Contaminant removal method
A drug and composition technology, applied in the field of ApoA-I preparations, can solve the problems of low protein recovery, low virus retention, high virus clearance is not optimal, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0139] The following example describes a sequence of method steps of a preferred embodiment of the method according to the invention. The process involves the fraction IV precipitate-derived feedstock being dissolved in the presence of GuHCl, filtered to remove filter aids, followed by pH adjustment, heat treatment, dilution and virus filtration. Alternatively, heat treatment can also be performed after the virus filtration step.
[0140] Methods and Materials
[0141] ApoA-I protein concentration
[0142] ApoA-I protein concentration is generally measured by measuring absorbance at 280 nm using WFI (Water for Injection) as a diluent, and it is usually 5 to 30 g / L. Protein is calculated as follows:
[0143]
[0144] Alternatively, ApoA-I protein concentration can be determined using nephelometry or high performance capillary electrophoresis (Hewlett Packard 3DCE, Agilent Technology). Briefly, for high-efficiency capillary electrophoresis, the method involves the followi...
Embodiment 2
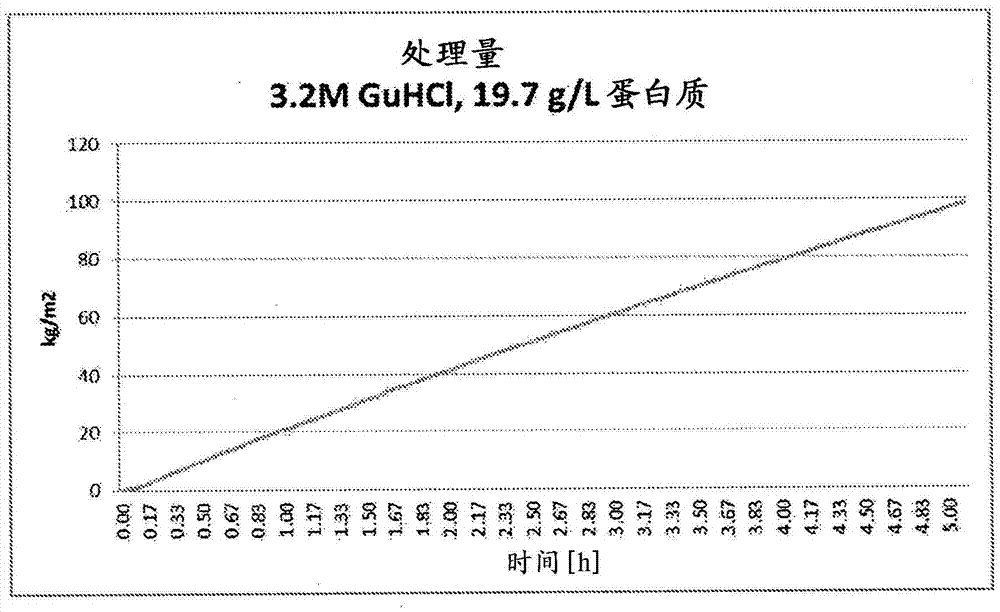
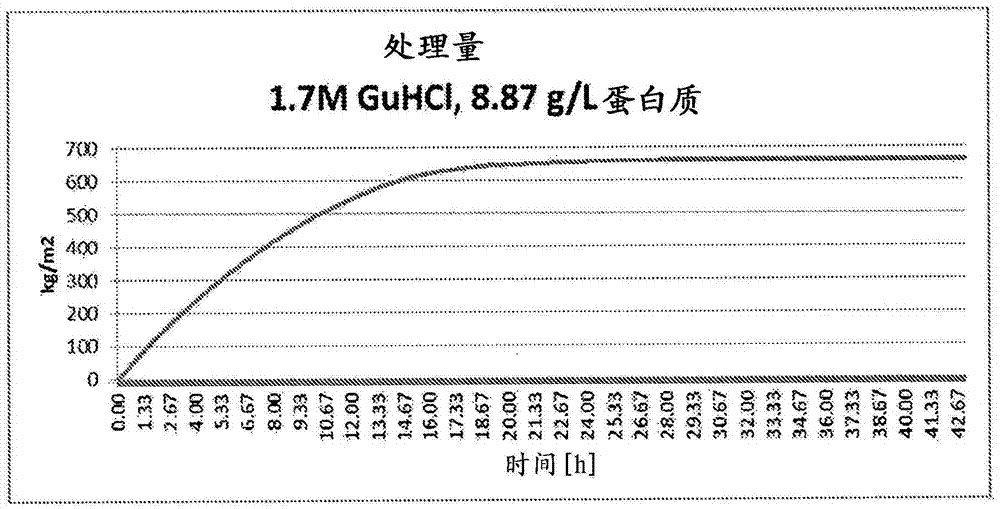
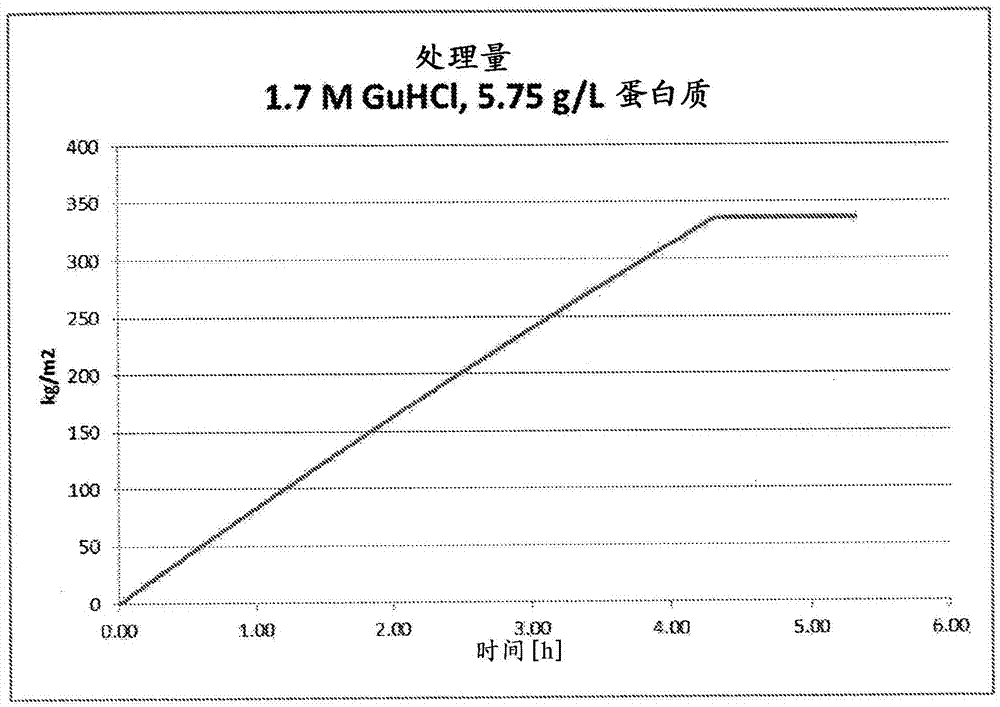
[0167] Filtration was compared using BioEx filters in the presence of different GuHCl concentrations (1.7M & 3.2M) and ApoA-I concentrations (5.8, 8.9, 19.7g / L) ( Figures 1 to 3 ). The virus filtration process was performed in a similar manner as described in Example 1 above.
[0168] Additional filtration studies confirmed that lower concentrations of GuHCl (1.0M & 1.3M) could lead to solution instability which caused filter plugging of the system. These results highlight the benefit of optimizing the concentration level of GuHCl to facilitate virus filtration.
Embodiment 3
[0170] ApoA-I samples were spiked with MVM at a ratio of 1:1000. Fortified samples were filtered through PlanovaBioEX virus removal filters in dead-end mode at a pressure of approximately 2.4 bar at a protein concentration of 10 to 12 g / L. Samples of the filtrate were taken and assayed for residual virus infectivity (Table 1). The results confirmed that complete viral retention was achieved over a range of GuHCl concentrations. Lower GuHCl concentrations resulted in increased log reduction values (LRV) of MVM.
[0171] Table 1
[0172]
[0173] In yet another virus filtration study performed under similar conditions, MVM virus penetration was observed in the presence of 3.4M GuHCl. Therefore, concentrations below about 3.0 M GuHCl are believed to improve the removal of viruses with a diameter of about 20 nm (eg, parvovirus) in the manufacture of ApoA-I preparations using virus removal filters such as BioEx.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com