High-energy-storage-density strontium-sodium-niobate-base glass ceramic energy storage material, and preparation and application thereof
A strontium niobate-based technology with high energy storage density, which is used in fixed capacitor parts, electrical components, and fixed capacitor dielectrics, etc., can solve the problems that restrict the miniaturization and lightness of pulse devices, and achieve excellent breakdown resistance. The effect of field strength performance, energy storage density improvement, and simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A method for preparing a strontium sodium niobate-based glass-ceramic energy storage material with high energy storage density, the method comprising the following steps:
[0031] (1) SrCO with a purity greater than 99wt% 3 、Na 2 CO 3 , Nb 2 o 5 and SiO 2 For raw material batching, the molar percentages of the above-mentioned components are 21%, 21%, 28% and 30%;
[0032] (2) The raw material ingredients are mixed by ball milling for 16 hours, dried, and melted at 1500°C for 3 hours to obtain a high-temperature melt;
[0033](3) Pouring the high-temperature melt obtained in step (2) into a metal mold, annealing for stress relief at 600° C. for 5 hours, and then cutting to obtain glass flakes with a thickness of 0.9 to 1.2 mm;
[0034] (4) The glass flakes prepared in step (3) were kept at 1000° C. for 3 hours for controlled crystallization to obtain a strontium sodium niobate-based glass-ceramic energy storage material with high energy storage density.
[0035] T...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) SrCO with a purity greater than 99wt% 3 、Na 2 CO 3 , Nb 2 o 5 and SiO 2 For raw material batching, the molar percentages of the above components are 29.4%, 12.6%, 28% and 30%, after mixing by ball milling for 16 hours, drying, and melting at 1500°C for 3 hours;
[0038] (2) Pouring the high-temperature melt obtained in step (1) into a metal mold, annealing for stress relief at 600° C. for 5 hours, and then cutting to obtain glass flakes with a thickness of 0.9 to 1.2 mm;
[0039] (3) The glass flakes prepared in step (2) were kept at 1000° C. for 3 hours for controlled crystallization to obtain glass ceramics.
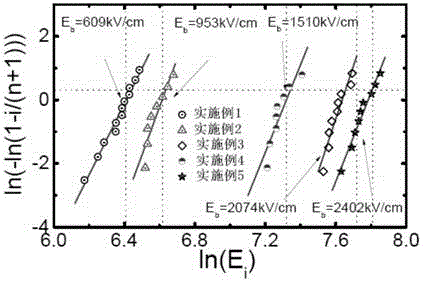
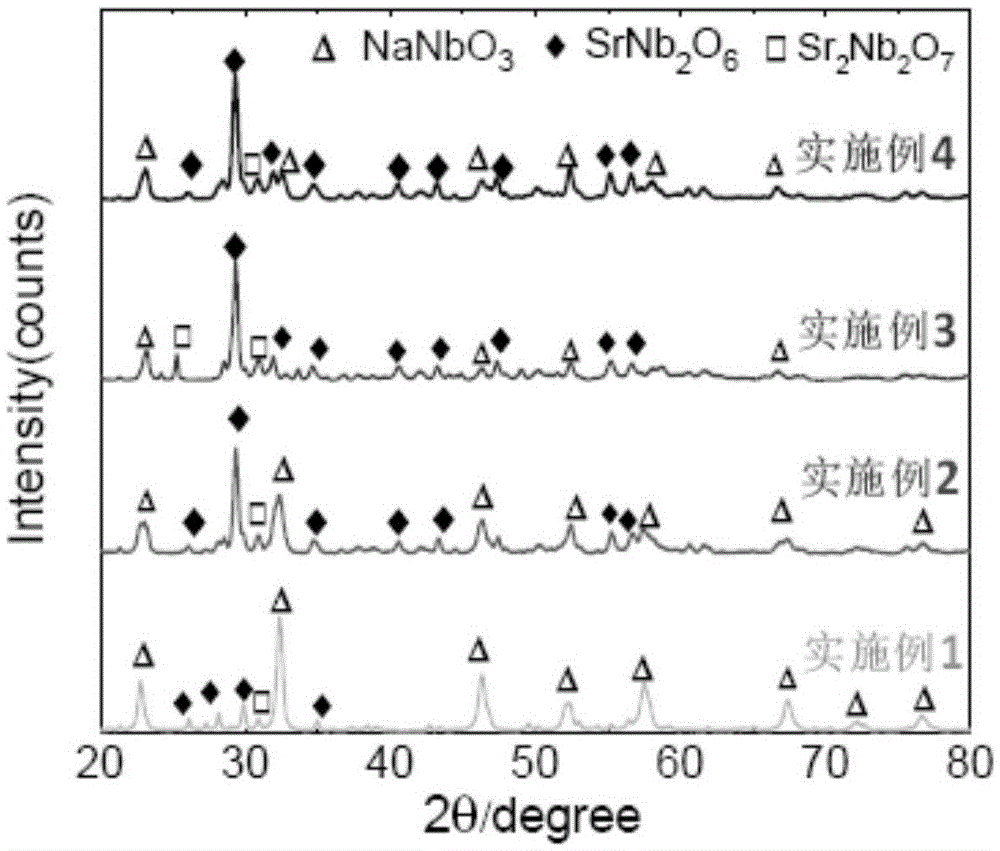
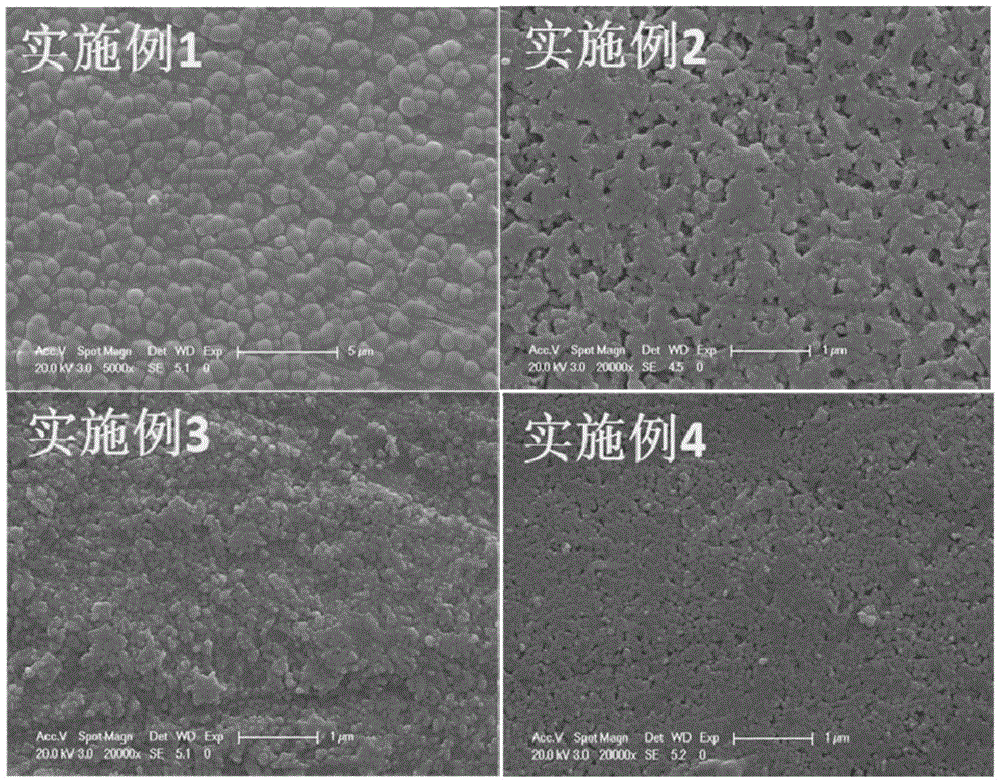
[0040] The XRD of the sample that present embodiment makes is as figure 1 As shown, SEM as figure 2 As shown, the dielectric properties are as image 3 As shown, the withstand voltage performance test is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the energy storage density is shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) SrCO with a purity greater than 99wt% 3 、Na 2 CO 3 , Nb 2 o 5 and SiO 2 For raw material batching, the molar percentages of the above components are 33.4%, 8.4%, 28% and 30%, after ball milling for 16 hours, drying, and melting at 1500°C for 3 hours;
[0043] (2) Pouring the high-temperature melt obtained in step (1) into a metal mold, annealing for stress relief at 600° C. for 5 hours, and then cutting to obtain glass flakes with a thickness of 0.9 to 1.2 mm;
[0044] (3) The glass flakes prepared in step (2) were kept at 1000° C. for 3 hours for controlled crystallization to obtain glass ceramics.
[0045] The XRD of the sample that present embodiment makes is as figure 1 As shown, SEM as figure 2 As shown, the dielectric properties are as image 3 As shown, the withstand voltage performance test is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the energy storage density is shown in Table 1.
[0046] In this embodiment, the breakdown field strength and energy storage ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| energy density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com