Method capable of promoting migration of dendritic cells to lymph nodes and achieving multi-mode imaging simultaneously
A multi-mode imaging and dendritic cell technology, applied in the field of biological sciences, can solve the problems of low DC migration efficiency, ineffective pre-stimulation, adverse reactions, etc., and achieve improved living migration efficiency, good biocompatibility, and biological good compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] 1) Preparation of mDCs: The preparation of DCs is derived from bone marrow extraction and isolation. The preparation of mDCs is obtained by conventional culture methods, which may carry tumor antigens or not contain tumor antigens. DC can be extracted from bone marrow or DC2.4 cell line.
[0035] 2) mDCs carry polypeptide antigens and magnetic substances: the mDCs are incubated with a magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle at 37°C for 6 hours to complete.
[0036] The magnetic fluorescent nanometer particle is formed by organically combining oleate-iron oxide particles, two kinds of phospholipids, a near-infrared probe and an antigen fusion peptide with lipid binding ability through self-assembly.
[0037] The oleate-iron oxide particles are nanoparticles modified with oleic acid, which has been put into commercial production (see http: / / www.nanoeast.net / cxnmklfzxs.html, oleic acid-modified trioxide tetroxide Ferromagnetic nanoparticles (OAFe 3 o 4 , coprecipitation or hi...
Embodiment 1
[0057] The antigen fusion polypeptide constituting the magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle is composed of α-helical polypeptide (R4F), connecting sequence and antigenic peptide (AP) in series in the form of covalent bonds. The amino acid sequence of the α-helical polypeptide is: FAEKFKEAVKDYFAKFWD, the amino acid sequence of the connecting sequence is GSG, and the amino acid sequence of the antigenic peptide is: KVPRNQDWL. The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is described in SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence listing.
[0058] Prepare magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles, the steps are:
[0059] Preparation of magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles: Weigh 5 mg each of DMPC and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose ether (MHPC) and place them in EP tubes, then add 200 μl of chloroform to the EP tube for dissolution, and dissolve the dissolved DPMC and MHPC were transferred into a chloroform solution containing iron oxide (10 mg / mL) with a volume of about 400 μl, and methanol was added at a rat...
Embodiment 2
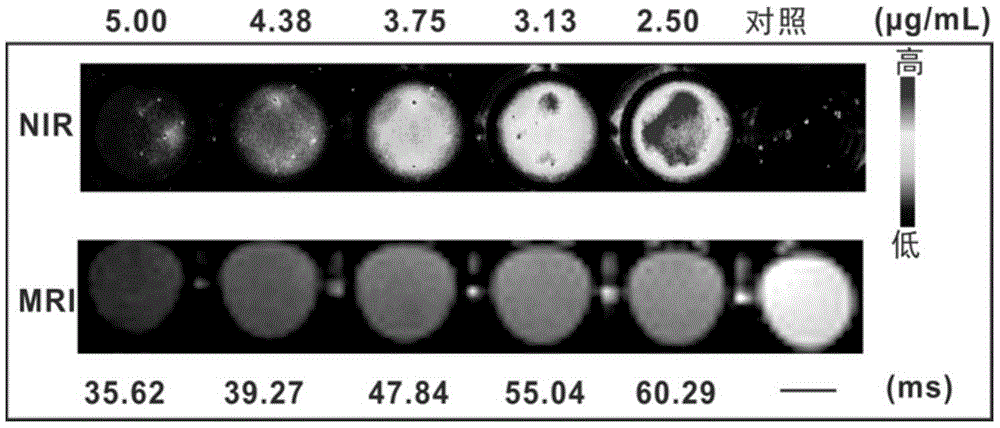
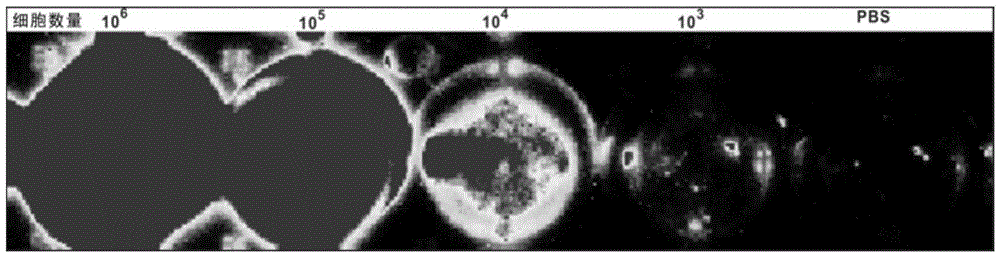
[0062] For the labeling ability of the magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 to mature DC (mDC), see image 3 . image 3 It shows that the magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles can efficiently fluorescently label mDC, and at 50 μg / mL, it has no great influence on the morphology of mDC (within 20%), and the concentration selected in the experiment is 20 μg / mL. Figure 4 Cell survival experiments after co-incubation of mDCs with different concentrations of magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles are shown, and the results show that within the concentration range of 50 μg / mL, magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles have no significant effect on the growth of mDCs. mDCs that uptake magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles have fluorescent properties ( Figure 5 ), the fluorescence intensity increased with the increase of the number of cells. At the same time, Prussian blue staining proved that mDCs that ingested magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles contained a large amount of magn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com