A kind of preparation method of high specific capacity lithium battery negative electrode material
A negative electrode material, high specific capacity technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of poor conductivity, large volume change, large irreversible capacity, etc., to achieve the effect of improved stability and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
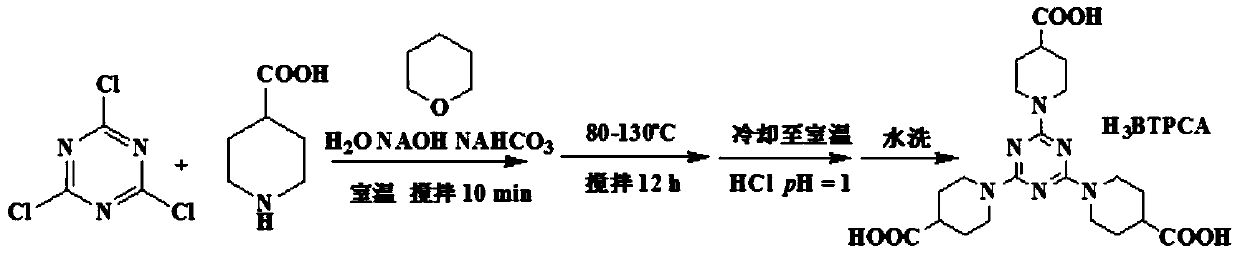
[0036] (1) Organic ligand H 3 Synthesis of BTPCA
[0037] Such as figure 1 Organic ligand H in the present invention 3 The schematic diagram of the synthetic reaction steps of BTPCA is shown, and the specific experimental steps are as follows:
[0038]4-piperidinecarboxylic acid (1 g, 10 mmol) was added into the flask, and then 3 ml of a 2 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution was added to the flask. And sodium bicarbonate (0.92 g, 11 mmol) and 0.6 g of cyanuric chloride were added thereto. The flask was stirred at normal temperature for ten minutes, and 5 ml of 1,4-dioxane was dropped thereinto during stirring. The flask was heated to a temperature ranging from 80-130°C for 12 hours. After the reaction, the flask was cooled to room temperature and diluted to pH=1 with dilute hydrochloric acid. Filtrate at room temperature and wash with water to obtain the ligand.
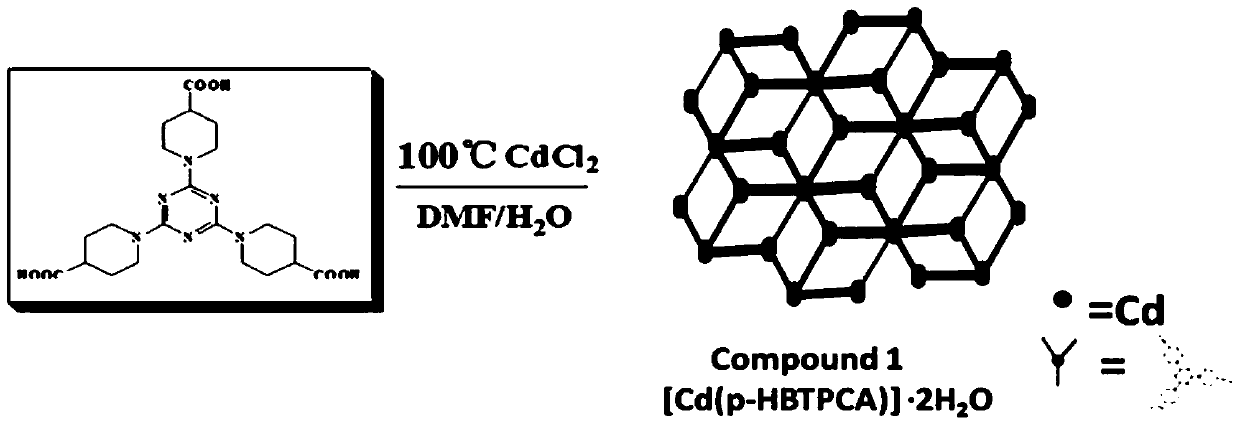
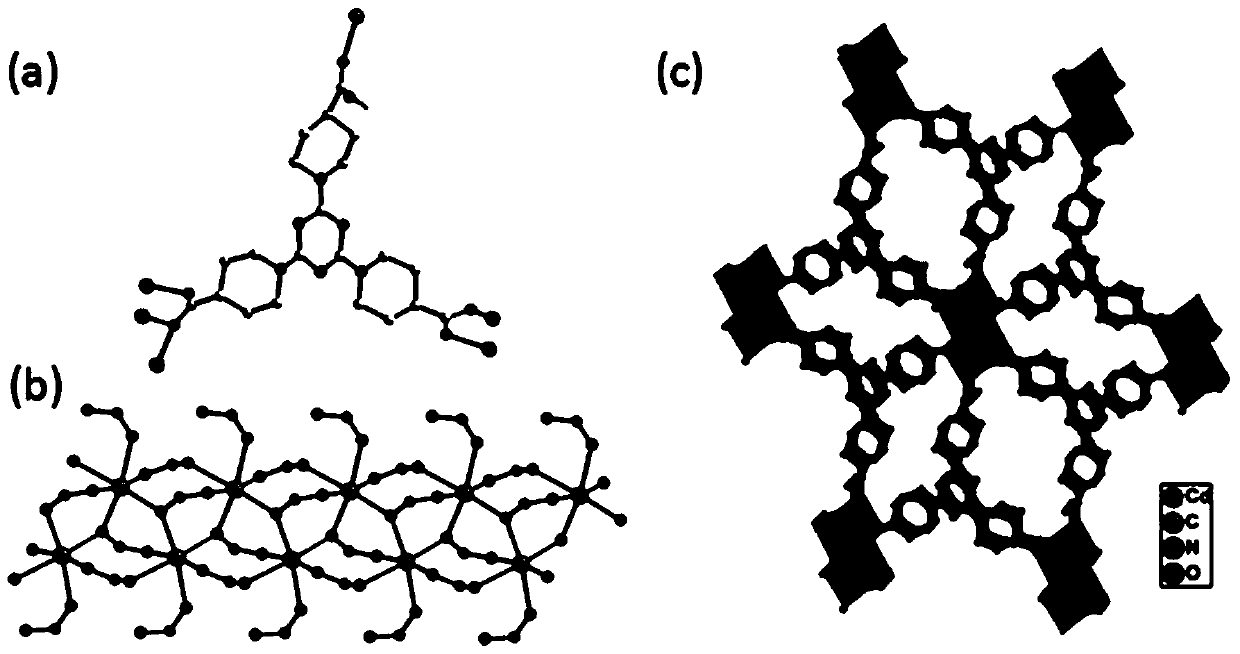
[0039] (2) Synthesis of metal-organic framework complexes (MOFs)
[0040] Such as figure 2 As shown in the s...
specific Embodiment 2
[0042] (1) Organic ligand H 3 Synthesis of BTPCA
[0043] Such as figure 1 Organic ligand H in the present invention 3 The schematic diagram of the synthetic reaction steps of BTPCA is shown, and the specific experimental steps are as follows:
[0044] 4-piperidinecarboxylic acid (2 g, 15 mmol) was added into the flask, and then 3 ml of a 2 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution was added to the flask. And sodium bicarbonate (0.92 g, 11 mmol) and 0.6 g of cyanuric chloride were added thereto. The flask was stirred at normal temperature for ten minutes, and 5 ml of 1,4-dioxane was dropped thereinto during stirring. The flask was heated to a temperature ranging from 80-130°C for 12 hours. After the reaction, the flask was cooled to room temperature and diluted to pH=1 with dilute hydrochloric acid. Filtrate at room temperature and wash with water to obtain the ligand.
[0045] (2) Synthesis of metal-organic framework complexes (MOFs)
[0046] Such as figure 2 As shown in the ...
specific Embodiment 3
[0048] (1) Organic ligand H 3 Synthesis of BTPCA
[0049] Such as figure 1 Organic ligand H in the present invention 3 The schematic diagram of the synthetic reaction steps of BTPCA is shown, and the specific experimental steps are as follows:
[0050] 4-piperidinecarboxylic acid (1.4 g, 13 mmol) was added into the flask, and then 3 ml of a 2 mol / L sodium hydroxide solution was added to the flask. And sodium bicarbonate (0.92 g, 11 mmol) and 0.6 g of cyanuric chloride were added thereto. The flask was stirred at normal temperature for ten minutes, and 5 ml of 1,4-dioxane was dropped thereinto during stirring. The flask was heated to a temperature ranging from 80-130°C for 12 hours. After the reaction, the flask was cooled to room temperature and diluted to pH=1 with dilute hydrochloric acid. Filtrate at room temperature and wash with water to obtain the ligand.
[0051] (2) Synthesis of metal-organic framework complexes (MOFs)
[0052] Such as figure 2 As shown in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com