Method for quickly identifying sugar
A recognition method and monosaccharide technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve problems such as the inability to determine the composition of sugar and monosaccharide residues, and the inability to analyze accurately
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] (1) Preparation of standard products
[0058] Sucrose, lactose, kojibiose, nigerbiose, maltose, isomaltose, sophorose, laminaribiose, cellobiose, gentiobiose, glucose, galactose were mixed with 50% methanol-water (v / v) , mannose and fructose standard substances were prepared into a solution with a concentration of 2 μM.
[0059] (2) IM-MS detection of standard products
[0060] The prepared standard was directly measured by ESI-IM-MS, and the injection speed of the peristaltic pump was 5 μL / min. ESI ion source conditions are as follows: positive ion mode, capillary voltage: 2.8kV, sample cone voltage: 50V, extraction cone voltage: 4V, source temperature: 120°C, desolvation temperature: 350°C, cone gas flow : 30L / h. IM-MS conditions: T-wave rate: 550-2500m / s, T-wave height: 40V, drift (nitrogen) flow rate: 90mL / min.
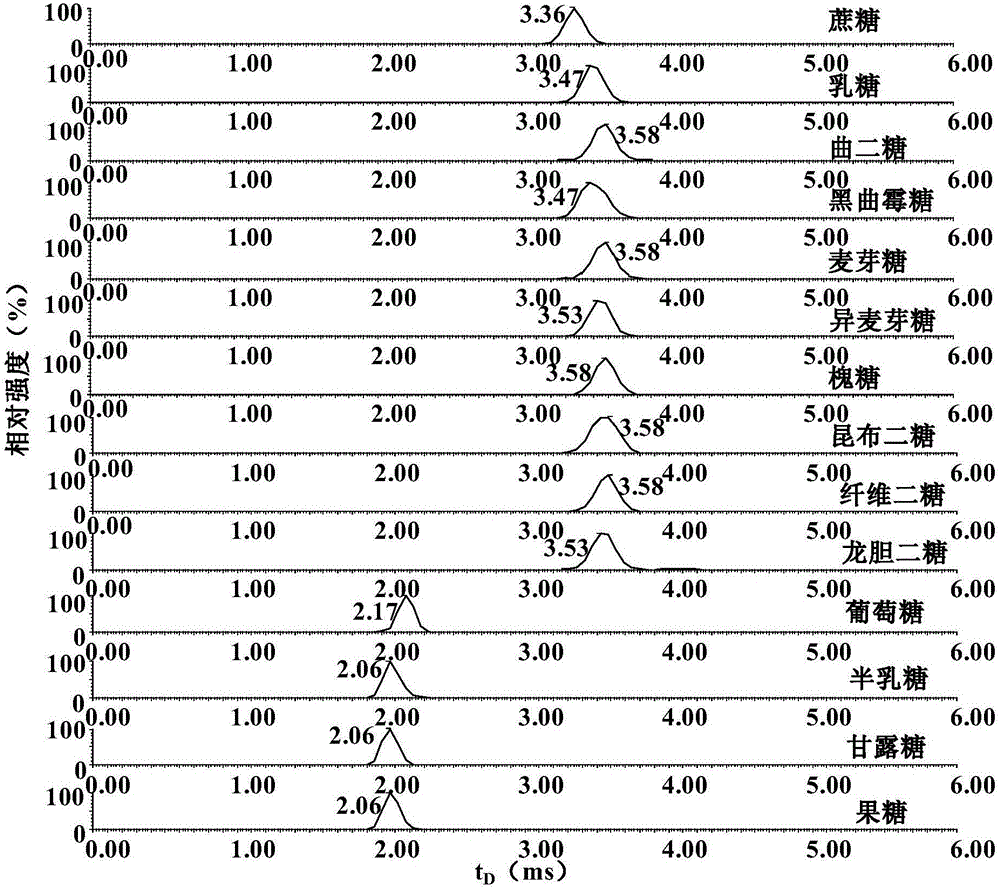
[0061] see results figure 1 , comparing the ion mobility mass spectra of monosaccharide and disaccharide isomers, according to t D , found that only ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] (1) Preparation of calibrators and standard substances to be tested
[0064] Calibrator (sucrose, lactose, cellobiose, maltose, melibiose, trehalose, melezitose, raffinose and maltotriose) and the standard substance to be measured (koji disaccharide, aspergillus niger, isomaltose, sophorose, laminaribiose, gentiobiose, glucose, galactose, mannose and fructose) were prepared into a solution with a concentration of 2 μM.
[0065] (2) Ammonia-methanol solution preparation
[0066] Take 500 μL of 28% NH 3 ·H 2 O, was added to 9.5mL methanol and shaken fully to obtain
[0067] Ammonia-methanol solution with a concentration of 0.82mol / L.
[0068] (3) Preparation of PMP derivative solution
[0069] Weigh 60.67mg of PMP and put it in a 10mL volumetric flask, fully dissolve it with ammonia-methanol solution, adjust to volume, fully oscillate, and prepare a concentration of 0.0349mol / L, and store it in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
[0070] (4) PMP derivatization proces...
Embodiment 3
[0085] The PHN derivatization process is the same as in Example 2, and the IM-MS detection conditions of the derivatized products are the same as in Example 1.
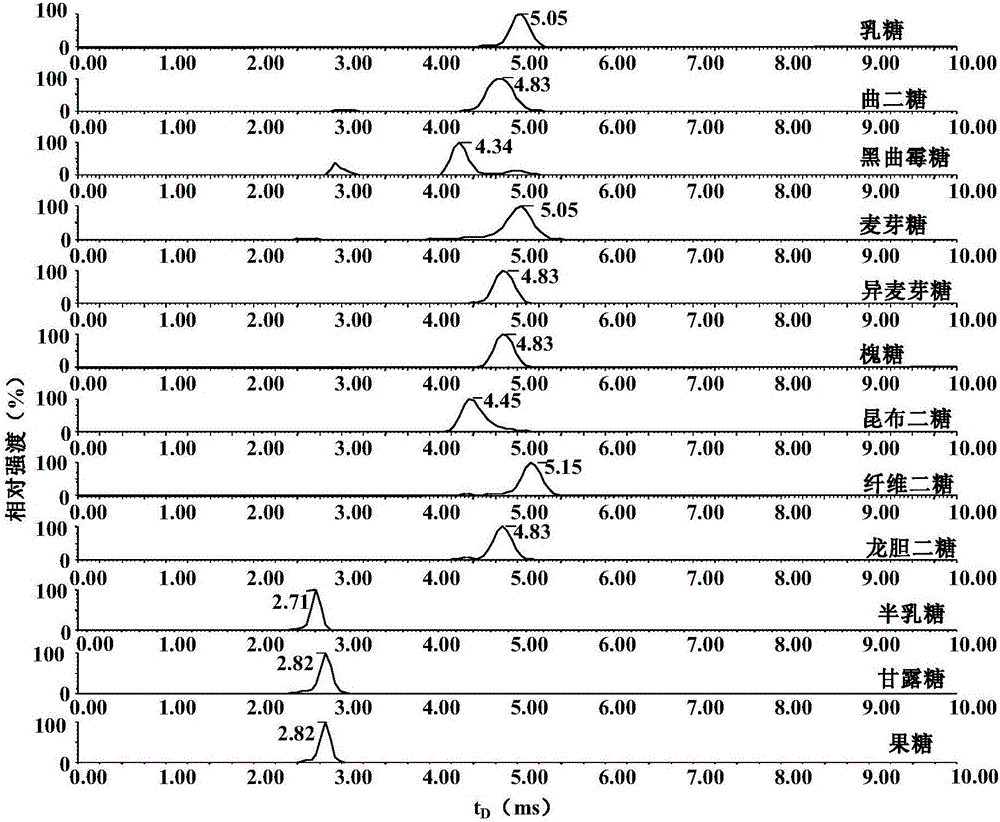
[0086] see results image 3 , comparing the ion mobility mass spectra of monosaccharide and disaccharide isomer PHN derivatized products, according to t D , found that Aspergillus nigerbiose PHN derivatives (t D =4.34ms), laminaribiose PHN derivatives (t D =4.45ms) and cellobiose PHN derivatives (t D =5.15ms) can be distinguished from other disaccharide isomer PHN derivatives, galactose PHN derivatives (t D =2.71ms) can be distinguished from other monosaccharide isomers PHN derivatives, and other monosaccharide and disaccharide isomers cannot be distinguished.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com