A strain of the genus Curaporia bacterium capable of transforming heavy metals and its application
A technology of heavy metals and copper greedy bacteria, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganism-based methods, and restoration of contaminated soil, etc., can solve the problems of unclear migration and transformation mechanism of arsenic, and achieve the effect of strong reduction and strong reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
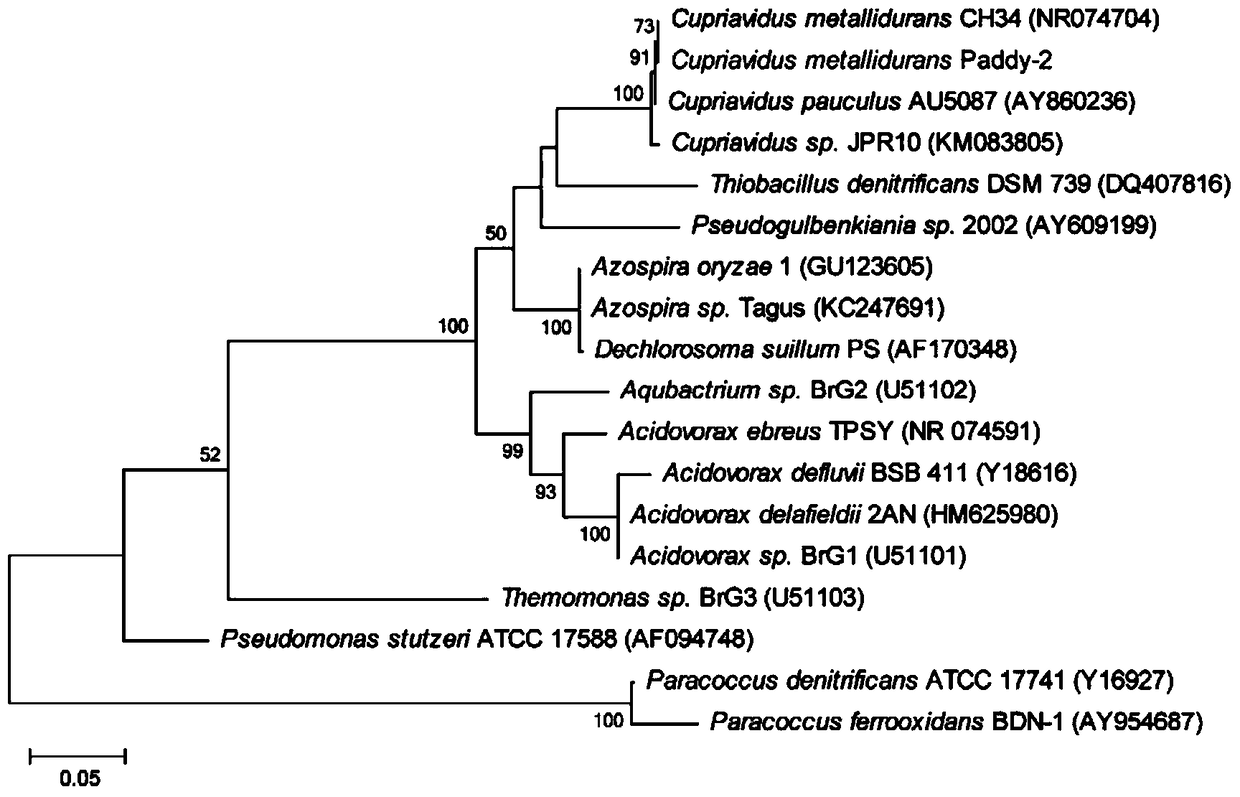
[0019] Example 1: Enrichment and isolation of nitrate-dependent ferrous oxidizing bacteria Paddy-2.
[0020] Enrichment is to take rice soil samples from Guangdong Province and inoculate them into liquid separation medium. The composition of each liter of liquid separation medium is: 20mM piperazine-1,4-diethanesulfonic acid (PIPES) buffer, 5.14mM NaCl , 1.03mM KH 2 PO 4 , 2.03mMMgCl 2 , 0.68mM CaCl 2 , 10.0ml trace elements and 10.0ml vitamin solution, and added with 5mM FeCl 2 4H 2 O, 10mM NaNO 3 and 5mM CH 3 COONa (solvent is deionized water), pH is adjusted to 7.0, wherein, vitamin solution contains 2.0mg biotin, 2.0mg folic acid, VB610.0mg vitamin, 5.0mg thiamine, 5.0mg riboflavin, 5.0 mg niacin, 5.0 mg calcium pantothenate, 0.1 mg vitamin B12, 5.0 mg p-aminobenzoic acid, 5.0 mg lipoic acid, dilute to 1 L with deionized water; the trace element solution contains 1.5 g nitrilotriacetic acid, 3.0 g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.5g MnSO 4 ·H 2 O, 1.0g NaCl, 0.1g FeSO 4 ·7H ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: Iron oxidation process of strain Paddy-2.
[0029] The liquid medium formula used: each liter of liquid medium contains 20mM PIPES buffer, 5.14mM NaCl, 1.03mM KH 2 PO 4 , 2.03mM MgCl 2 , 0.68mM CaCl 2 , 5mM CH 3 Each of COONa, vitamin solution and trace element solution was 10.0mL (vitamin solution and trace element solution composition were the same as in Example 1), and the solvent was deionized water.
[0030] The bacteria lawn was picked from the slope of the preserved strain Paddy-2 and inoculated into the liquid medium, and the bacteria were activated on a shaker at 30°C and 180rpm for 18 hours, so that the number of bacteria reached the exponential growth phase. Centrifuge at 4°C and 6000rpm for 10min, remove the supernatant, resuspend with 20mMPIPES buffer, repeat the above operation twice, and suspend the precipitated bacterial suspension in the liquid medium to prepare the bacterial suspension.
[0031] Inoculate the bacterial suspension in the...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: The action process of strain Paddy-2 on ferrous oxidation ore formation.
[0035] The preparation of liquid medium and the making of bacterial suspension are the same as in Example 2.
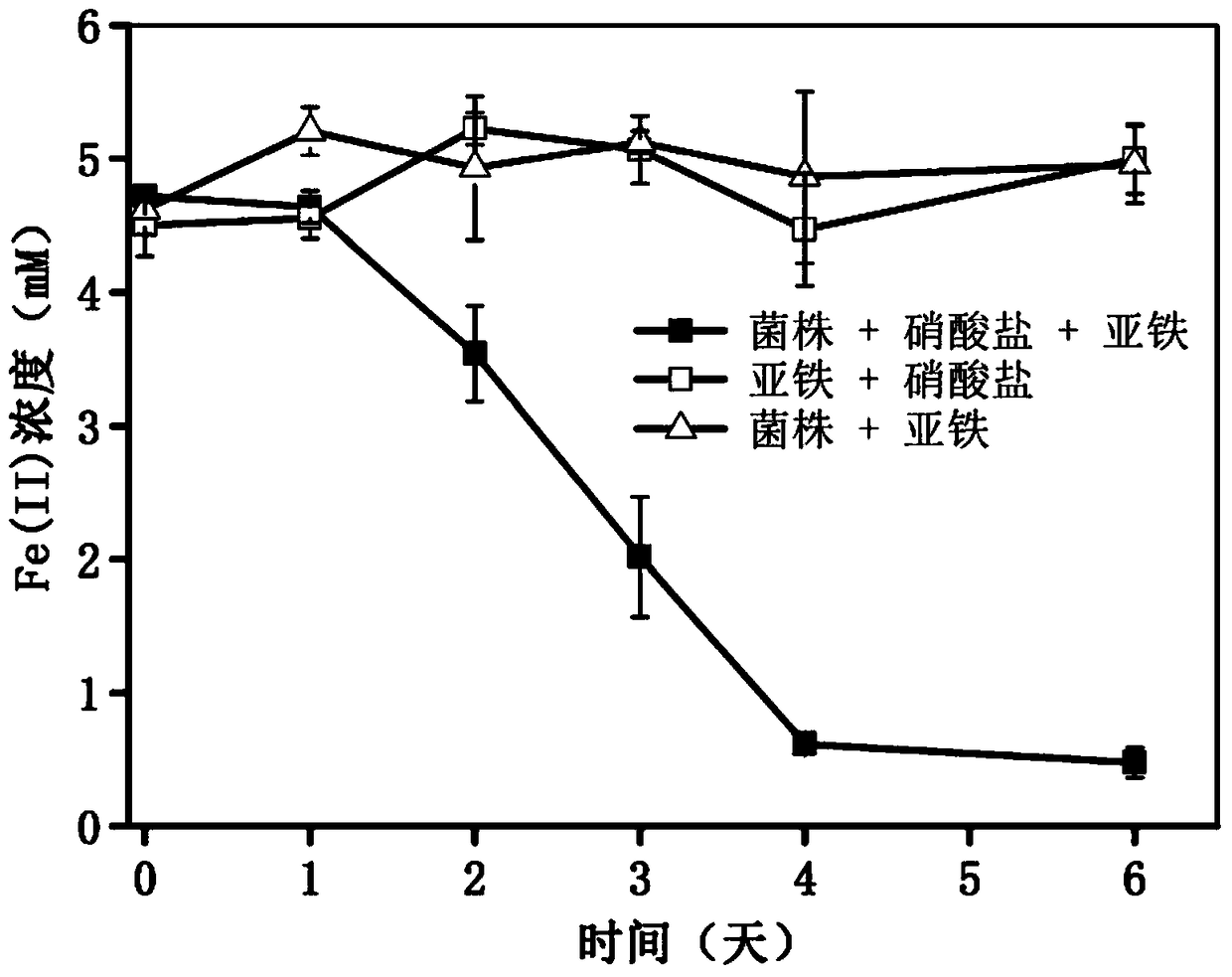
[0036] According to the result of embodiment 2, only under the condition that nitrate exists, bacterial strain just shows the ability of ferrous oxidation. Bacterial suspension was inoculated in liquid medium, and the experimental treatment was bacterial strain + nitrate + ferrous, and the culture solution without bacteria was used as a control to investigate the effect of bacterial strain on ferrous oxidation and mineralization.
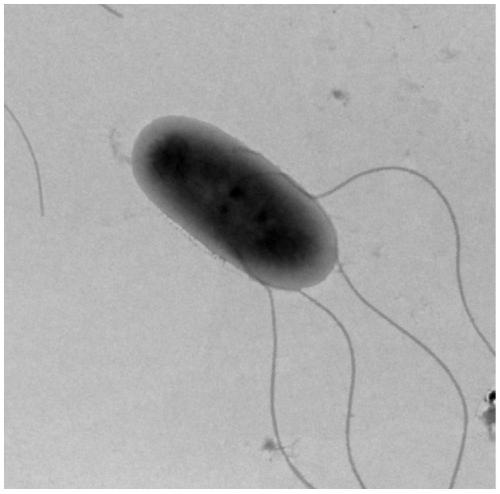
[0037] The precipitate formed by ferrous oxidation was washed twice with phosphate buffer (10 mM, pH 7.0) under anaerobic conditions, freeze-dried, and tested. The attachment relationship between the formed precipitate and the bacterial strain was observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM).
[0038] Test results such as Figure 4 As shown...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com