosis kit applicable to clinical application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CELLPRO BIOTECH
Application of serum exosomal miRNA markers in the early diagnosis of endemic arsenicosis
InactiveCN106435004BEasy extractionReduce the amount of serum drawnMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSerum igeExosomal mirnas
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and clinical medicine and particularly relates to an endemic arsenism early diagnosis associated serum exosome miRNAs marker and application thereof. The marker is a combination of has-miR-155 and has-miR-191. The marker and a primer thereof can be used for preparation of a kit for early diagnosis of endemic arsenism.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Marker and kit for diagnosing early esophageal cancer
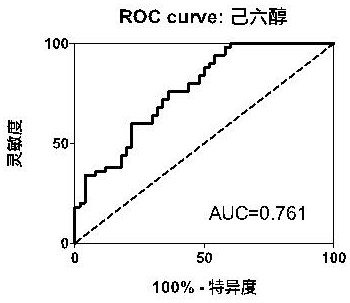
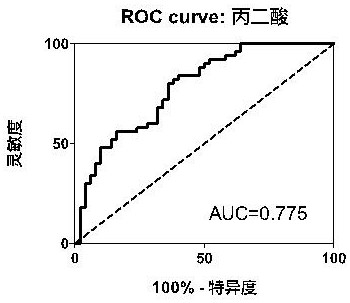
PendingCN113777181ADiagnostic test worksEfficient detectionComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDiseaseMalonic acid
The invention belongs to the field of disease detection and diagnosis, and particularly discloses a marker and a kit for diagnosing early esophageal cancer. The marker for diagnosing the early esophageal cancer is at least one of hexanehexol, malonic acid and sebacic acid, and a detection reagent of the marker can be used for preparing an early esophageal cancer diagnosis product. The invention further provides the kit for diagnosing the early esophageal cancer, the kit contains the detection reagent for detecting the mentioned marker, and the detection reagent is a reagent for detecting the marker in a sample through chromatography, mass spectrometry or chromatography-mass spectrometry. The esophageal cancer can be effectively detected by detecting the expression levels of hexanehexol, malonic acid and sebacic acid in human serum, the detection sensitivity is as high as 84%, the specificity reaches 76%, and the kit and the marker can be used for large-scale screening of asymptomatic crowds in esophageal cancer high-incidence areas and are beneficial to screening and early discovery of asymptomatic high-risk crowds.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Application of a marker for auxiliary diagnosis of macrosomia
The invention belongs to the field of analytic chemistry and clinical medicine and discloses a fetal macrosomia auxiliary diagnostic marker and application thereof. The marker is the combination of nicotinamide and citric acid and can be used for manufacturing a fetal macrosomia diagnosing or monitoring kit. The marker has the better auxiliary diagnostic effect on fetal macrosomia, can lower the detection cost and reduce economical burdens of a patient and is beneficial to clinical usage and popularization.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Combination of capric acid and prostaglandin e2 as auxiliary diagnostic markers for macrosomia and its application
The invention belongs to the fields of analytical chemistry and clinical medicine, and discloses a capric acid and prostaglandin E2 combination as a giant baby auxiliary diagnosis marker and the application thereof. The auxiliary diagnosis marker is a combination of micromolecular capric acid and prostaglandin E2, can be used for preparing a giant baby auxiliary diagnosis or monitoring kit, is relatively high in sensitivity and specificity and rapid in detection, and has a relatively high clinical application value.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com