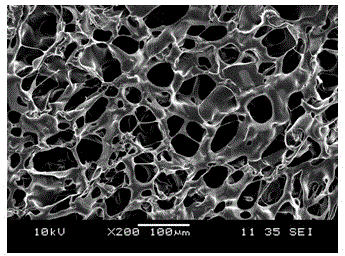
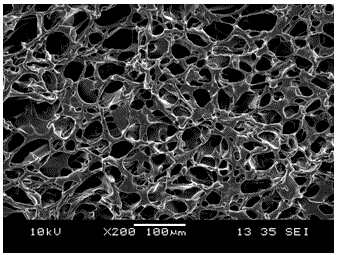
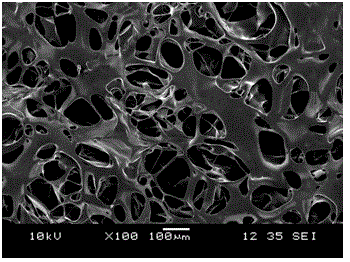
Artificial dermal scaffold and production method thereof
A dermal and artificial technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of stents being easily dissolved, collapsed or degraded in a short period of time, unable to support cells and blood vessels, and poor permeability of dermal stents, etc., to achieve good three-dimensional shape and Strength, good biocompatibility, and no adverse effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] An artificial dermis support, prepared as follows:
[0054] S1. Slowly add 6 grams of hydroxyethyl cellulose into 200 milliliters of ultrapure water, wherein the pH value of the solution is adjusted to 3 with dilute hydrochloric acid; then add 0.6 grams of calcium chloride and stir evenly;
[0055] S2. Add 0.12 ml of glutaraldehyde with a concentration of 25% to the solution treated in S1. Stir and heat up to 80° C. to allow the cross-linking reaction to proceed. The time for the cross-linking reaction is 60 minutes to obtain a uniform solution;
[0056] S3. Add 1.2 grams of glycerin to the solution after the cross-linking reaction in S2. Mix well and stir for 60 minutes at a stirring speed of 1500r / min. A large number of bubbles will be generated, and the foaming volume will reach twice the volume of the original solution. In a dry dish, the thickness is 0.3cm;
[0057] S4. Immediately place the freeze-drying tray of S3 in a freeze dryer pre-adjusted to -80°C for low-...
Embodiment 2
[0061] An artificial dermis support, prepared as follows:
[0062] S1. Slowly add 5 grams of hydroxypropyl cellulose into 125 milliliters of ultrapure water, wherein the pH value of the solution is adjusted to 2.9 with formic acid; then add 0.25 grams of potassium chloride and stir evenly;
[0063] S2. Add 0.2ml of glutaraldehyde with a concentration of 25% to the solution treated in S1. Stir and heat up to 70°C to allow the crosslinking reaction to proceed. The time for the crosslinking reaction is 40min to obtain a uniform solution;
[0064] S3. Add 0.5 g of glycerin to the solution after the cross-linking reaction in S2, mix well and stir at a stirring speed of 1800r / min, stir for 30min, a large number of bubbles will be generated, and the volume of the foam will reach 3 times the volume of the original solution, pour into frozen In a dry dish, the thickness is 0.4cm;
[0065] S4. Immediately place the freeze-drying tray of S3 in a freeze dryer pre-adjusted to -80°C for lo...
Embodiment 3
[0069] An artificial dermis support, prepared as follows:
[0070] S1. Slowly add 2.5 grams of hydroxypropyl cellulose and 2.5 grams of hydroxyethyl cellulose into 62.5 milliliters of ultrapure water, wherein the pH value of the solution is adjusted to 2.95 with dilute hydrochloric acid; then add 1 gram of sodium chloride and stir Uniform;
[0071] S2. Add 0.25ml of formaldehyde to the solution treated in S1. Stir and heat up to 90°C to allow the crosslinking reaction to proceed. The crosslinking reaction time is 100min to obtain a uniform solution;
[0072] S3. Add 2 grams of glycerin to the solution after the cross-linking reaction in S2. Mix well and stir for 40 minutes at a stirring speed of 1300r / min. A large number of bubbles will be generated, and the volume of foaming will reach twice the volume of the original solution. In a dry dish, the thickness is 0.3cm;
[0073] S4. Immediately place the freeze-drying tray of S3 in a freeze dryer pre-adjusted to -20°C for low-t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com