Ethyl carbamate hydrolase mutants with improved thermostability
A technology of urethane and thermostability, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, and can solve problems such as non-elimination and complex formation mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0010] Example 1 Preparation of urethane hydrolase mutants
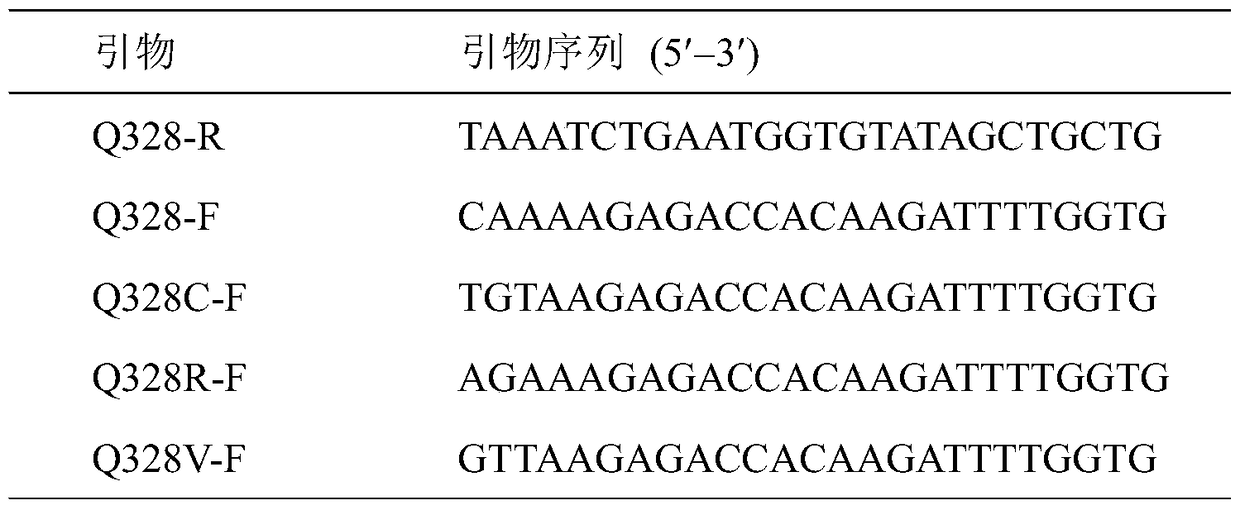
[0011] By analyzing the structure of carbamate hydrolase, we chose to mutate its amino acid at position 328 and designed corresponding site-directed mutagenesis primers (Table 1). Using the recombinant plasmid pET20b-UH as a template, the recombinant plasmid pET20b-UH was amplified by using PCR enzyme and mutant primers. The amplified fragments were recovered and purified using a gel recovery kit. The purified fragments were phosphorylated using phosphorylase. The phosphorylated fragment was ligated with ligase, transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3) competent, screened for positive transformants, and the plasmid was extracted. After identification by enzyme digestion, it was sent to Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd. for sequencing verification. The E. coli recombinant engineering bacteria containing the correctly sequenced plasmids were inoculated into LB medium, and cultured overnight at 37°C and 220 r / min. The seed...
Embodiment 2
[0015] Example 2 Enzyme activity assay method
[0016] Take 1 mL of enzyme solution and 1 mL of ultrapure water (control), add 1 mL of 3% EC solution to each, and react in a constant temperature water bath at 37 °C for 15 min, then add 1 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid to terminate the reaction. After the reaction was terminated, 1mL of developer I (15g phenol and 0.625g sodium nitroferricyanide were added to the volume to 250mL) and 1mL of developer II (13.125g NaOH and 7.5mL sodium hypochlorite were added to the volume to 250mL), after mixing. Incubate in a 37° C. water bath for 20 min, and after the reaction, dilute to 10 mL with ultrapure water, and measure the absorbance at 625 nm. Definition of enzymatic activity: Under the conditions of normal pressure, 37℃, pH 7.0, the amount of enzyme required to decompose EC to produce 1 μmol of ammonia in 1 min is one unit of enzyme activity (U).
Embodiment 3
[0017] Example 3 Mutation improves the thermostability and half-life of urethane hydrolase
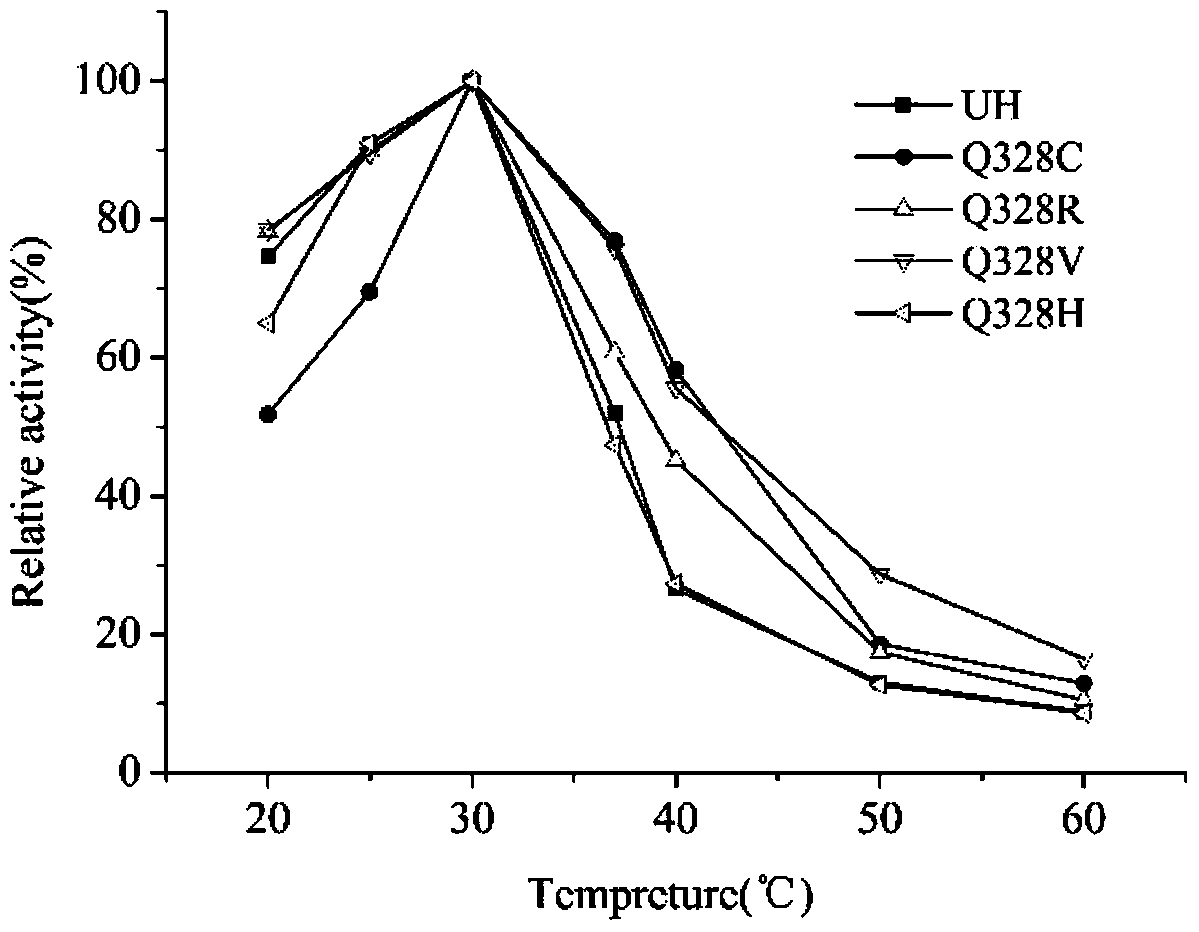
[0018] The purified wild enzyme and its mutants were subjected to enzymatic reactions at different temperatures (20°C to 65°C, with an interval of 5°C), and the optimum reaction temperature was determined. The optimum reaction temperature of both wild enzyme and mutant was 30℃, but the stability of mutant Q328C, Q328R and Q328V was better than that of wild enzyme above 30℃. After incubation at 37°C for 1 time, the residual enzyme activities of Q328C, Q328R, Q328V and UH were 76.9%, 60.8%, 75.8% and 51.9%, respectively, which were 24.0%, 8.9% and 23.9% higher than the original enzyme. At 40°C, the residual enzyme activities of the mutants were increased by 31.7%, 19.7% and 28.9% compared with the original enzyme, respectively ( figure 1 ).
[0019] The purified wild enzyme and its mutant were incubated at 40°C, and samples were taken at regular intervals to measure the enzyme activity...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com