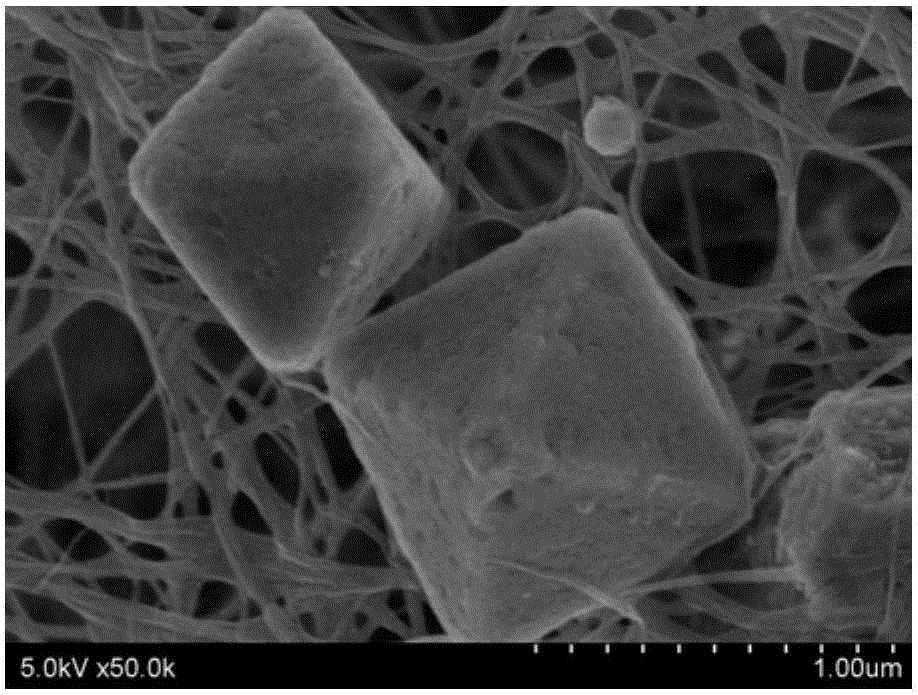
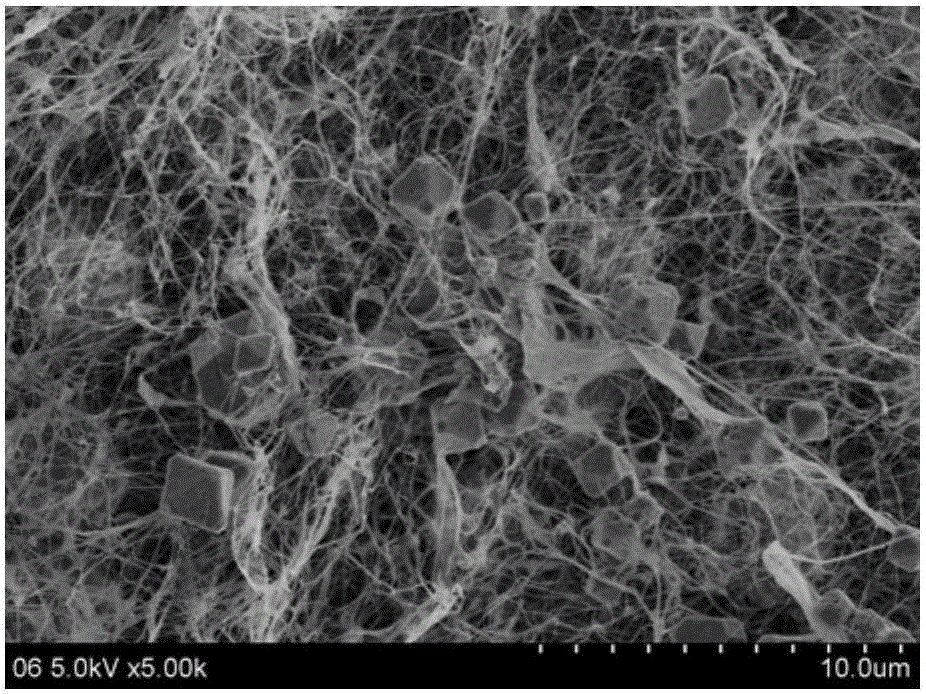
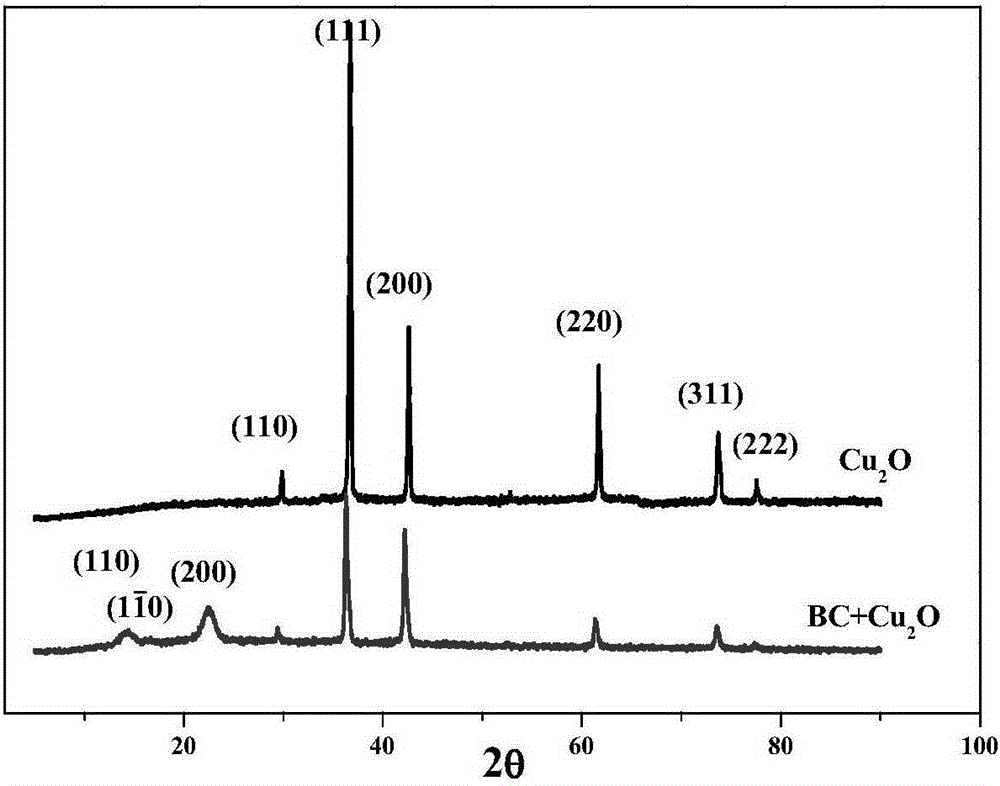
Bacterial cellulose compound cuprous oxide antimicrobial dressing and preparation method thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose and cuprous oxide, applied in medical science, bandages, absorbent pads, etc., can solve problems such as limited application, and achieve the effects of excellent antibacterial properties, simple and controllable preparation method, and high water content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A preparation method of bacterial cellulose composite cuprous oxide antibacterial dressing, firstly, a bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is prepared, and the bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is used as a base material, which is obtained after the pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is processed ; The pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is produced by the secretion of Acetobacter xylinum, and the bacteria protein and the residual medium adhered to the cellulose film are separated and purified to reach the bacterial dressing grade of bacterial cellulose. The mass percentage of pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is 1%. Separation and purification refers to that the secreted bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is soaked in 5% NaOH aqueous solution at a temperature of 80°C. Heat for 3 hours, and then rinse repeatedly with double distilled water until neutral. The grade of medicinal dressings refers to the hygienic standard GB15980-1995 for disposable medical supplies...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A preparation method of bacterial cellulose composite cuprous oxide antibacterial dressing, firstly, a bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is prepared, and the bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is used as a base material, which is obtained after the pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is processed ; The pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is secreted by Acetobacter acetogenes, after separation and purification to remove bacterial protein and residual culture medium adhering to the cellulose film, the bacterial cellulose reaches the grade of medicinal dressings, and the bacterial cellulose accounts for The mass percentage of pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is 5%. Separation and purification refers to that the secreted bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is soaked in a 5% NaOH aqueous solution at a temperature of 100°C. Heat for 4 hours, then rinse repeatedly with double distilled water until neutral. The grade of medicinal dressings refers to the hygienic standar...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A preparation method of bacterial cellulose composite cuprous oxide antibacterial dressing, firstly, a bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is prepared, and the bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is used as a base material, which is obtained after the pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is processed The pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is secreted by Acetobacter acetibacterium, after separation and purification to remove the bacteria protein and the residual culture medium adhered to the cellulose film to reach the bacterial dressing grade of bacterial cellulose, the bacterial cellulose accounts for The mass percentage of pure bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is 3%, and the separation and purification refers to that the secreted bacterial cellulose hydrogel film is soaked in a 5% NaOH aqueous solution at a temperature of 90°C. Heat for 3 hours, then rinse repeatedly with double distilled water until neutral. The grade of medicinal dressings refers to the hygienic s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com